Published online Nov 9, 2021. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v10.i6.159
Peer-review started: January 10, 2021
First decision: February 12, 2021
Revised: April 6, 2021
Accepted: July 15, 2021
Article in press: July 15, 2021
Published online: November 9, 2021
Processing time: 302 Days and 18.2 Hours
Surgical intervention is usually a traumatic event that causes stress and anxiety in the pediatric patient and the family environment. To reduce the harmful effects of presurgical anxiety, parental presence during induction of anesthesia (PPIA) is one of the more notable interventions used in medical centers. However, data on this measure are difficult to evaluate and often face resistance from healthcare staff.
To analyze the perception of the healthcare workers after the implementation of a PPIA program.
A survey was developed and sent by email to all the healthcare staff working in the children’s area of a tertiary hospital. It consisted of 14 items divided into positive aspects of PPIA and negative aspects of PPIA evaluated with the use of a Likert scale (1 to 5). The demographics of the respondents were included in the data collected. The answers to the questions were interpreted through the Net Promoter Score (NPS). The statistical analysis compared the differences in the responses to each question of the survey made by the different groups of health personnel included.
A total of 141 surveys were sent out, with a response rate of 69%. Of the total number of responses, 68% were from women and 32% from men. The average age of the participants was 42.3 ± 10.6 years. As for the positive questions about the PPIA, 83% had an NPS > 50, and only one had a score between 0 and 50, which means that the quality of the service was rated as excellent or good by 100% of the respondents. On the other hand, 100% of the negative questions about the PPIA had a negative NPS. Responses to the question “PPIA increases patient safety” were significantly different (P = 0.037), with a lower percentage of pediatric surgeons (70%) thinking that PPIA increased patient safety, compared with ane
The personnel who participated in the PPIA program at our center were in favor of implementation. There were no validated arguments to support worker resis
Core Tip: Surgical intervention is usually a traumatic event that causes stress and anxiety in the pediatric patient and the family environment. To reduce the harmful effects of presurgical anxiety, the parental presence during induction of anesthesia (PPIA) is one of the more notable interventions used in medical centers. However, data on this measure are difficult to evaluate and often face resistance from healthcare staff. With our work, we want to emphasize the acceptance and support of the health per
- Citation: Velayos M, Estefanía K, Álvarez M, Sarmiento MC, Moratilla L, Sanabria P, Hernández F, López Santamaría MV. Healthcare staff as promoters of parental presence at anesthetic induction: Net Promoter Score survey. World J Clin Pediatr 2021; 10(6): 159-167
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2808/full/v10/i6/159.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5409/wjcp.v10.i6.159
Surgical interventions are traumatic events that causes stress and anxiety in the pediatric patient and the family environment. Several studies have shown that this type of anxiety is related to undesirable events such as negative results of anesthetic induction, increased pain in the postoperative period, increased postsurgical delirium, decreased adherence to subsequent medical treatment, and behavioral changes including sleep disorders, nutritional problems, enuresis, fear of separation, and aggression[1-4]. Various strategies have been developed to mitigate presurgical anxiety in both children and their family environment, with variable results that are controversial and difficult to evaluate. The use of pharmacological interventions remains one of the most widely used tools. However, in recent years, the use of nonpharmacological measures has gained great relevance in this field, with parental presence during induction of anesthesia (PPIA) being one of the most discussed[5].
It has been reported that families prefer to participate and be present during high-stress procedures such as surgery, and those who are present generally report fa
Implementation of the PPIA program was motivated by the pediatric surgery and child anesthesia and resuscitation services at our center to achieve more patient- and family-centered medicine and after having positive experience with the same program in other centers at our medical center.
