©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Psychiatry. Feb 19, 2022; 12(2): 264-285
Published online Feb 19, 2022. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v12.i2.264
Published online Feb 19, 2022. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v12.i2.264
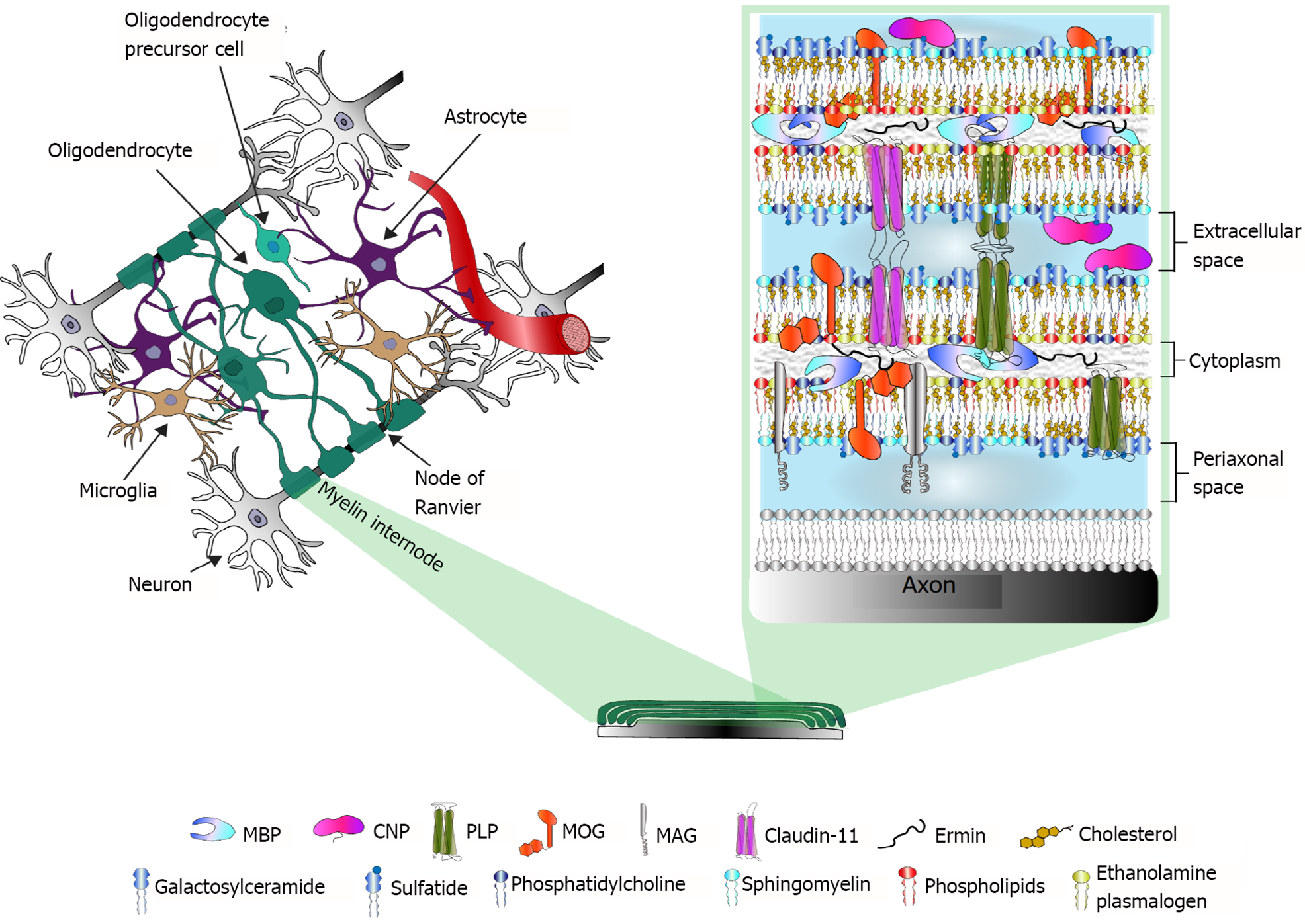
Figure 1 Myelin in the central nervous system.
