©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Exp Med. Dec 20, 2025; 15(4): 114368
Published online Dec 20, 2025. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v15.i4.114368
Published online Dec 20, 2025. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v15.i4.114368
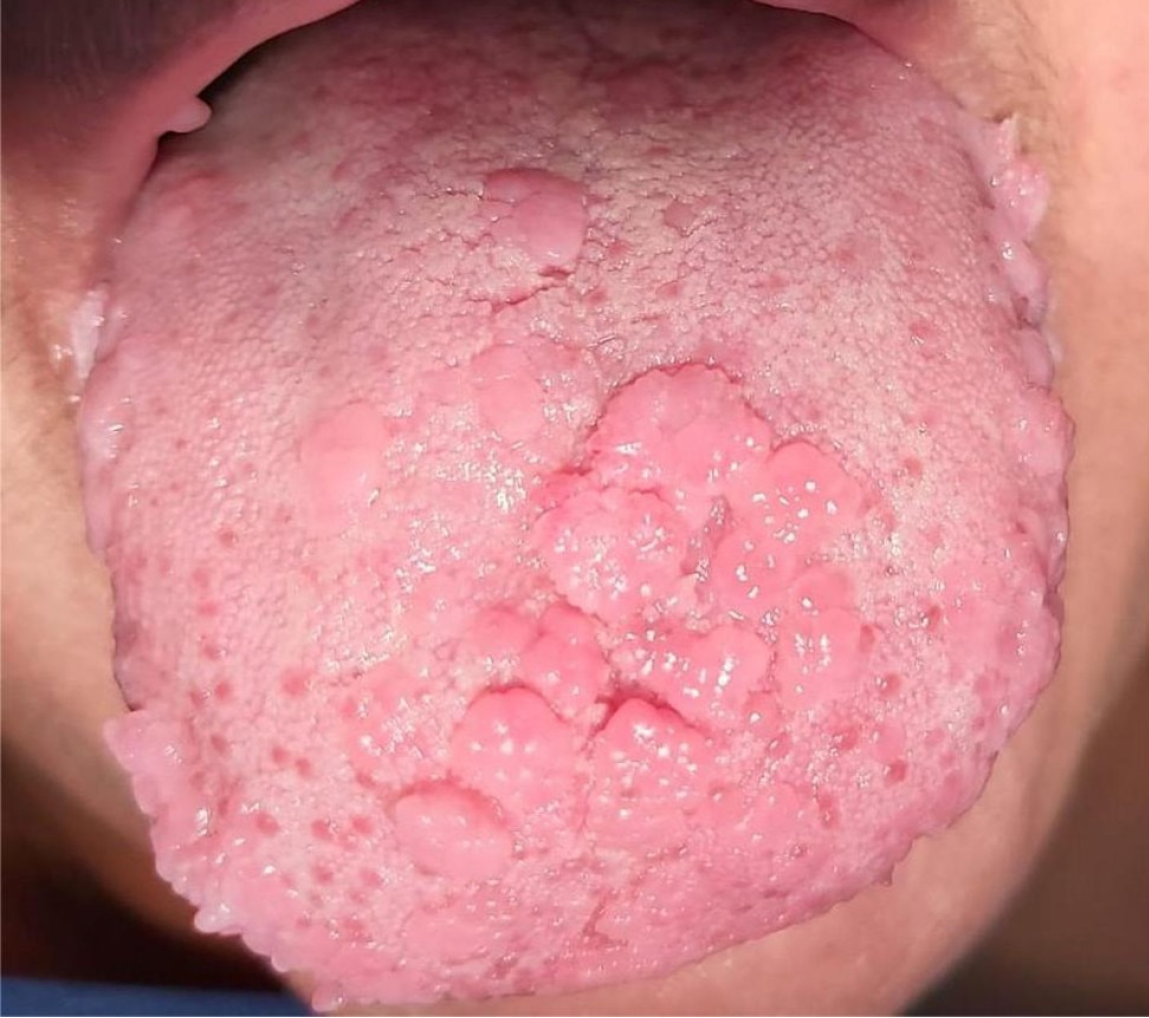
Figure 1
Clinical presentation of multifocal epithelial hyperplasia on the dorsal surface of the tongue, presenting as multiple well-circumscribed, pink papules and nodules.
