©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Immunol. Jan 8, 2026; 16(1): 111511
Published online Jan 8, 2026. doi: 10.5411/wji.v16.i1.111511
Published online Jan 8, 2026. doi: 10.5411/wji.v16.i1.111511
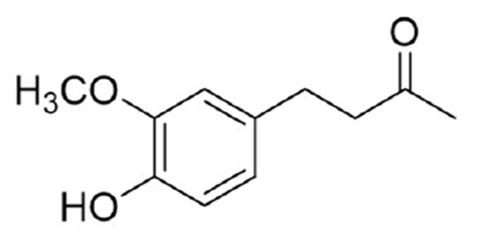
Figure 1
Chemical structure of zingerone.
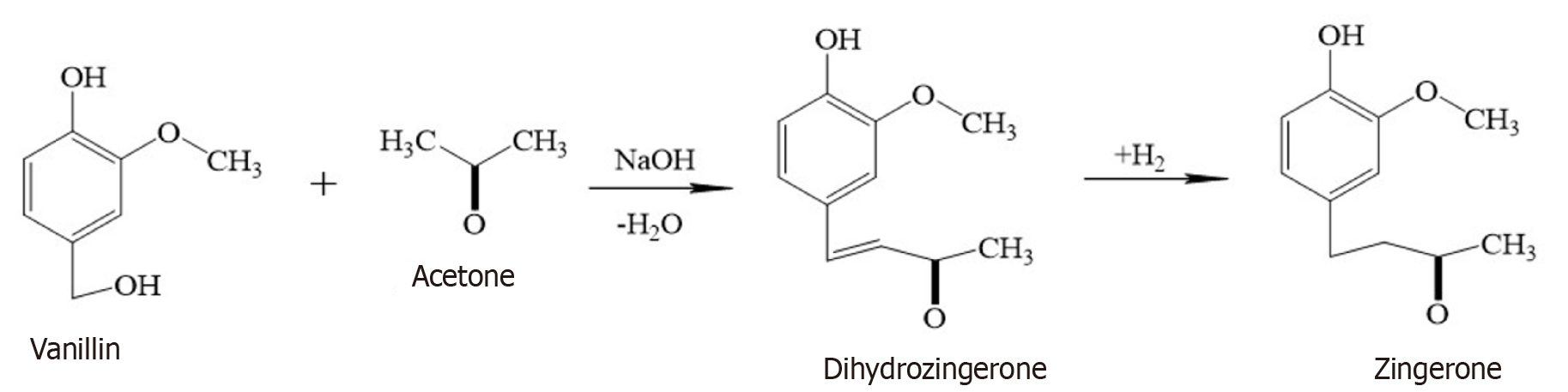
Figure 2 Chemical synthesis of zingerone involves condensation of vanillin and acetone and hydrogenation of dihydrozingerone.
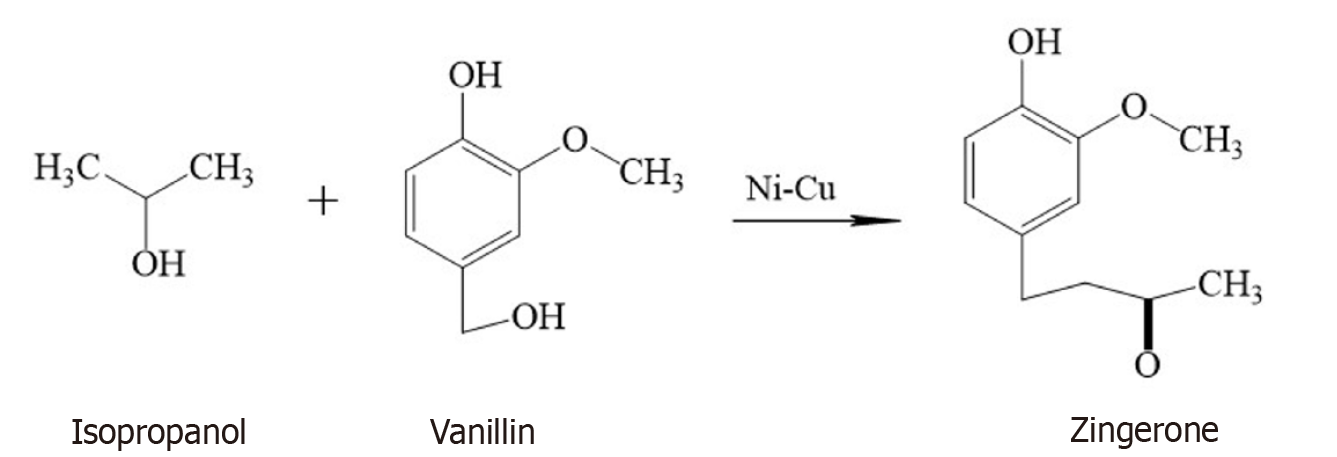
This method consists of two stages: (1) Production of dihydrozingerone by the condensation of acetone with vanillin in the presence of effective heterogeneous catalysts; and (2) Hydrogenation of dihydrozingerone to form zingerone in the catalytic activity of hydrotalcite (Figure 3).
Figure 3
Chemical synthesis of zingerone by the combination of isopropanol and vanillin.
