©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Psychiatr. Jun 19, 2021; 11(6): 222-231
Published online Jun 19, 2021. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v11.i6.222
Published online Jun 19, 2021. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v11.i6.222
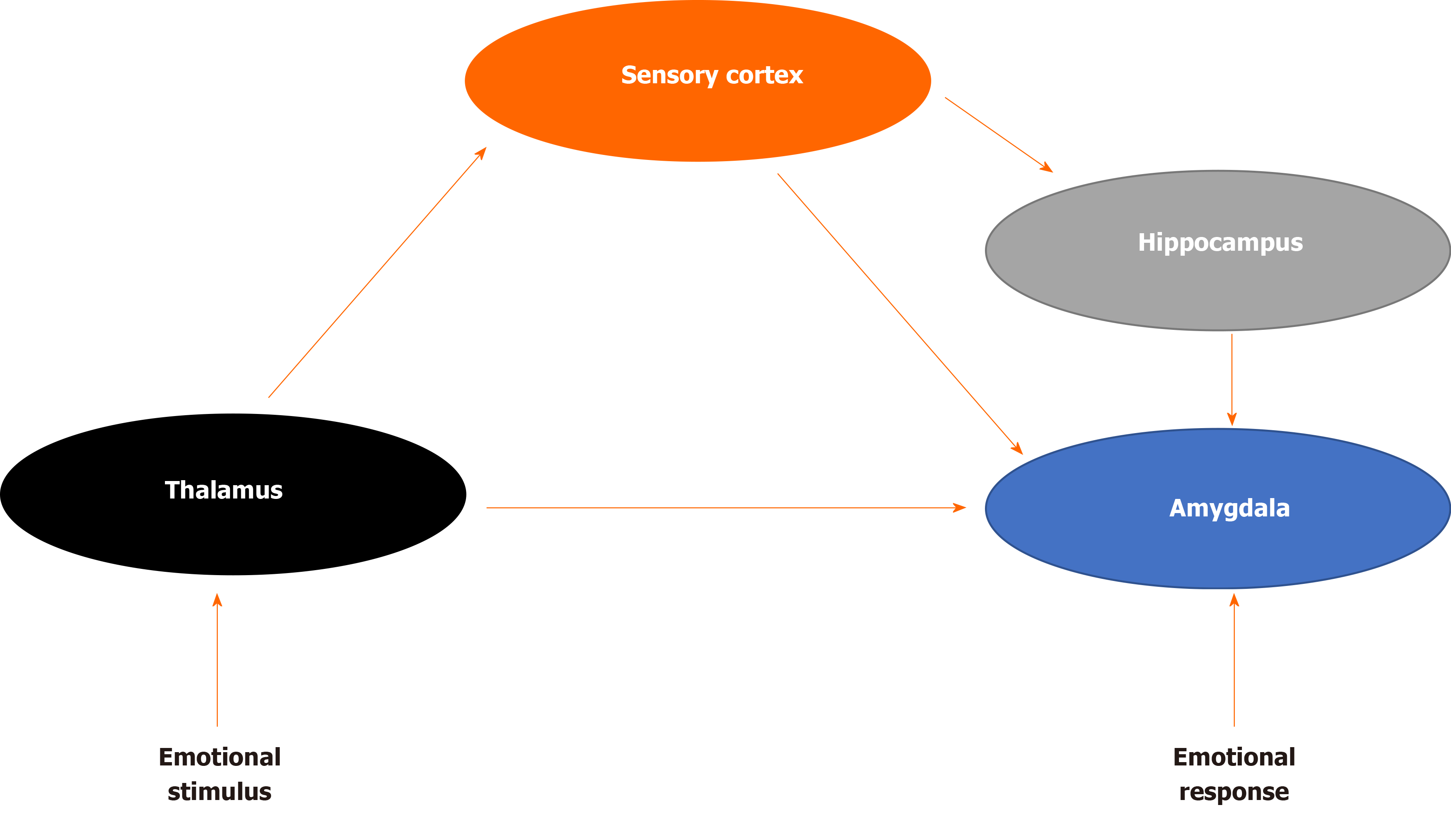
Figure 1 Fear brain circuitry.