The program was implemented in June 2019 after approval by the ethics committee. The necessary space for the different phases of the program were set up, all the necessary material for the entrance to the operating room was obtained, and all the personnel involved were properly instructed in every step of the process. A pilot phase was initiated with 57 patients undergoing major outpatient surgery without the need for hospitalization (e.g., epigastric herniorrhaphy, umbilical herniorrhaphy, inguinal herniorrhaphy, circumcision, hydrocelectomy, orchidopexy, and other minor surgical procedures). A future objective of this measure is potentially extending it to children undergoing conventional inpatient surgery and invasive diagnostic-therapeutic tests such as magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, and interventional radiology. The participating patients were between 2 and 12 years of age, were classified as American Society of Anesthesiologists status I, and 48% were premedicated with oral midazolam depending of the criteria used by the responsible anesthesiologist.
The possibility of PPIA was offered to all parents or legal guardians of children cited for major outpatient surgery. The decision to be present or absent was made vo
An internal survey was sent by email to all healthcare personnel involved in the process (i.e. pediatric surgeons, pediatric anesthesiologists, nursing and other medical staff) during the month of November 2019. The survey was composed of 14 items that were subdivided into positive aspects for PPIA and negative aspects for PPIA. The responses were graded on a Likert scale that ranged from totally disagree (1) to totally agree (5). The same questionnaire collected the demographic data of the respondents including age, gender, and the health group to which they belonged. The survey results were interpreted by the Net Promoter Score (NPS), which is a quality indicator that measures customer loyalty to companies based on recommendations. In the original version, each item has a score of from 0 to 10 where 0 is very unlikely to be recommended and 10 is strongly recommended. Scores between 9 and 10 are classified as promoters, those between 7 and 8 are passive, and those ≤ 6 are detractors. The final score is obtained by subtracting the detractors from the promoters and obtaining a percentage ranging from −100 to 100 that measures the quality of service, where an score > 0 is good, a score > 50 is excellent and a negative NPS is not a recommendation[11].