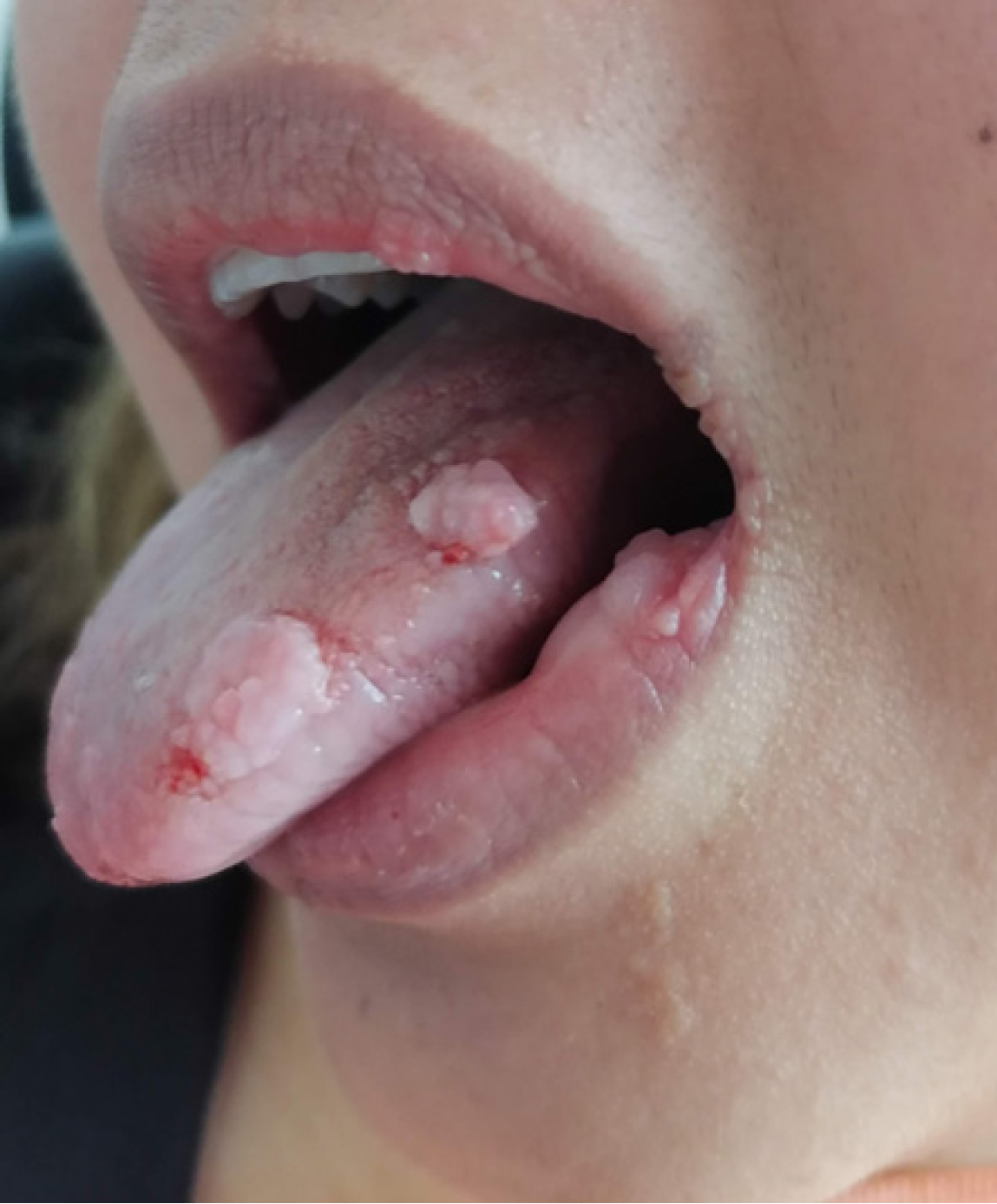
Figure 2 Multifocal epithelial hyperplasia involves the lateral surface of the tongue.
The image shows multiple pinkish white, exophytic papules and nodules with a smooth to papillomatous surface.