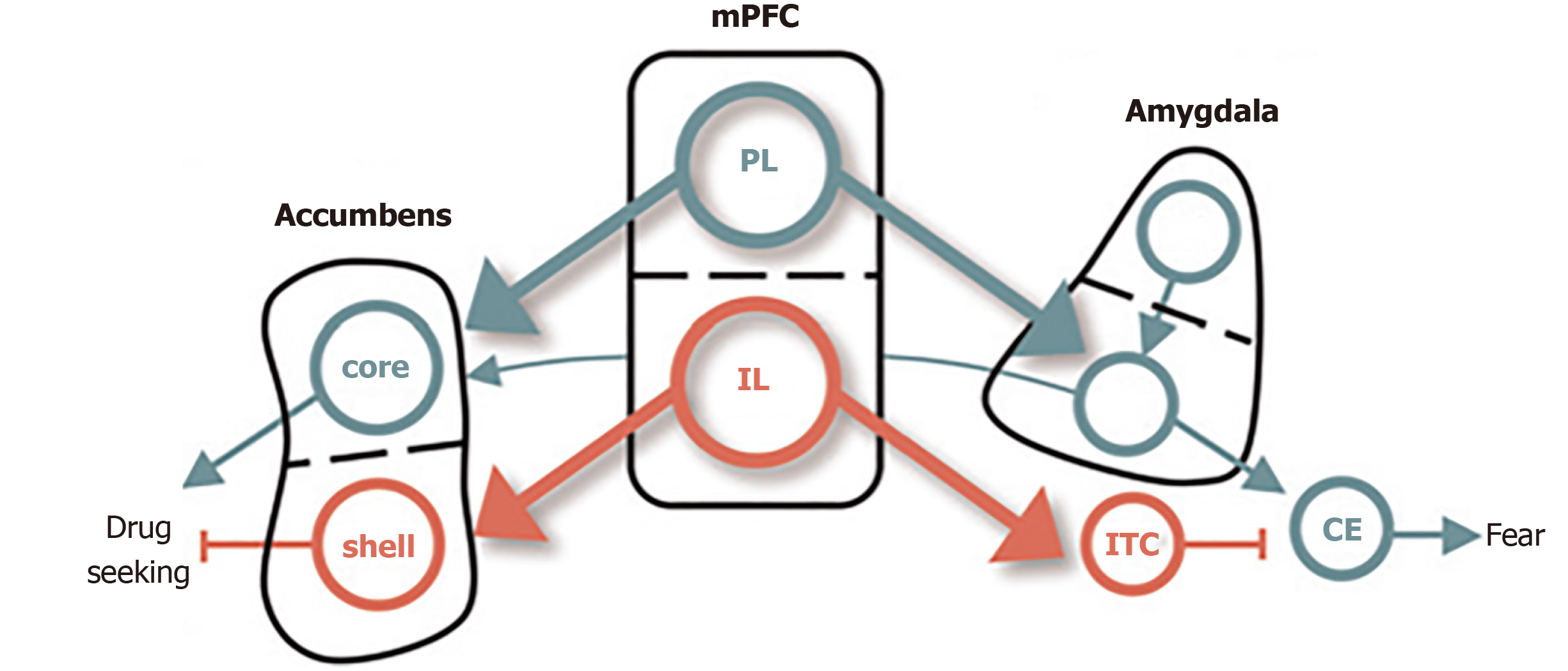
Figure 2 Conditioned fear in cocaine use.
The dorsal and ventral subdivisions of medial prefrontal cortex are shown at the center, with their respective outputs to the amygdala controlling fear shown at right, and those to the nucleus accumbens, controlling cocaine, seeking shown at left. Green depicts pathways that activate fear and cocaine seeking. Red depicts pathways that inhibit fear and cocaine seeking[65]. Citation: Peters J, Kalivas PW, Quirk GJ. Extinction circuits for fear and addiction overlap in prefrontal cortex. Learn Mem 2009; 16(5): 279-288. Copyright ©Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press 2009. Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press[65].