Left, a schematic representation of central nervous system (CNS) cells and their multidirectional interactions. Right, the main protein and lipid components of CNS myelin. Proteomic studies have revealed altered expression of myelin proteins in postmortem brain samples from patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. MBP: Myelin basic protein; CNP: 2’,3’-cyclic nucleotide 3’-phosphodiesterase; PLP: Proteolipid protein; MOG: Myelin-oligodendrocyte glycoprotein; MAG: Myelin-associated glycoprotein.
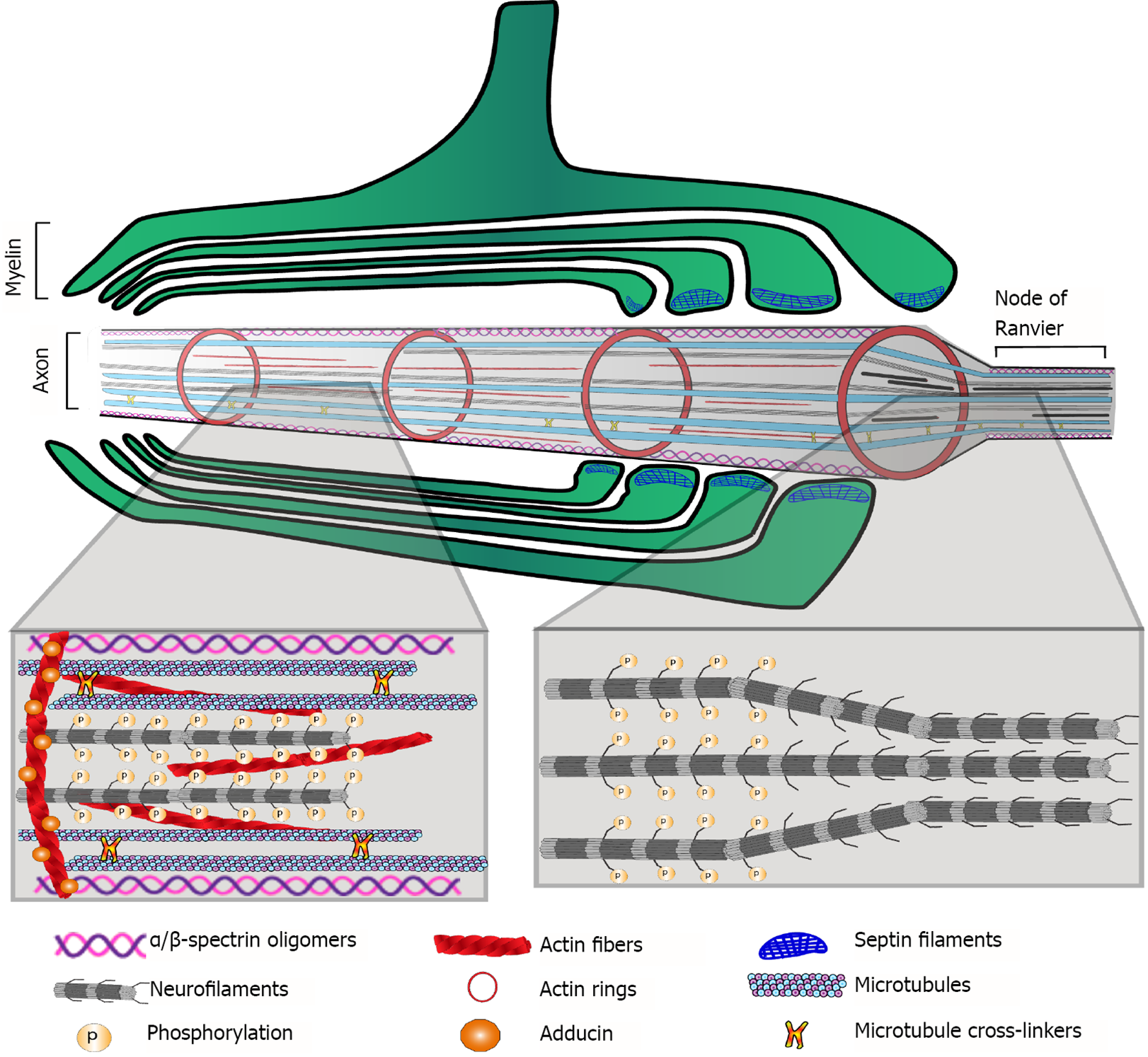
Figure 2 Main cytoskeletal components of the myelinated axon.