After obtaining the Likert scale scores for each item, these were transformed into values used by the NPS. Thus, scores of 4 or 5 on the Likert scale were considered as 9 or 10 in the NPS and were therefore promoters. Scores of 1 or 2, were considered as ≤ 6 and were therefore detractors. Finally, scores of 3 on the Likert scale were considered as 7 or 8 on the NPS, were passive, and were not taken into account in the study. After the total numbers and percentages of promoters and retractors in percentage for each item of the questionnaire were obtained, the percentage of promoters was subtracted from the percentage of retractors of each item of the survey. An NPS > 0% indicated good quality, an NPS > 50% indicated excellent quality, and an NPS < 0% indicated poor quality. Finally, a statistical analysis was comparing the demographic characteristics and survey responses of each group was performed. Responses of < 75% were excluded.
The data were collected using Microsoft Excel version 16.35. Statistical analysis was performed with the IBM SPSS 25.0 statistical package. Quantitative variables were reported as means and standard deviation and qualitative variables as absolute frequencies and percentages. After checking the normality of distributions of the variables with the Kolmogorov-Smirnoff test (corrected by the Lilliefors test), quan
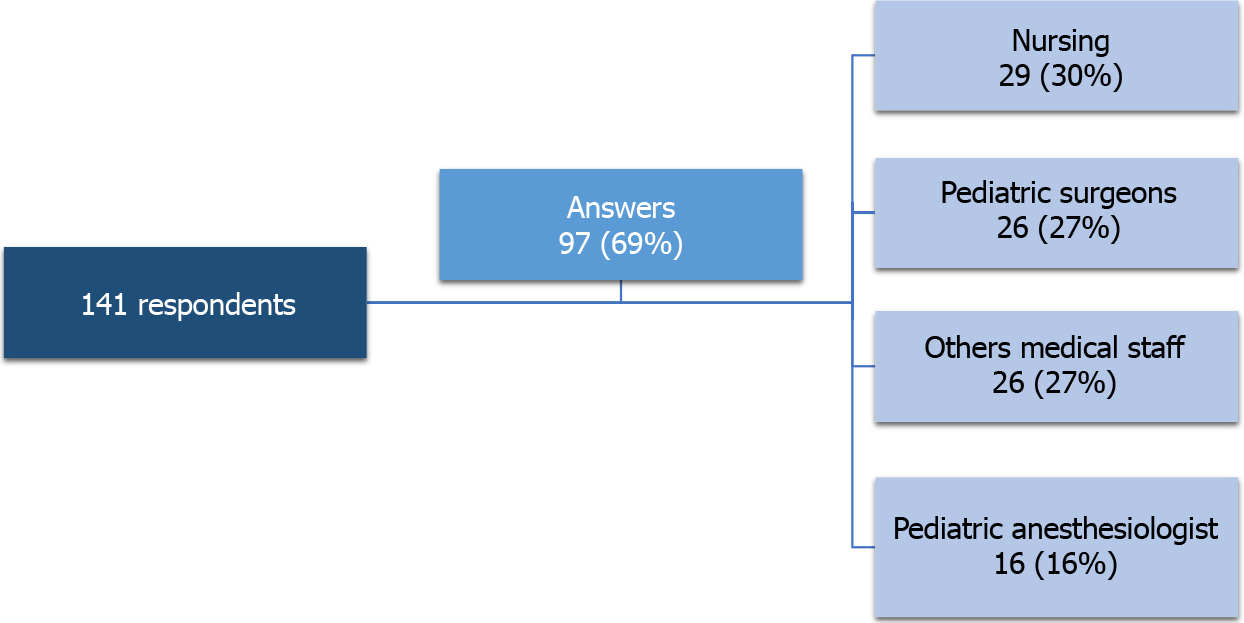
The survey was sent to 141 people; the response rate was 69%. The group with the highest participation was nursing, with 30% of the total respondents, followed by pediatric surgeons (27%), and other medical staff (27%), and pediatric anesthesiologists (16%, Figure 1). Of the total number of responses, 68% were women and 32% were men. The average age was 42.3 ± 10.6 years. The demographic data for each group are shown in Table 1.
| Pediatric surgeons | Pediatric anesthesiologists | Nursing | Other medical staff | P value | |
| Age, yr | 40.8 ± 11.5 | 43 ± 8.5 | 41.7 ± 9.8 | 44.2 ± 11.7 | 0.56 |
| Age subgroups, yr | |||||
| < 50 | 70 | 83 | 79 | 73 | 0.77 |
| > 50 | 30 | 17 | 21 | 27 | |
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 46 | 44 | 7 | 38 | 0.006 |
| Female | 54 | 56 | 93 | 62 |
Table 2 shows the percentages of promoters, retractors and passive respondents as well as the NPS results. Table 3 shows the percentage of promoters in each group for each question and the comparative analysis of group responses. Questions rated positive for PPIA had NPS values > 50 (excellent service quality), except for the question “PPIA decreases use of presurgical medication” which had an NPS of between 0 and 50 (good service quality), meaning that 100% of respondents agreed fully and agreed with the positive aspects of PPIA. On the other hand, all questions considered negative for PPIA had a negative NPS (poor quality of service), meaning that the respondents all disagreed that PPIA has negative aspects for the patients, their families, and for the development of surgical care activities. Comparing the results by group, statistically significant differences were found only for the question “PPIA increases patient safety,” with a lower percentage of pediatric surgeons who think that PPIA increases patient safety, compared with anesthetists (69.6% vs 90%), nurses (69.6% vs 92%), and other medical staff (69.6% vs 90% vs 96%, P = 0.037).