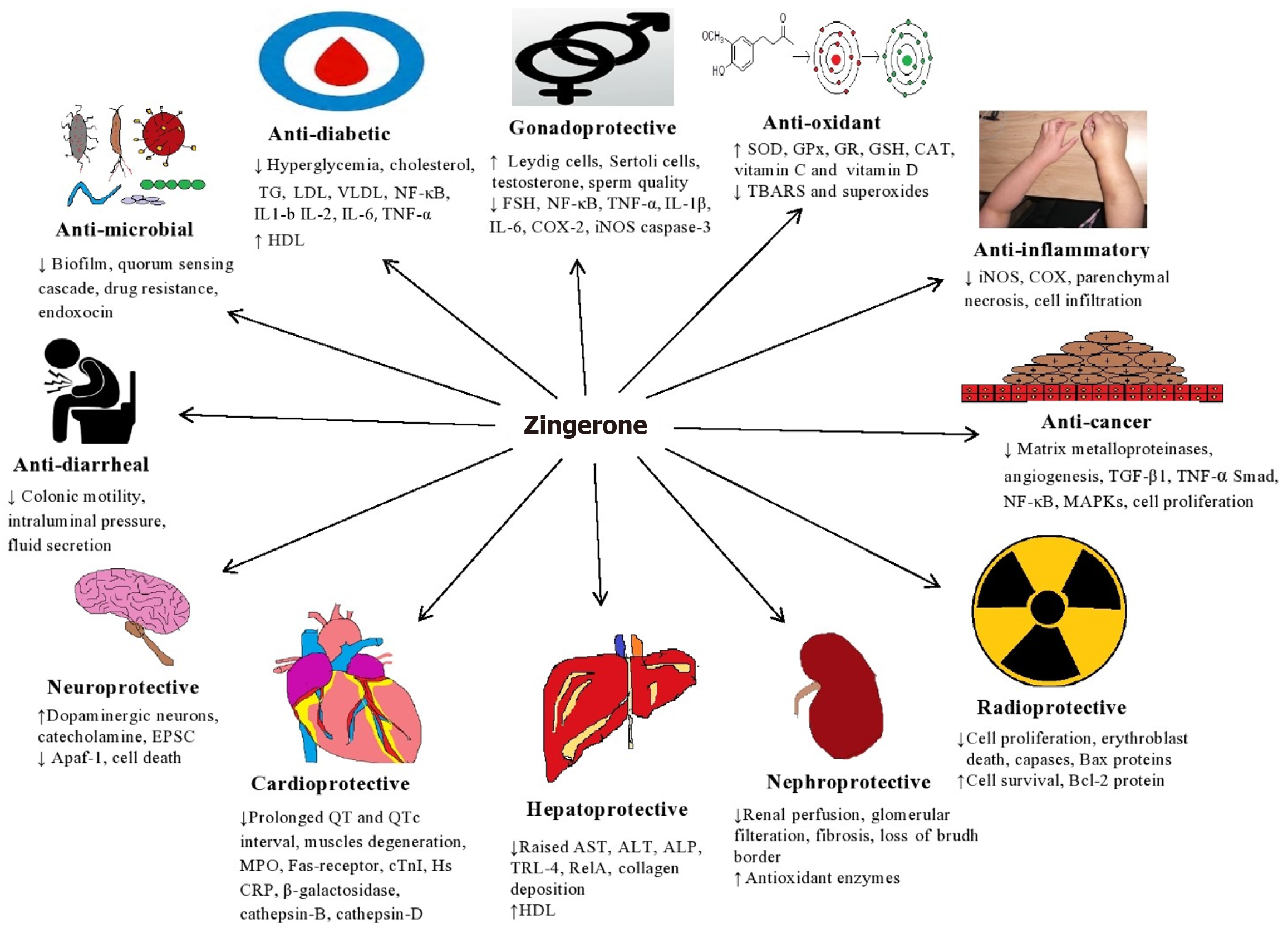
Figure 4 Graphical abstract: Several pharmacological activities of zingerone with mechanism of actions.
EPSC: Excitatory post-synaptic current; TG: Triglycerides; LDL: Low density lipoprotein; VLDL: Very low density lipoprotein; HDL: High density lipoproteins; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; GPx: Glutathione peroxidase; GSH: Glutathione; CAT: Catalase; TBARS: Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor-beta 1; Bcl-2: B cell lymphoma-2; MPO: Myeloperoxidase; CRP: C-reactive protein; AST: Aspartate transaminase; ALT: Alanine transaminase; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; TRL-4: Toll-like receptor-4.
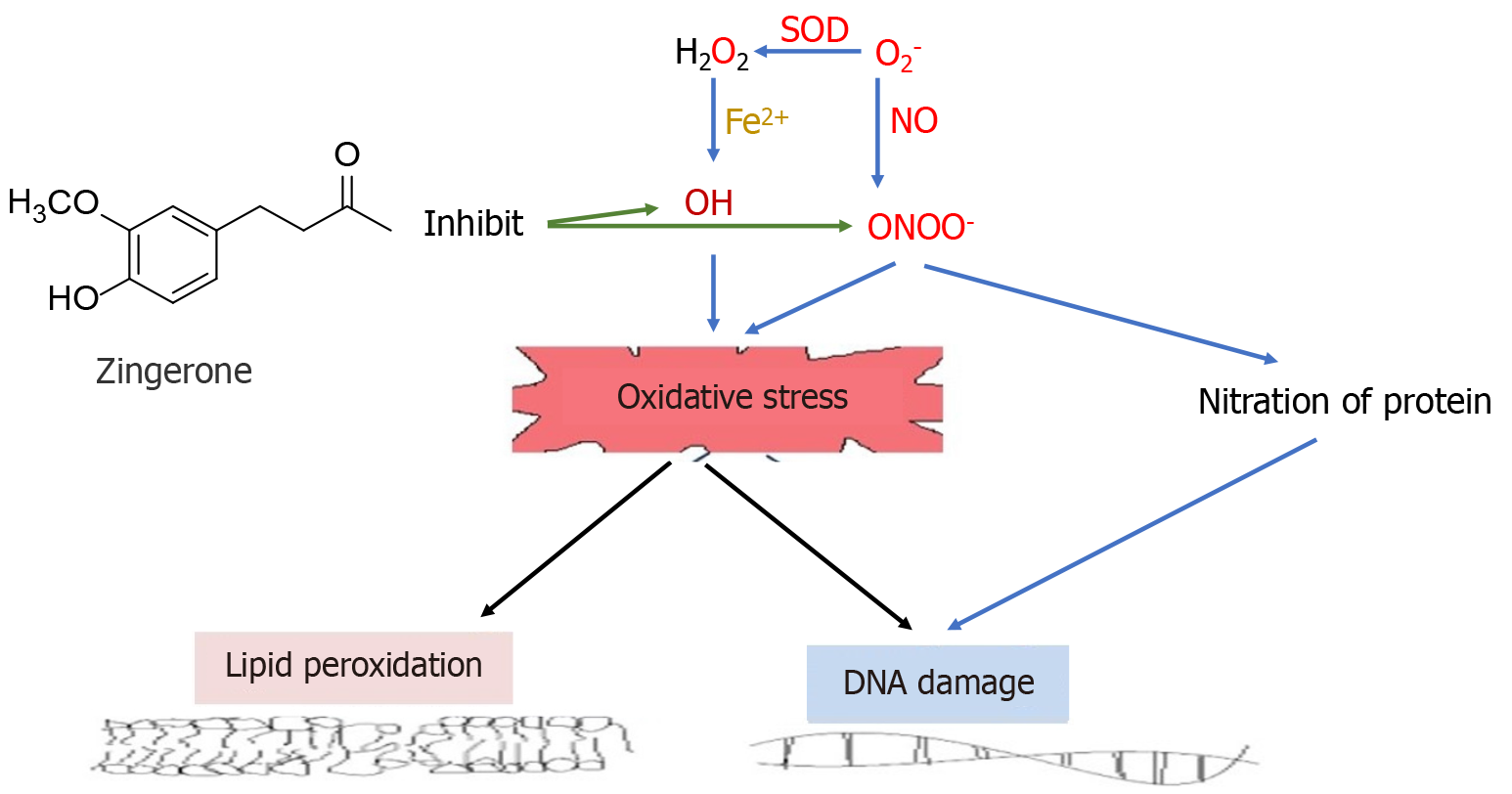
Figure 5 Diagrammatic representation of the antioxidant effects of zingerone against oxidative stress-induced lipid peroxidation and deoxyribose nucleic acid damage in cells.
SOD: Superoxide dismutase; NO: Nitric oxide.