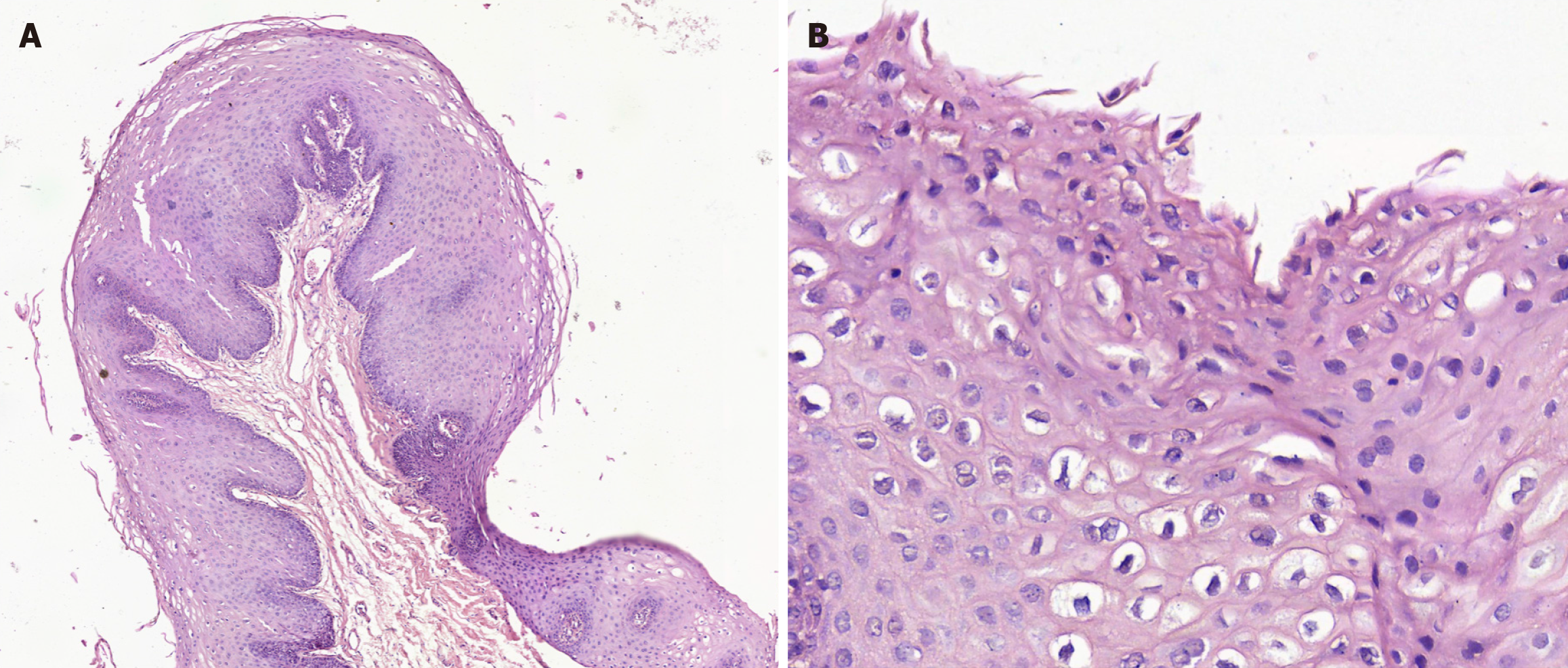
Figure 3 Histopatological image.
A: A lesion characterized by the presence of a stratified squamous epithelium parakeratinized with acanthosis and thick and elongated epithelial processes, which give a papillomatous appearance. In some areas, mitosoid and koilocytic figures are observed (50 ×). The connective tissue was well vascularized and free of injury; B: Mitosoid and koilocytic figures (200 ×).
