©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Exp Med. Dec 20, 2025; 15(4): 109762
Published online Dec 20, 2025. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v15.i4.109762
Published online Dec 20, 2025. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v15.i4.109762
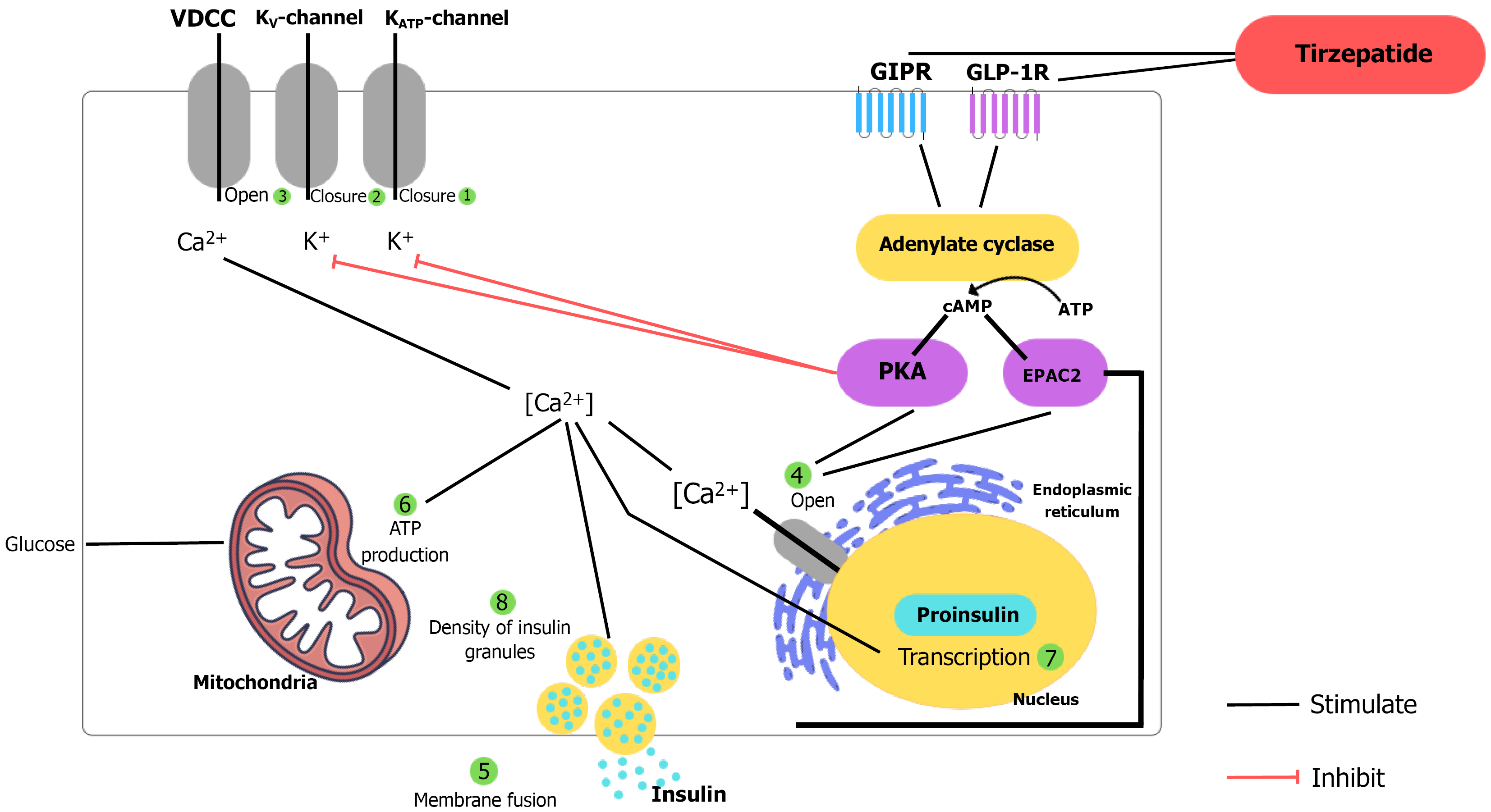
Figure 1 Schematic representation of the mechanism of action of tirzepatide.