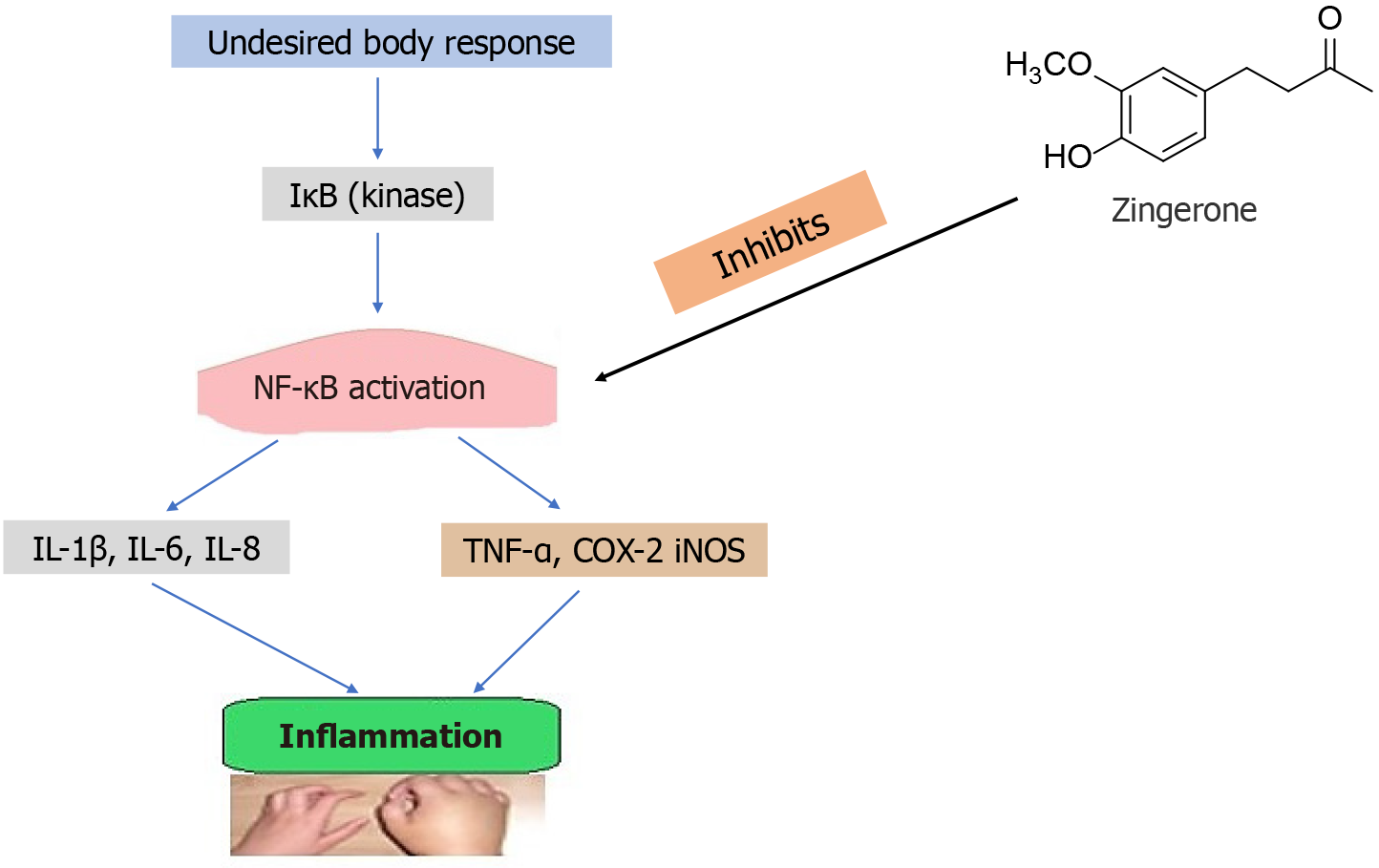
Figure 6 Zingerone showed anti-inflammatory effect by suppressing nuclear factor kappa B, tumor necrosis factor alpha, cyclooxy
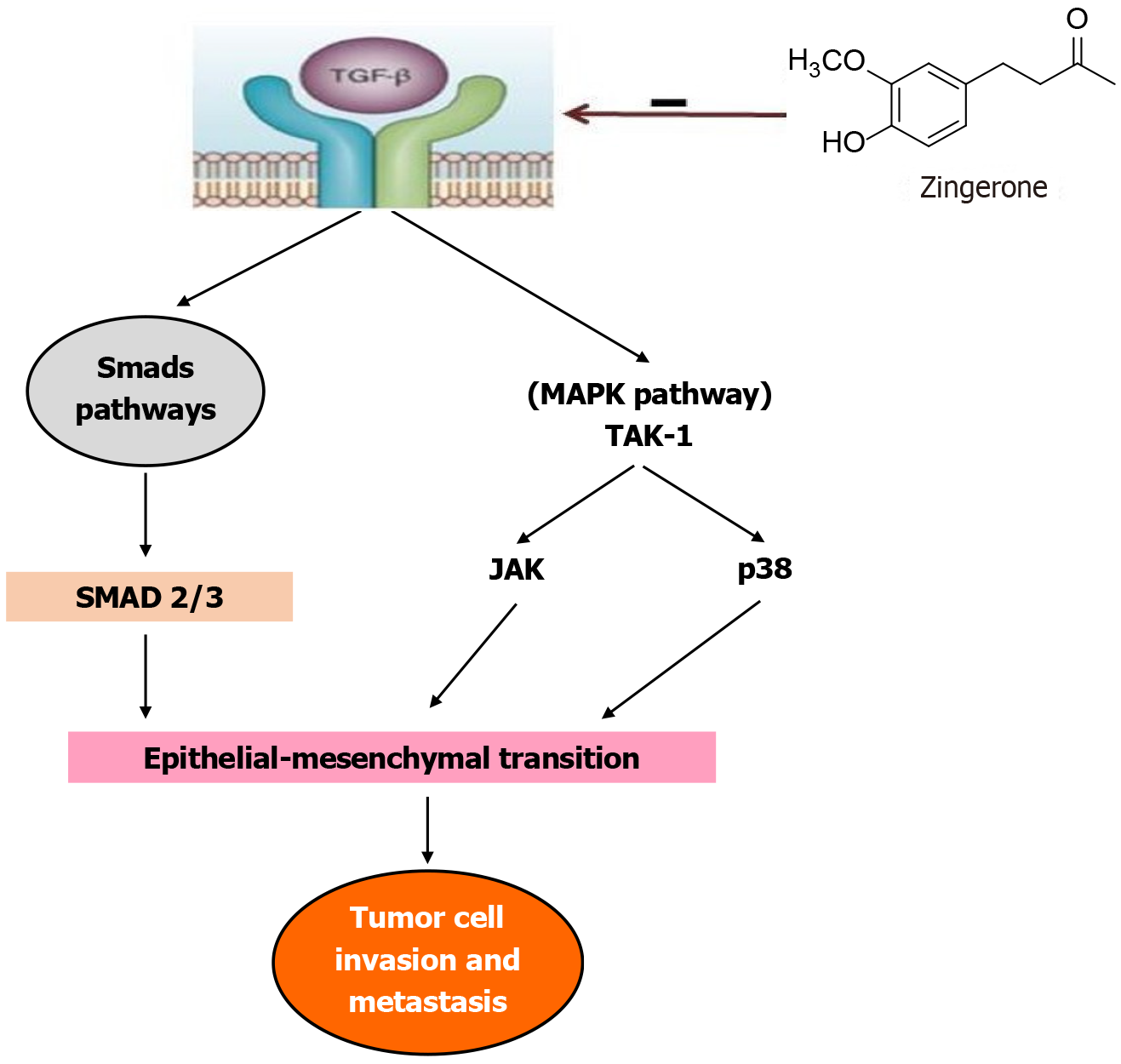
Figure 7 Diagrammatic illustration showing the anti-tumor activity of zingerone by reducing the expression of transforming growth factor-beta.
TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-beta; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinases; TAK-1: Transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase 1; JAK: Janus kinase.
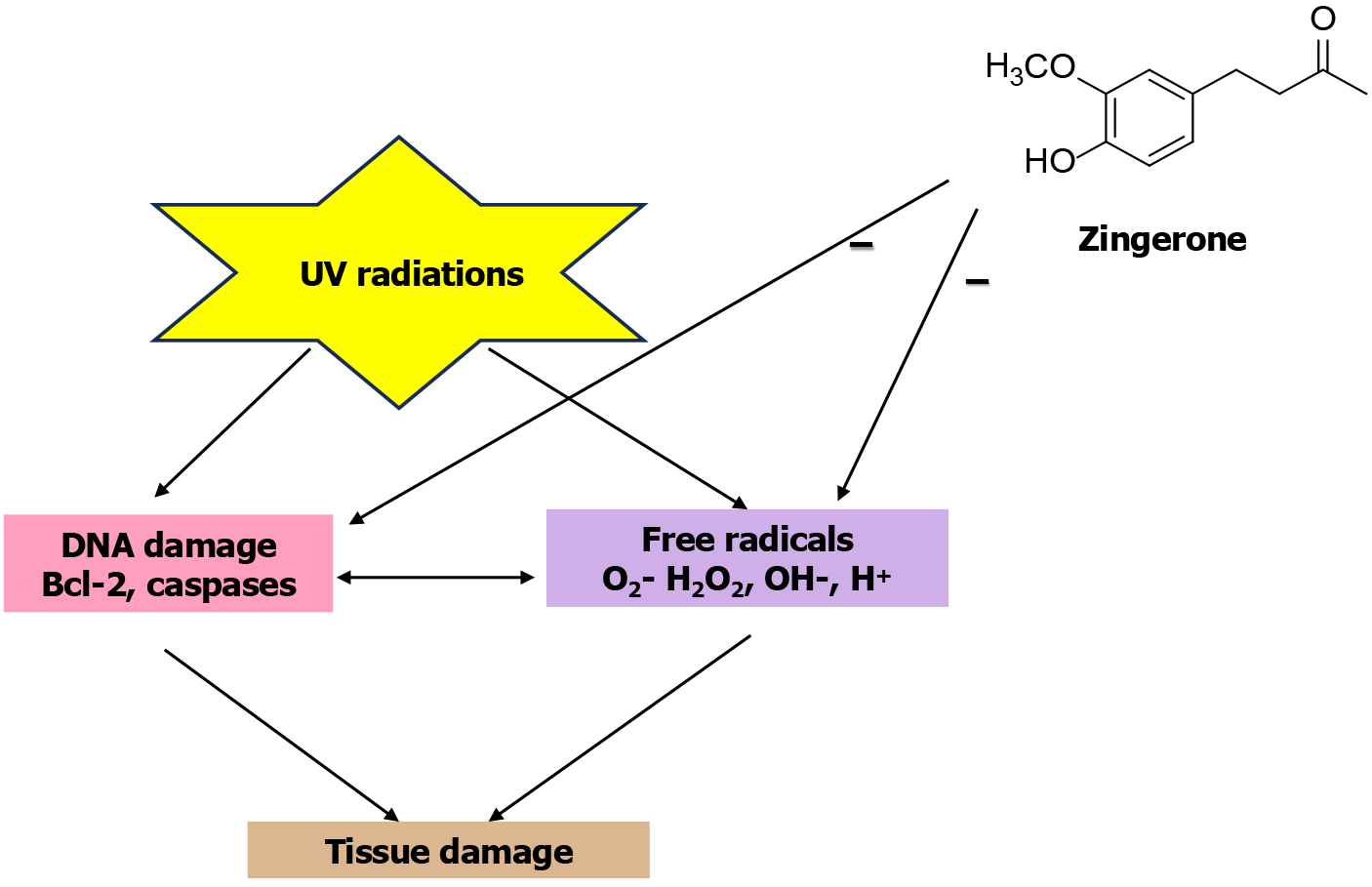
Figure 8 Protective effects of zingerone against ultraviolet radiation.
Bcl-2: B cell lymphoma 2; UV: Ultraviolet.
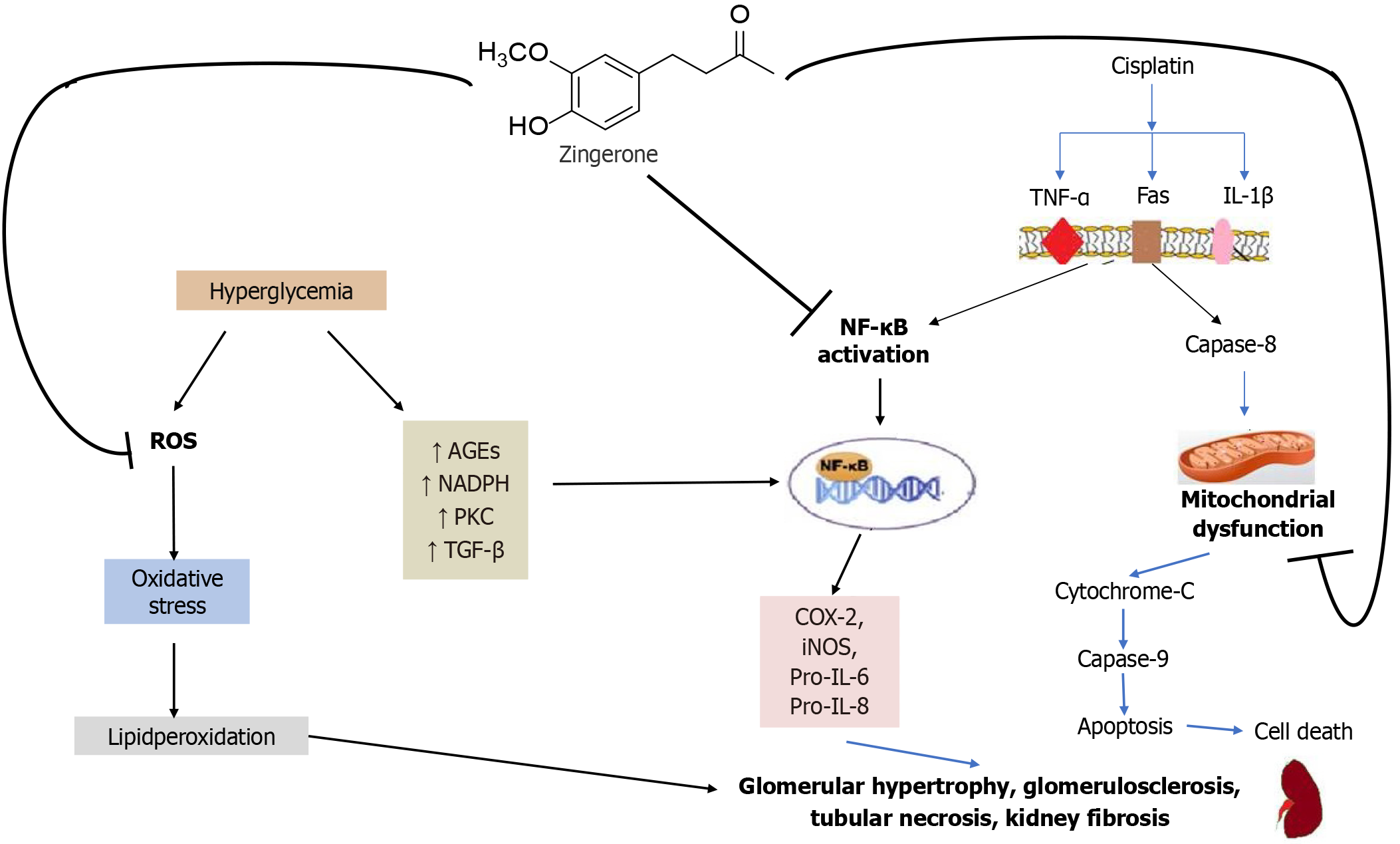