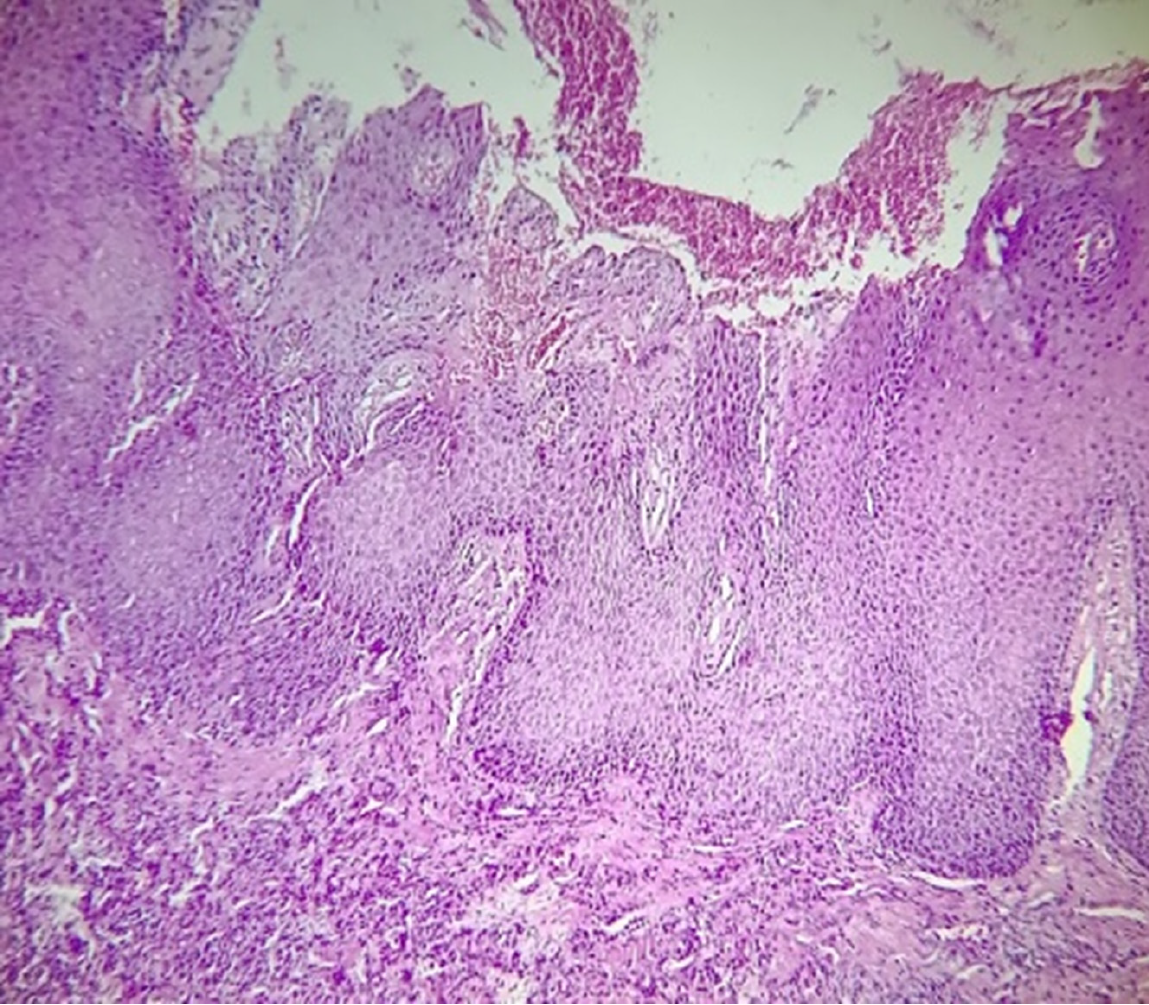
Figure 4 In multifocal epithelial hyperplasia samples, the stratified squamous epithelium presents pronounced hyperorthokeratosis, accompanied by acanthosis and the presence of koilocytes in the intermediate layers.
At the base of the epithelium, dense, well-vascularized connective tissue with chronic inflammatory infiltration is present, which is distributed abundantly and diffusely (100 ×).
- Citation: Ramos-Gregorio CO, Tremillo-Maldonado O, Silveira F, Schuch LF, Pereira-Prado V, Sicco E, Soto-Najera AC, GómezPalacio-Gastélum M, Isiordia-Espinoza M, Muñoz-Ibarra JJ, Toral-Rizo V, Bologna-Molina R. Multifocal epithelial hyperplasia: Clinical features, diagnosis and management challenges. World J Exp Med 2025; 15(4): 114368
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315x/full/v15/i4/114368.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v15.i4.114368