| Survey question | Promotors | Retractors | Passive | NPS (promotors − retractors) |
| Positive for PPIA | ||||
| PPIA improves the child’s surgical experience | 83.5 | 13.4 | 3.1 | 70.1 |
| PPIA improves the parent’s surgical experience | 81.4 | 6.2 | 12.4 | 75.2 |
| PPIA improves the relationship of the patient and his/her environment with health professionals at all levels | 81.4 | 4.2 | 14.4 | 77.2 |
| PPIA increases parental satisfaction | 82.5 | 3 | 14.4 | 79.5 |
| PPIA increases patient safety | 71.1 | 11.3 | 17.5 | 59.8 |
| PPIA decreases the use of presurgical medication | 47.4 | 19.6 | 33 | 27.8 |
| Negative for PPIA | ||||
| PPIA decreases surgical efficiency | 5.1 | 71.1 | 23.7 | -66 |
| PPIA should be exclusive por patients in ambulatory surgery | 12.4 | 71.1 | 6.2 | -58.7 |
| PPIA increases parental anxiety | 23.7 | 54.6 | 21.6 | -30.9 |
| PPIA increases child’s anxiety | 3.1 | 86.6 | 10.3 | -83.5 |
| PPIA increases the duration of anesthetic induction | 16.5 | 54.6 | 28.8 | -38.1 |
| PPIA increases the number of infections | 4.1 | 63.9 | 32 | -59.8 |
| PPIA increases the cost of health care | 20.6 | 59.8 | 19.6 | -39.2 |
| PPIA increases fear of legal problems | 24.7 | 52.6 | 23.7 | -27.9 |
| Survey question | Pediatric surgeons | Pediatric anesthesiologist | Nursing | Other medical staff | P value |
| Positive for PPIA | |||||
| PPIA improves the child’s surgical experience | 95 | 100 | 92 | 100 | 0.36 |
| PPIA improves the parent’s surgical experience | 83 | 100 | 92 | 100 | 0.07 |
| PPIA improves the relationship of the patient and his/her environment with health professionals at all levels | 86 | 100 | 96 | 100 | 0.11 |
| PPIA increases parental satisfaction | 85 | 100 | 100 | 96 | 0.07 |
| PPIA increases patient safety | 70 | 90 | 92 | 96 | P < 0.05 |
| PPIA decreases the use of presurgical medication | 62 | 80 | 55 | 88 | 0.11 |
| Negative for PPIA | |||||
| PPIA decreases surgical efficiency | 12 | 8 | 0 | 12 | 0.45 |
| PPIA should be exclusive por patients in ambulatory surgery | 13 | 23 | 8.3 | 22 | 0.52 |
| PPIA increases parental anxiety | 38 | 31 | 36 | 14 | 0.27 |
| PPIA increases child’s anxiety | 0 | 0 | 7 | 3 | 0.45 |
| PPIA increases the duration of anesthetic induction | 29 | 21 | 23 | 22 | 0.94 |
| PPIA increases the number of infections | 5 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 0.91 |
| PPIA increases the cost of health care | 19 | 25 | 36 | 19 | 0.50 |
| PPIA increases fear of legal problems | 37 | 21.4 | 37 | 32 | 0.77 |
The results of our survey showed full approval of the implementation of the PPIA program at our center. The intervention was considered by pediatric surgeons, anesthesiologists, nurses, and other medical staff as an excellent quality service by more than 80% of the respondents. This conclusion is in line with other recent studies that showed that pediatric surgery departments and other healthcare providers approved of PPIA and consider it beneficial for the patient[7,12]. To our best know
We launched the project because we consider the presence of parents during anesthetic induction as part of a comprehensive, family-centered approach that respects their requirements and decisions. That was not always the case in pediatric healthcare. In 1895 D’Arcy Power wrote: “When an operation has been decided upon, it will generally be seen that better results are obtained if the child is removed from his usual environment and placed in the care of those who have special experience in the care of sick children”[13]. The idea of separating the pediatric surgical patient from the family environment was maintained during the first half of the 20th century. Later, Gross[14] and Caniano et al[15] emphasized and assumed the role of the family in the child’s surgical experience. It has been in recent decades that PFCC has grown and evolved to become a goal to be achieved in all medical areas including pediatric surgery[8]. Participation and collaboration are the basic concepts of PFCC, and numerous studies have tested strategies such as preoperative family preparation or the impact of the PPIA. The data on family preparation for the reduction of preoperative anxiety are positive[16,17]; in contrast, the results obtained regarding the impact of PPIA are controversial and not clear, as the latest Cochrane review showed[5]. However, even though Sadeghi et al[18] and Hussain and Khan[19] found no benefit of PPIA with respect to preoperative anxiety, they did find other positive aspects, such as improved patient cooperation at the time of anesthetic induction, better acceptance of the face mask, or increased parental satisfaction, suggesting that PPIA may improve those aspects. In line with those findings, we found that the group with the highest percentage of promoters in most of the positive questions for PPIA was pediatric anesthesiologists, probably because behavior of children during anesthetic induction was better when a parent was present. However, Luehmann et al[7], showed that the median response to PPIA was most favorable for perioperative nurses, who are involved in all aspects of patient care and can give a more comprehensive opinion. The findings reinforce the support to the program from different points of view of the same process.