Figure 9 Diagrammatic representation of the protective effects of zingerone against hyperglycaemia and cisplatin-induced nephroto
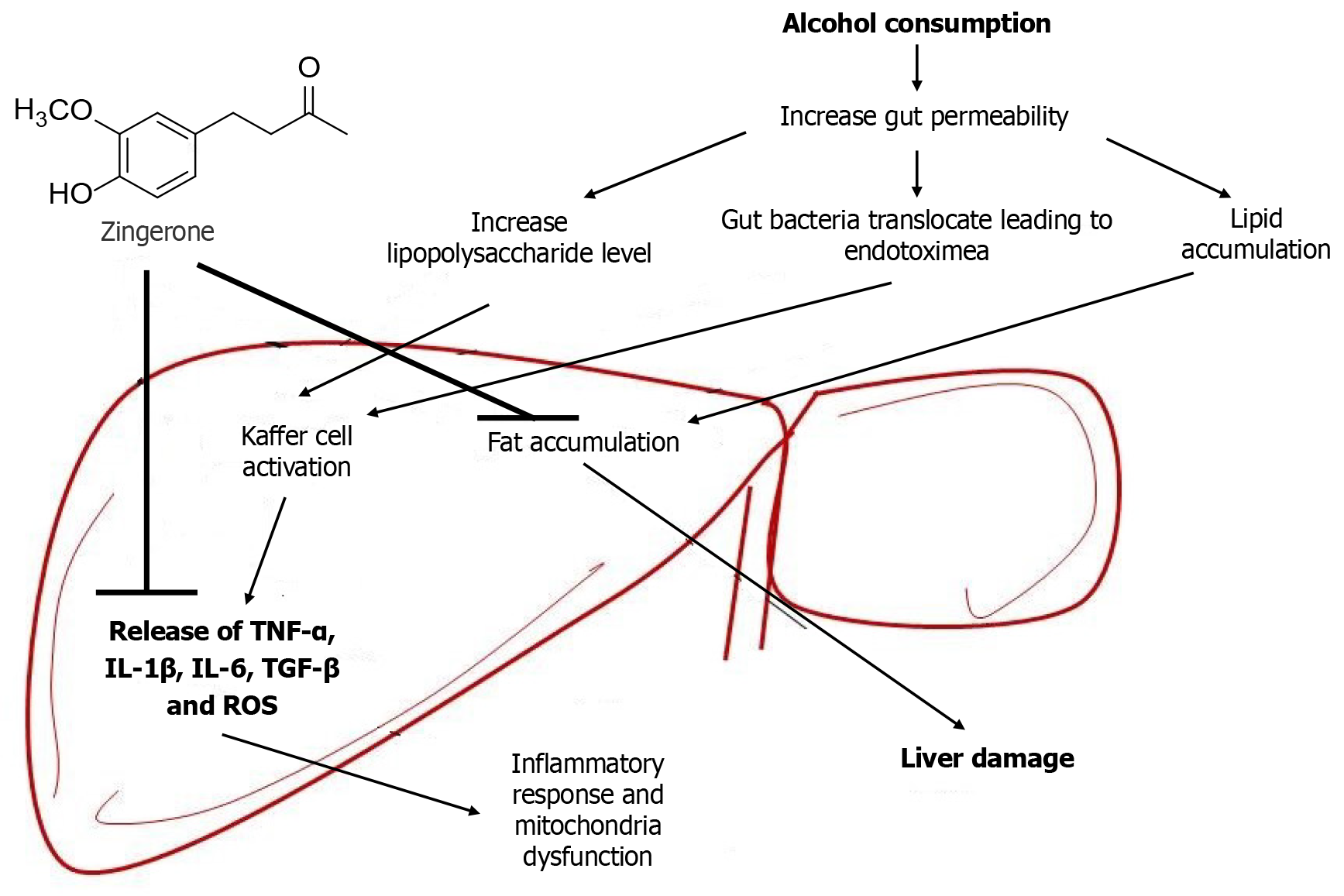
Figure 10 Diagrammatic representation of the ameliorative effects of zingerone against alcohol-induced liver damage.
ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-beta; IL: Interleukins; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha.
