©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Crit Care Med. Sep 9, 2025; 14(3): 106496
Published online Sep 9, 2025. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v14.i3.106496
Published online Sep 9, 2025. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v14.i3.106496
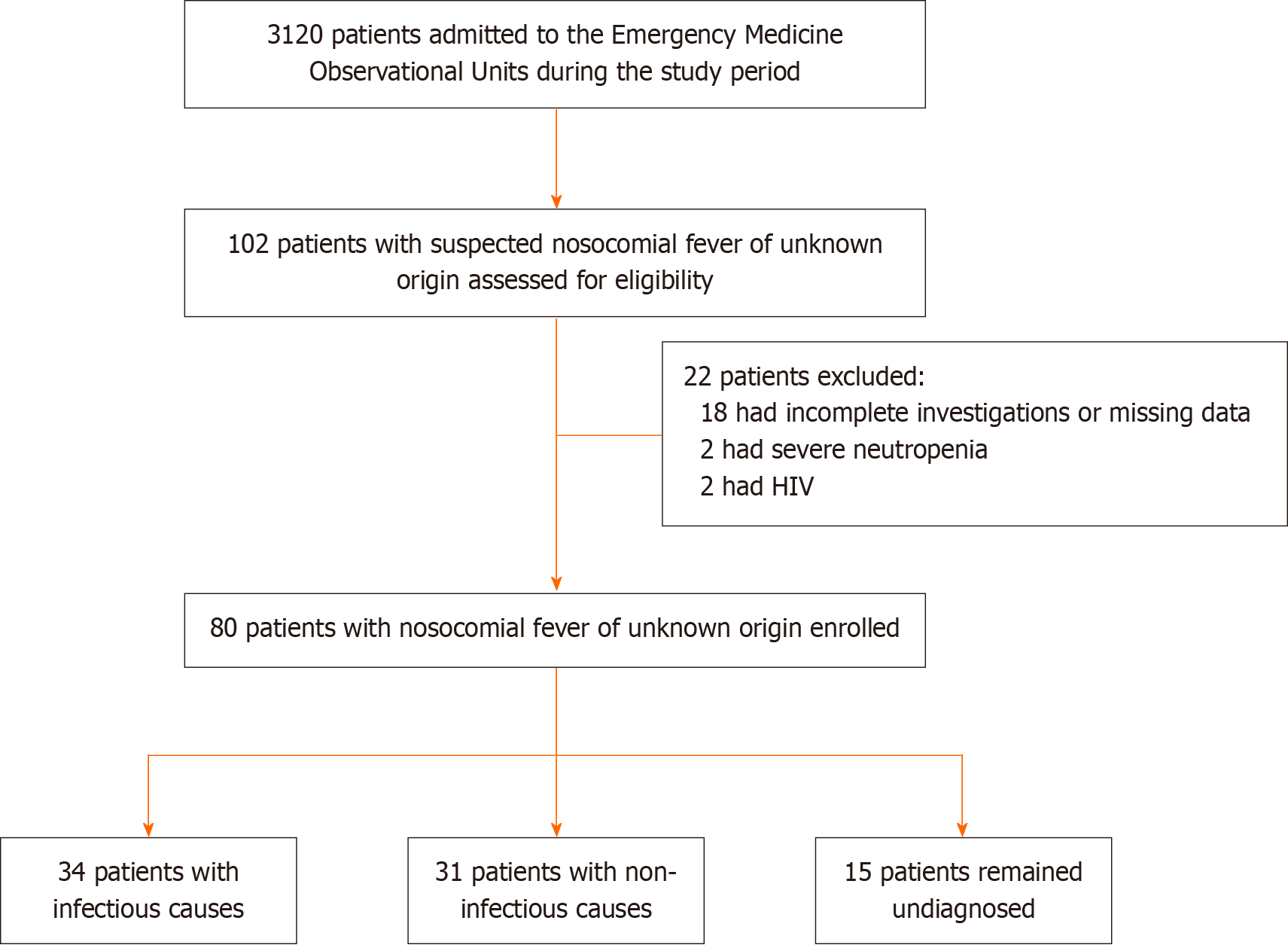
Figure 1 Flowchart showing patient enrollment and etiological classification of nosocomial fever of unknown origin.
HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus.
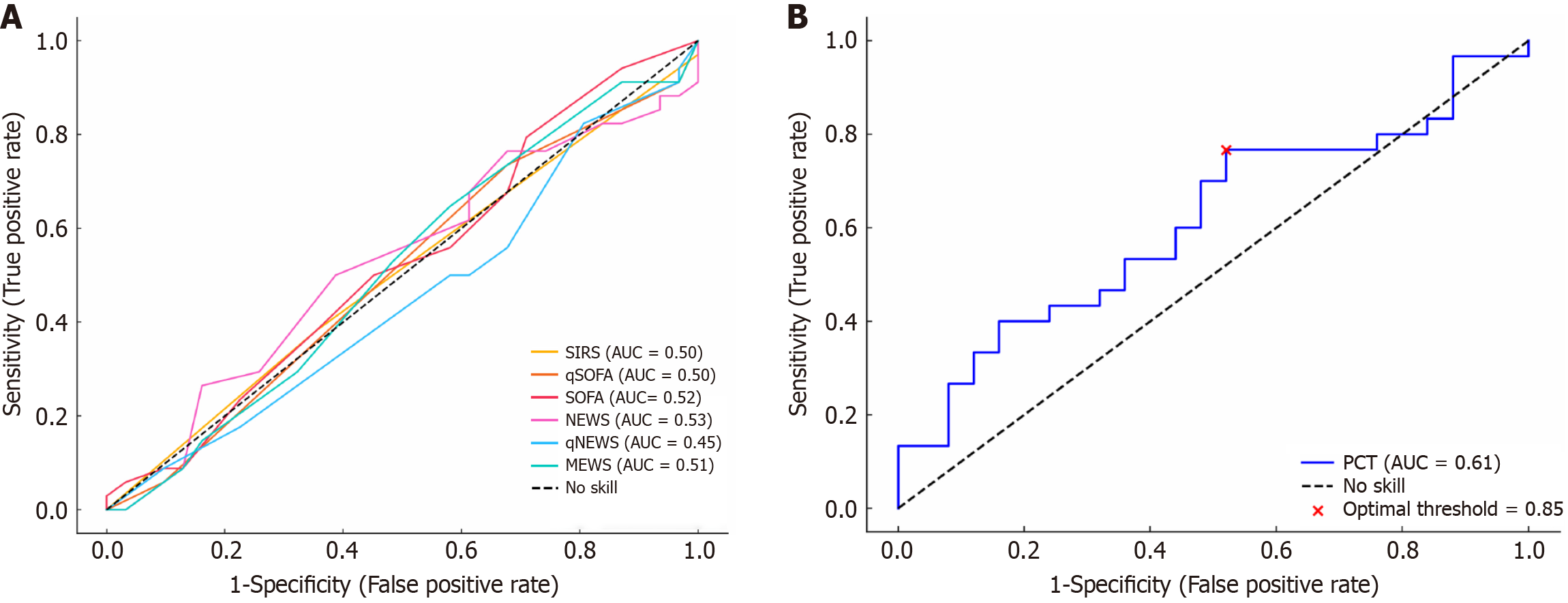
Figure 2 Diagnostic accuracy of sepsis screening tools and biomarkers.
A: The receiver operating characteristic curves (ROC) and the areas under ROC curves for sepsis screening tools in predicting infectious causes of nosocomial fever of unknown origin; B: The ROC curve and the areas under ROC curve for procalcitonin in predicting infectious causes of nosocomial fever of unknown origin. AUC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; MEWS: Modified Early Warning Score; NEWS: National Early Warning Score; qNEWS: Quick National Early Warning Score; qSOFA: Quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; SIRS: Systemic inflammatory response syndrome; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; PCT: Procalcitonin.
- Citation: Saini S, Pahil S, Mohindra R, Sachdeva N, Sharma N, Pannu AK. Diagnostic utility of sepsis screening tools, procalcitonin, and C-reactive protein in nosocomial fever of unknown origin. World J Crit Care Med 2025; 14(3): 106496
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v14/i3/106496.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v14.i3.106496