Many prejudices had to be overcome before the project could be launched. There are still common points of contention against this measure on the part of the medical staff, who believe that the presence of the parents could be disturbing, the induction of anesthesia and surgical intervention delayed, and the possibility of generating medical-legal problems. For example, Paice et al[6] reported significantly less support from medical staff for the presence of parents during invasive procedures compared with parents. In our results, pediatric surgeons were less positive than other groups when asked whether PPIA increased patient safety, which could be explained by fear of unwanted events. However, no related adverse effects were found in other studies, and there are no valid arguments to justify medical staff resistance to the imple
Unfortunately, despite the rationale and supporting evidence, PPIA is far from being a widespread and applicable procedure for all surgical procedures and invasive testing. Pediatric surgery has changed enormously over the last century, and we believe that family involvement in day-to-day clinical practice will eventually become a well-established part of pediatric surgical patient care. Finally, the acceptance and commitment of the healthcare personnel in the application of the PPIA at our center is highlighted. We suggest that all surgical centers should have programs that include family involvement, such as parental presence at anesthetic induction.
Our study has the typical limitations of a qualitative survey. We cannot draw objective conclusions that can be tested if we do not offer an in-depth understanding of the acceptance of PPIA at our center with the belief in its expansion to other centers. Although we included the sex and age of respondents, other influential factors such as years of experience or previous experience with PPIA programs were not included in the analysis. We also did not take passive responses into account, assuming that they would not be relevant to the results. Finally, we are aware of the difficulty of applying a quality score from the business world to a measure of preoperative anxiety, but we believe in it here.
The results highlight the acceptance and commitment of healthcare personnel in the application of the PPIA in our center. We suggest that all surgical centers should have programs that include family involvement, such as parental presence at anesthesia induction.
Medicine is getting closer and closer to the human side of the patient and family. Family knowledge, understanding, and accompanying their children, offers them an opportunity to contribute in the surgical process, and helps to reduce the stress caused by those situations.
We were motivated by the importance of avoiding the anxiety and stress that a surgical intervention causes in pediatric patients and their family environment, improving our relationship with them, and promoting their welfare.
The objective was to analyze the responses of healthcare workers to the imple
A survey was designed and sent to the personnel involved in the process. It was analyzed and reinterpreted by applying a novel “Net Promoter Score”.
The personnel involved in the process support the implementation of the program
Based on the good acceptance of the program in our center, we suggest the deve
More studies are needed to demonstrate the effectiveness of parental presence during the induction of anesthesia (PPIA) and the support of healthcare workers for measures such as PPIA or similar programs. We must demonstrate the importance and in
The authors would like to thank all the health personnel who have supported and made possible the development and implementation of this program.