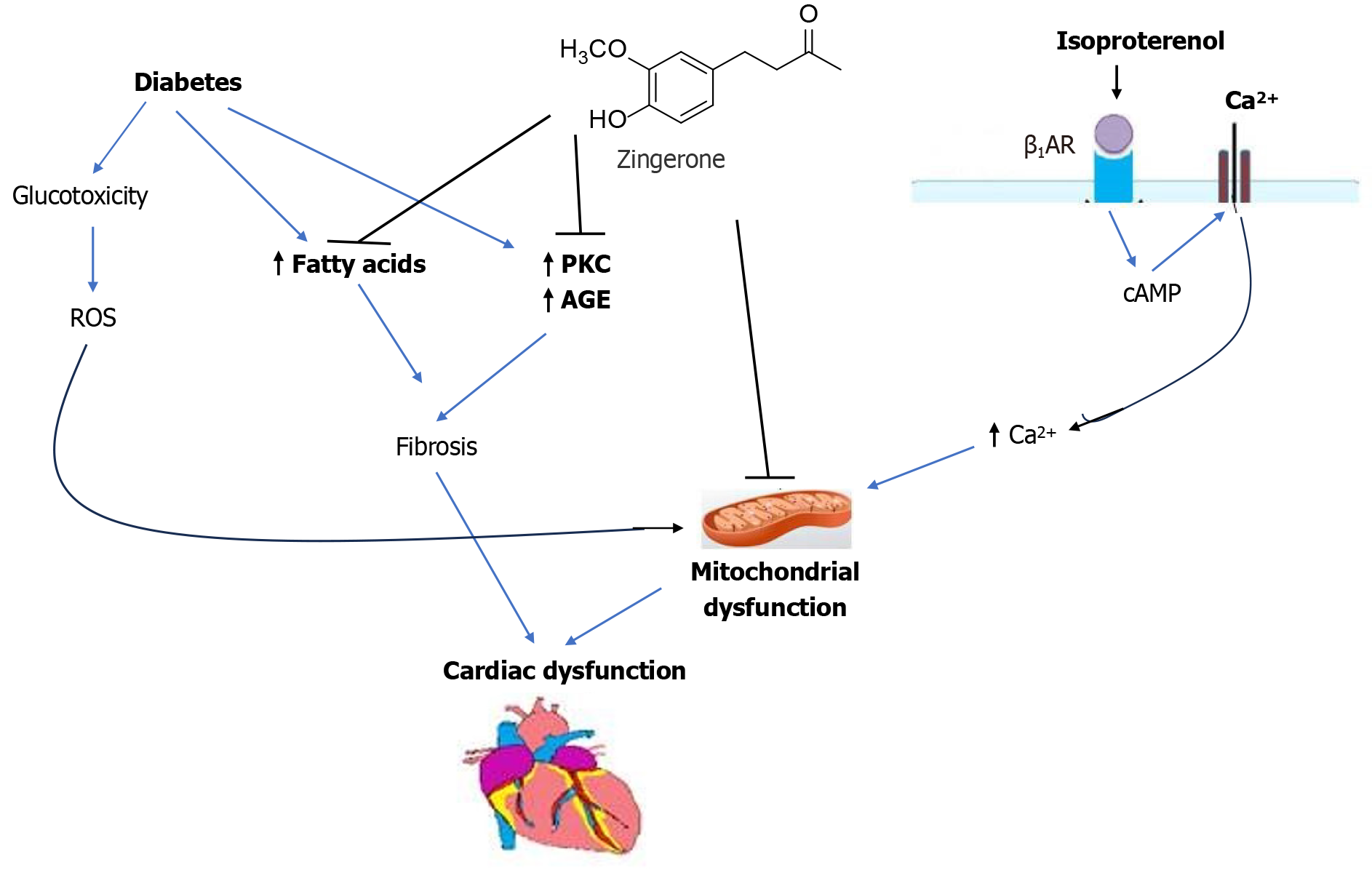
Figure 11 Diagrammatic representation of the protective role of zingerone in diabetes and isoproterenol induced cardiac dysfunctions.
PKC: Protein kinase C; cAMP: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate; AGE: Advanced glycation end product; β1AR: Beta-1 adrenergic receptor.
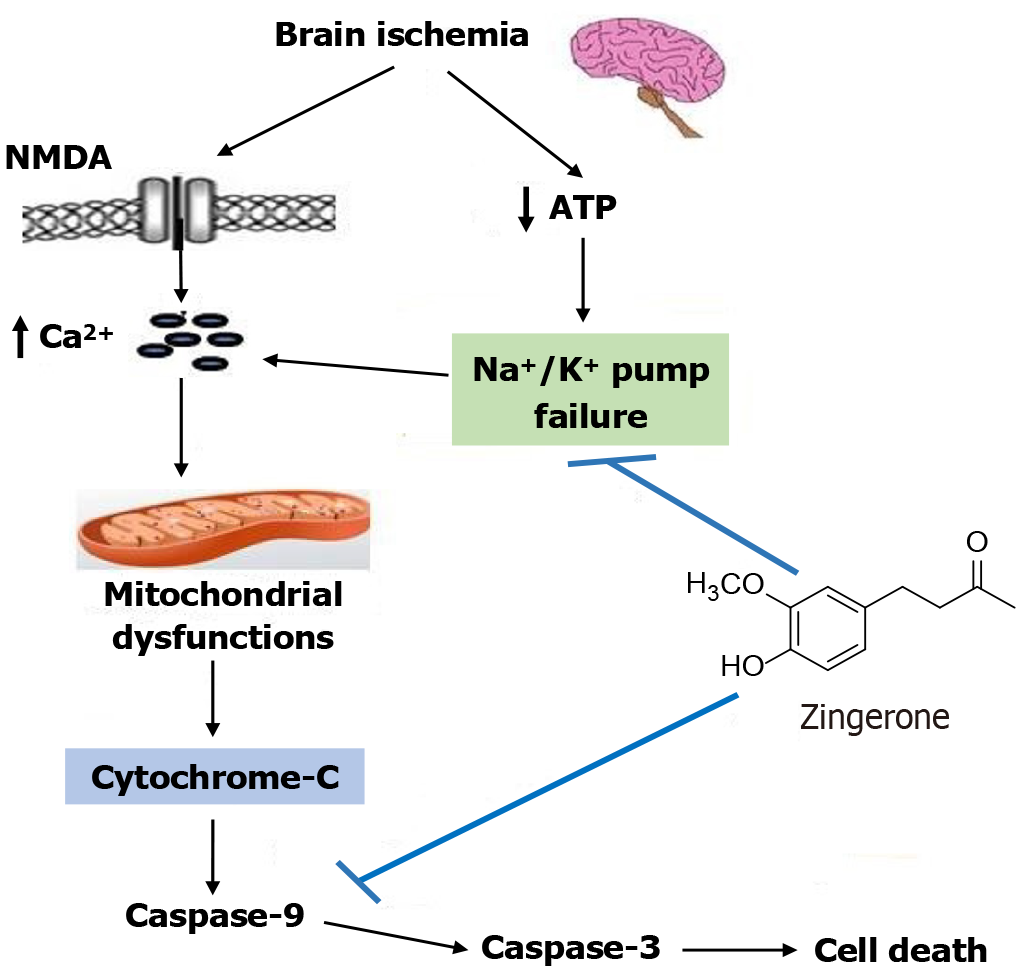
Figure 12 Diagrammatic representation of the neuronal protective effects of zingerone.