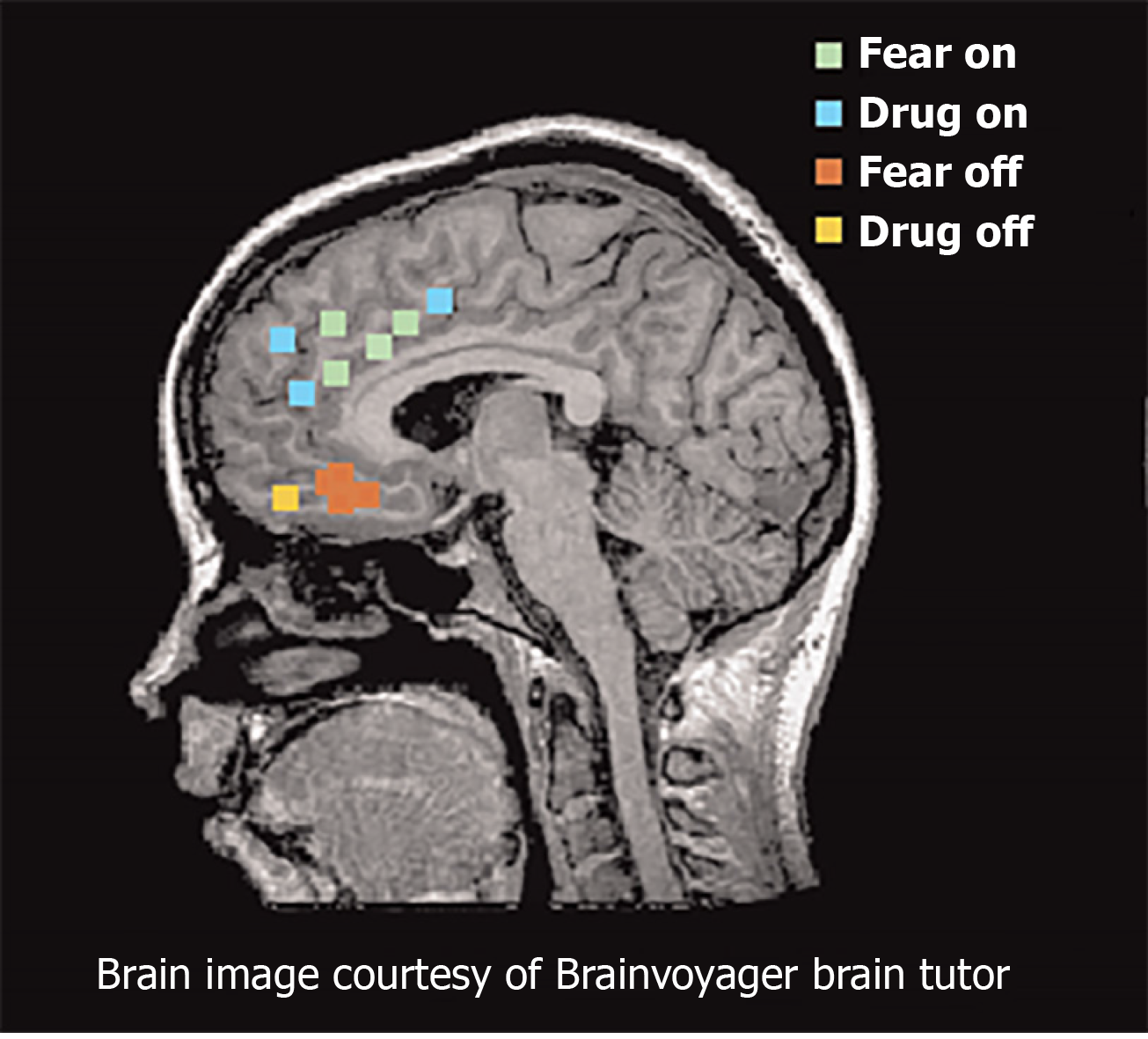
Figure 3 Functional magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography studies of fear and addiction.
Green dots represented human dorsal anterior cingulate cortex that correlated with fear expression functional magnetic resonance imaging[65]. Blue dots represent regions that correspond with drug cravings after exposure to cocaine-related cues. Red dots represent regions associated with fear extinction recall. Yellow dots represent regions activated during addiction-related cues. Citation: Peters J, Kalivas PW, Quirk GJ. Extinction circuits for fear and addiction overlap in prefrontal cortex. Learn Mem 2009; 16(5): 279-288. Copyright ©Brain Innovation 2009. Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press[65].
- Citation: Michaels TI, Stone E, Singal S, Novakovic V, Barkin RL, Barkin S. Brain reward circuitry: The overlapping neurobiology of trauma and substance use disorders. World J Psychiatr 2021; 11(6): 222-231
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v11/i6/222.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v11.i6.222