Proteomic approaches revealed alterations in most of these components in postmortem brain samples of schizophrenia patients.
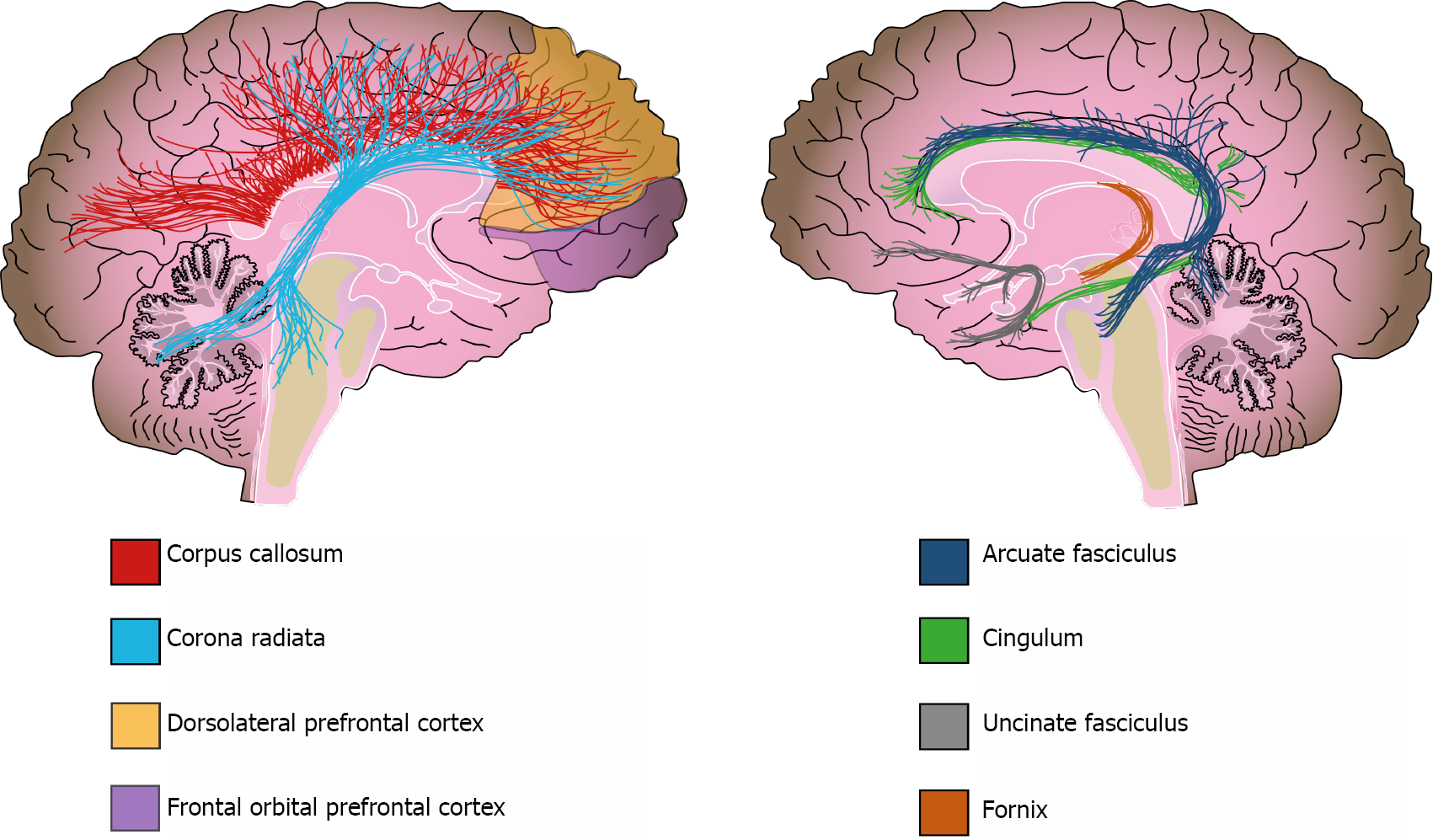
Figure 3 White matter alterations in schizophrenia.
Solid lines represent the path of the affected white matter tracts, whereas shadowed areas (purple and yellow) show brain regions with diminished white matter density.