NMDA: N-methyl-D-aspartate; ATP: Adenosine tripho
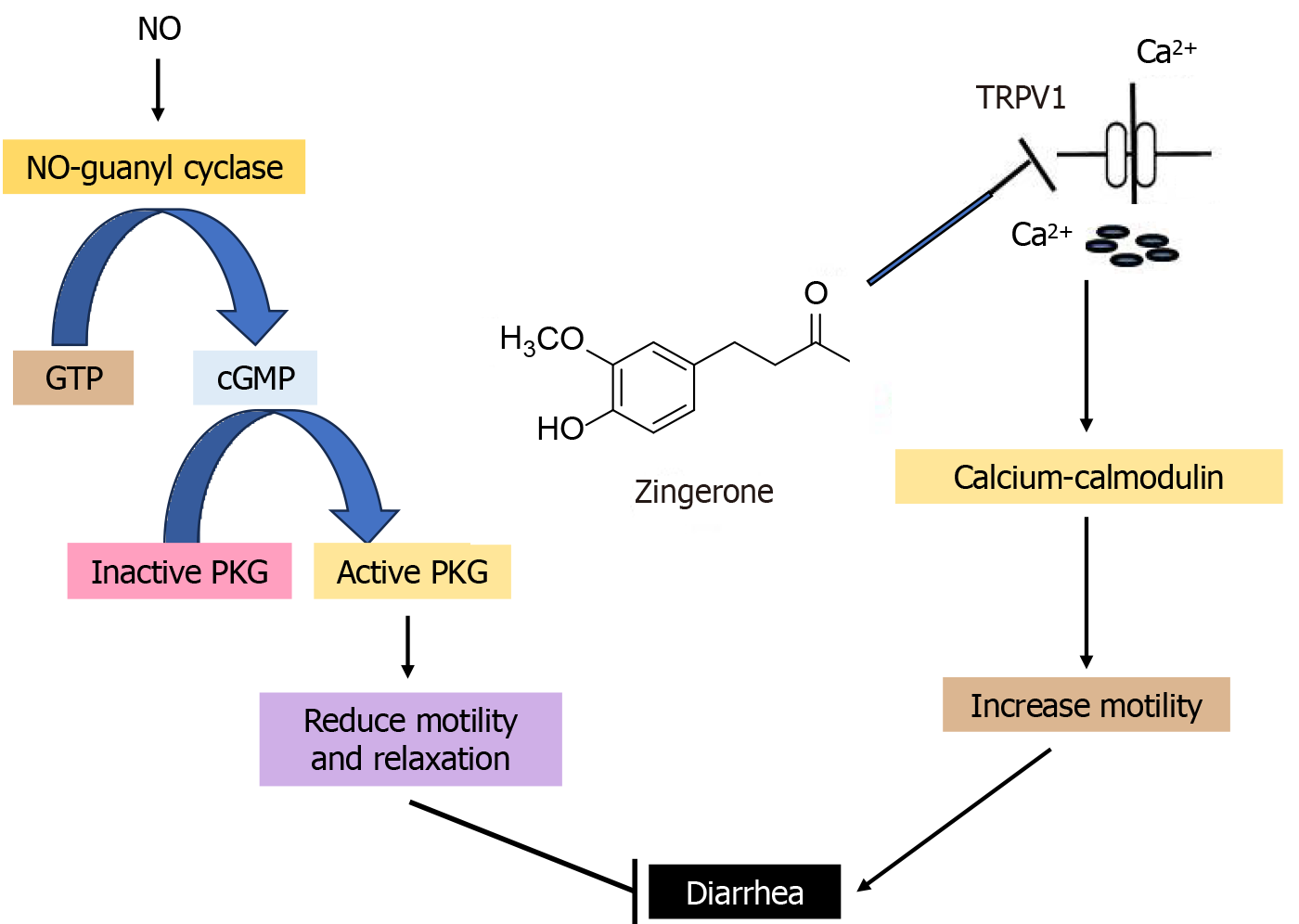
Figure 13 Zingerone possessed protective effect against diarrhoea.
TRPV1: Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1; NO: Nitric oxide; GTP: Guanosine triphosphate; cGMP: Cyclic guanosine monophosphate; PKG: Protein kinase G.
Figure 14
Zingerone showing anti-microbial activity.
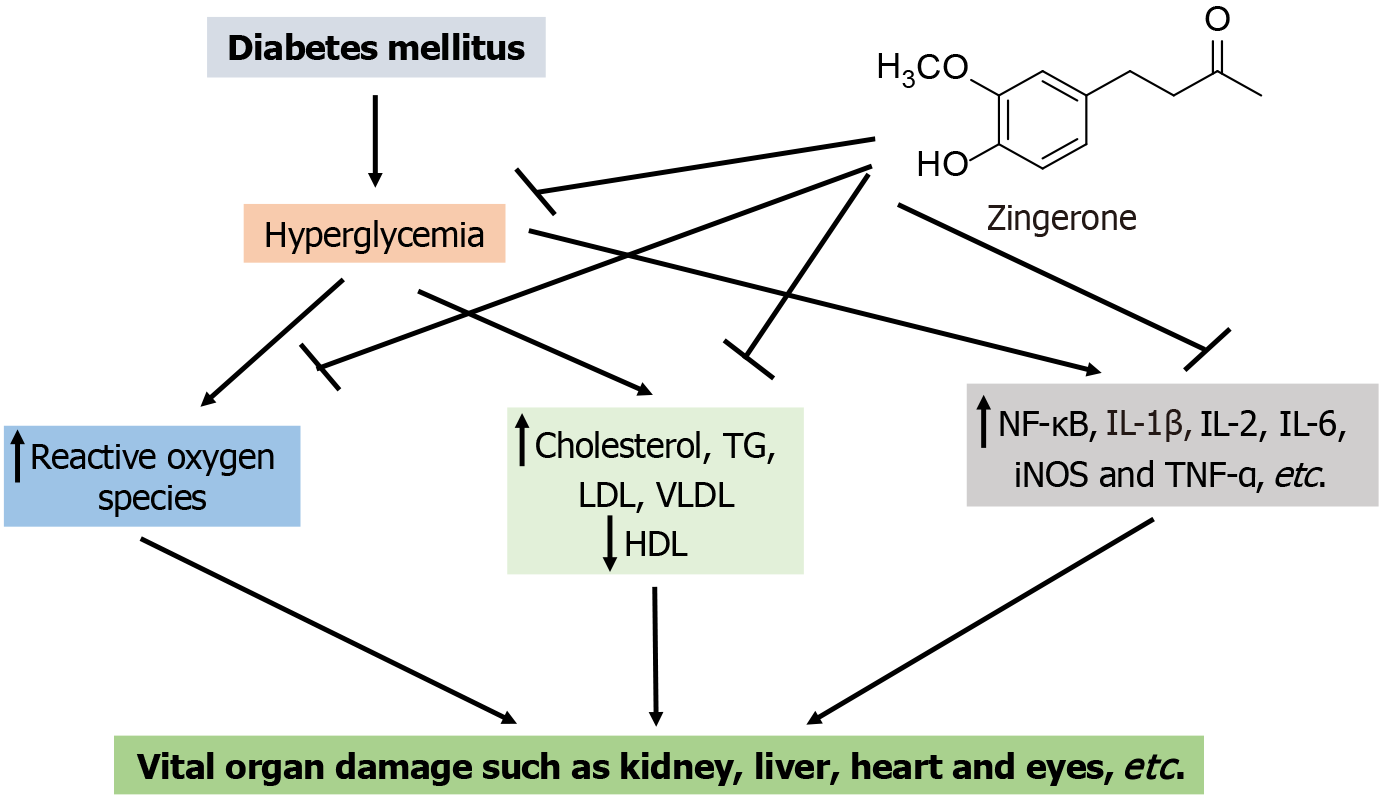
Figure 15 Diagrammatic representation of zingerone-mediated protection against diabetes mellitus induced harms to kidneys, heart, liver, and eyes.