| 1. | Kain ZN, Mayes LC, Caramico LA. Preoperative preparation in children: a cross-sectional study. J Clin Anesth. 1996;8:508-514. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 120] [Cited by in RCA: 112] [Article Influence: 3.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Fortier MA, Del Rosario AM, Martin SR, Kain ZN. Perioperative anxiety in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2010;20:318-322. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 127] [Cited by in RCA: 158] [Article Influence: 9.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Rice M, Glasper A, Keeton D, Spargo P. The effect of a preoperative education programme on perioperative anxiety in children: an observational study. Paediatr Anaesth. 2008;18:426-430. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 40] [Cited by in RCA: 42] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Felder-Puig R, Maksys A, Noestlinger C, Gadner H, Stark H, Pfluegler A, Topf R. Using a children's book to prepare children and parents for elective ENT surgery: results of a randomized clinical trial. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2003;67:35-41. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 65] [Cited by in RCA: 67] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Manyande A, Cyna AM, Yip P, Chooi C, Middleton P. Non-pharmacological interventions for assisting the induction of anaesthesia in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;CD006447. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 71] [Cited by in RCA: 98] [Article Influence: 8.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Paice A, Ogunboye K, Patel S, Ade-Ajayi N. A parent in the operating theater: a survey of attitudes. J Pediatr Surg. 2009;44:711-719. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Luehmann NC, Staubach ME, Akay B, Collier PJ, Han RE, Riggs TW, Novotny NM. Benefits of a family-centered approach to pediatric induction of anesthesia. J Pediatr Surg. 2019;54:189-193. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Ferrari LR, Antonelli RC, Bader A. Beyond the Preoperative Clinic: Considerations for Pediatric Care Redesign Aligning the Patient/Family-Centered Medical Home and the Perioperative Surgical Home. Anesth Analg. 2015;120:1167-1170. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Erhaze EK, Dowling M, Devane D. Parental presence at anaesthesia induction: A systematic review. Int J Nurs Pract. 2016;22:397-407. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Wright KD, Stewart SH, Finley GA. When are parents helpful? Can J Anaesth. 2010;57:751-758. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Reichheld FF. The one number you need to grow. Harv Bus Rev. 2003;81:46-54, 124. [PubMed] |
| 12. | Yousef Y, Drudi S, Sant'Anna AM, Emil S. Parental presence at induction of anesthesia: perceptions of a pediatric surgical department before and after program implementation. J Pediatr Surg. 2018;53:1606-1610. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Power DA. General surgical considerations. The Surgical Disease of Children. HK Lewis London, 1895: 1-9. |
| 14. | Gross RE. Preoperative and postoperative care. The Surgery of Infancy and Childhood. WB Saunders Philadelphia, 1953: 6-37. |
| 15. | Caniano DA, Baylis F. Ethical considerations in prenatal surgical consultation. Pediatr Surg Int. 1999;15:303-309. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Kain ZN, Caldwell-Andrews AA, Mayes LC, Weinberg ME, Wang SM, MacLaren JE, Blount RL. Family-centered preparation for surgery improves perioperative outcomes in children: a randomized controlled trial. Anesthesiology. 2007;106:65-74. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 259] [Cited by in RCA: 273] [Article Influence: 14.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | West N, Christopher N, Stratton K, Görges M, Brown Z. Reducing preoperative anxiety with Child Life preparation prior to intravenous induction of anesthesia: A randomized controlled trial. Paediatr Anaesth. 2020;30:168-180. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 39] [Article Influence: 6.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Sadeghi A, Khaleghnejad Tabari A, Mahdavi A, Salarian S, Razavi SS. Impact of parental presence during induction of anesthesia on anxiety level among pediatric patients and their parents: a randomized clinical trial. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2017;12:3237-3241. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 32] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 4.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Hussain A, Khan FA. Effect of Two Techniques of Parental Interaction on Children's Anxiety at Induction of General Anaesthesia-A Randomized Trial. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2018;46:305-310. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Manuscript source: Invited manuscript
Specialty type: Health care sciences and services
Country/Territory of origin: Spain
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B, B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Ghannam WM, Kvolik S, Mondardini MC S-Editor: Liu M L-Editor: Filipodia P-Editor: Yuan YY