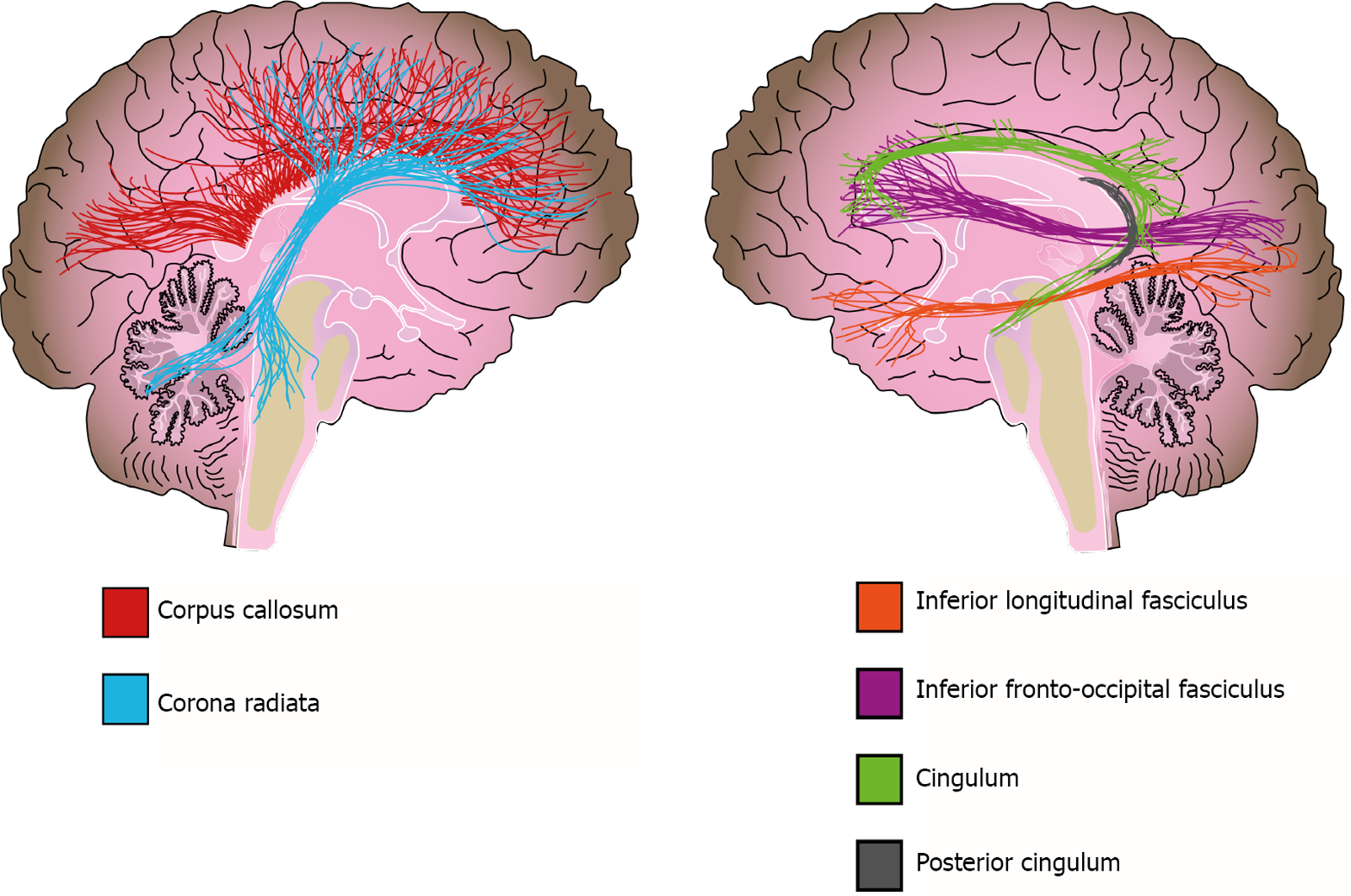
Figure 4 White matter alterations in bipolar disorder.
Solid lines represent the path of the affected white matter tracts.
- Citation: Valdés-Tovar M, Rodríguez-Ramírez AM, Rodríguez-Cárdenas L, Sotelo-Ramírez CE, Camarena B, Sanabrais-Jiménez MA, Solís-Chagoyán H, Argueta J, López-Riquelme GO. Insights into myelin dysfunction in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. World J Psychiatry 2022; 12(2): 264-285
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v12/i2/264.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v12.i2.264