©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Immunol. Nov 27, 2014; 4(3): 158-173
Published online Nov 27, 2014. doi: 10.5411/wji.v4.i3.158
Published online Nov 27, 2014. doi: 10.5411/wji.v4.i3.158
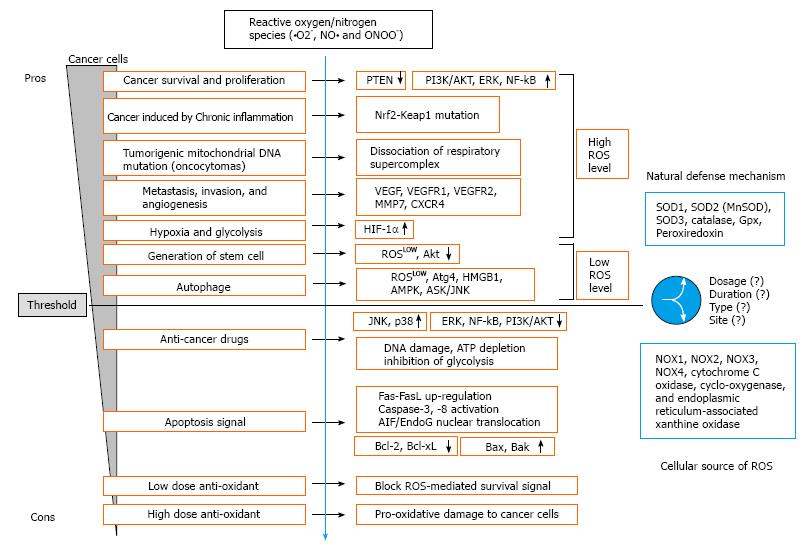
Figure 1 The role of reactive oxygen species on cancer cells to explain the different effects at each condition.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) level inside cancer cell appears varied even within a given type of cancer cells. A so-called “double-edged sword strategy” uses to manipulate the opposite role of ROS sequentially to kill cancer cells more effectively. VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; PI3K: Phosphoinositide-3 kinase; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog; HIF-1α: Hypoxia inducible factor-1α; JNK: C-Jun N-terminal kinase; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; SOD: superoxide dismutase; NOX: NAD(P)H oxidase.
- Citation: Kim D, Park GB, Hur DY. Apoptotic signaling through reactive oxygen species in cancer cells. World J Immunol 2014; 4(3): 158-173
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2824/full/v4/i3/158.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5411/wji.v4.i3.158