(1) Closure of K-adenosine triphosphate channels; (2) Closure of K-voltage channels; (3) Opening of voltage-dependent calcium channels; (4) Opening of calcium channels on the endoplasmic reticulum; (5) Fusion of insulin granules with the cell membrane; (6) Increased adenosine triphosphate production; (7) Transcription of proinsulin; and (8) Increased density of insulin granules. VDCC: Voltage-dependent calcium channel; V: Voltage; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; GIPR: Glucose dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor; GLP-1R: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; cAMP: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
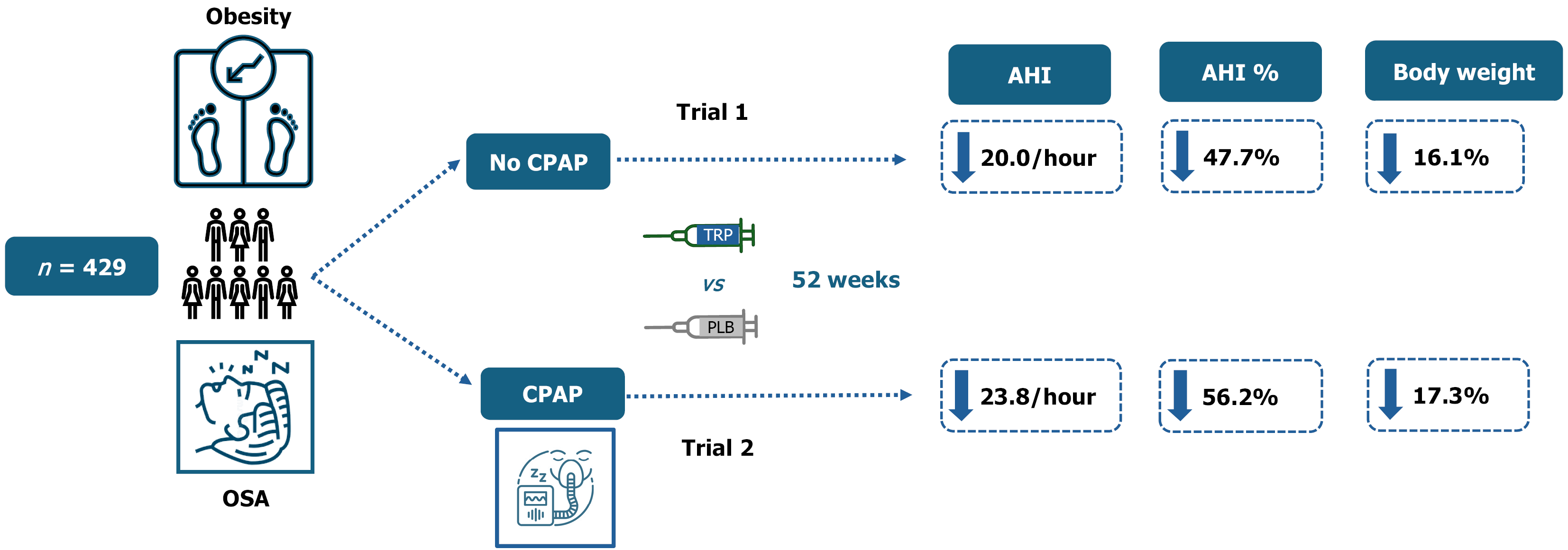
Figure 2 The design and conduct of the SURMOUNT-obstructive sleep apnoea study.
There were two parts of the study - part 1 was done on patients without background continuous positive airway pressure therapy while part 2 enrolled patients on background continuous positive airway pressure therapy. Tirzepatide was administered as once weekly injections in doses of 10 mg or 15 mg. AHI: Apnoea hypopnea index; CPAP: Continuous positive airway pressure; OSA: Obstructive sleep apnoea; TRP: Tirzepatide; PLB: Placebo.
- Citation: Bajpai J, Saxena M, Agarwal U, Pradhan A. Dual incretin analogue tirzepitide - SURMOUNTing the challenge of obesity induced obstructive sleep apnea. World J Exp Med 2025; 15(4): 109762
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315x/full/v15/i4/109762.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v15.i4.109762