TG: Triglycerides; LDL: Low density lipoprotein; VLDL: Very low density lipoprotein; HDL: High density lipoproteins; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase.
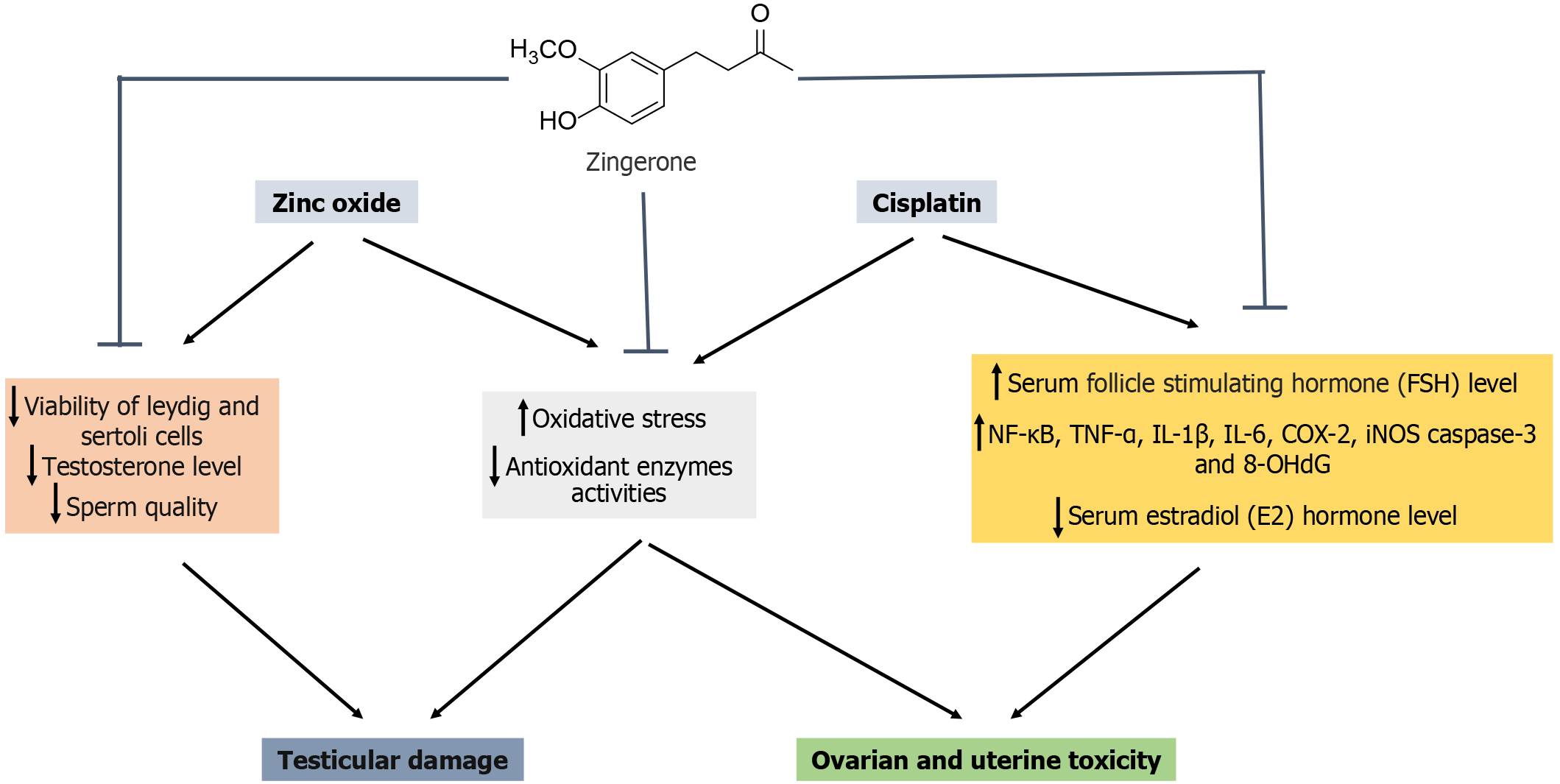
Figure 16 Reproductive toxicological evaluation of zingerone in male and female rats.
NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; IL: Interleukins; 8OHdG: 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine.
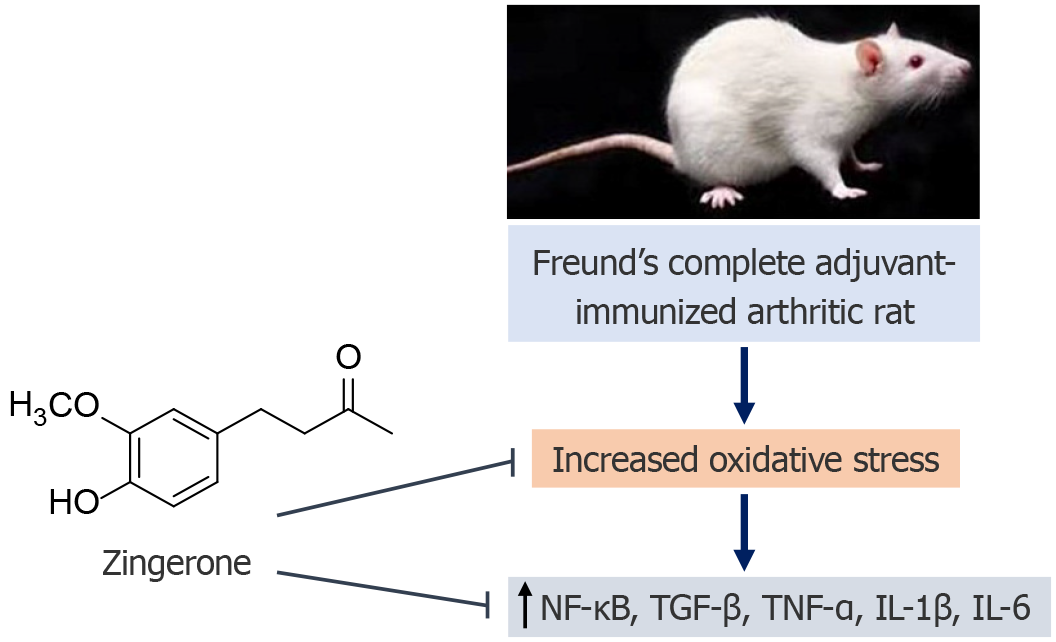
Figure 17 Zingerone showing protective effect at Freund’s complete adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats.
NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-beta; IL: Interleukins.
- Citation: Singh B, Singh H, Kaur S, Singh B. Preclinical pharmacology studies of zingerone with special reference to potential therapeutic applications. World J Immunol 2026; 16(1): 111511
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2824/full/v16/i1/111511.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5411/wji.v16.i1.111511