Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Respirol. Jul 28, 2015; 5(2): 78-92
Published online Jul 28, 2015. doi: 10.5320/wjr.v5.i2.78
Published online Jul 28, 2015. doi: 10.5320/wjr.v5.i2.78
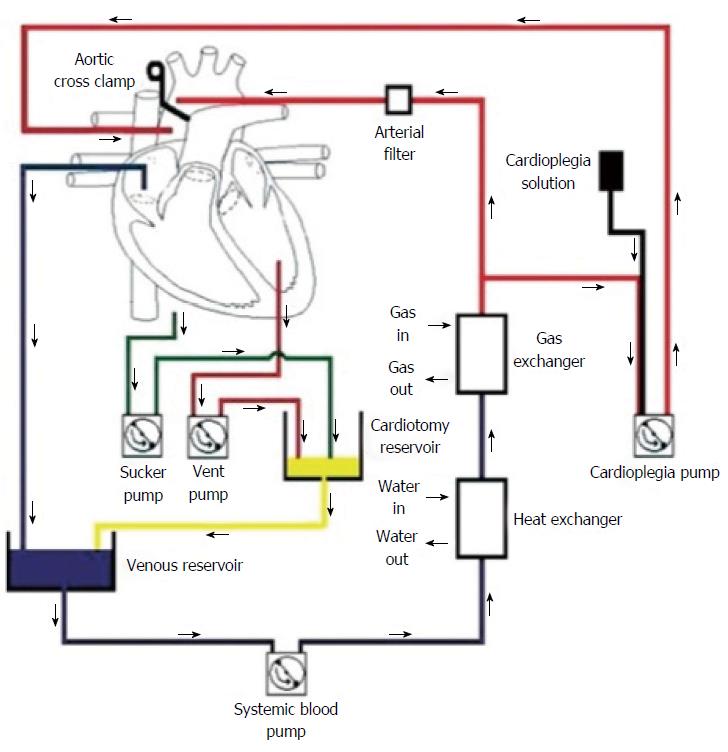
Figure 1 Cardiopulmonary bypass circuit is an open circuit in which venous blood drains into the venous reservoir by gravity (40-70 cm below the level of the heart) or siphonage.
Cardiopulmonary bypass circuit is considered an open circuit: blood from the cardiotomy reservoir, blood transfusions, or other fluids may be added into the circuit. Blood then passes through an oxygenator or gas-exchanger and is returned to the arterial system by utilizing a roller or centrifugal pump[8]. Figure from Machin et al[8], with permission of Oxford University Press.
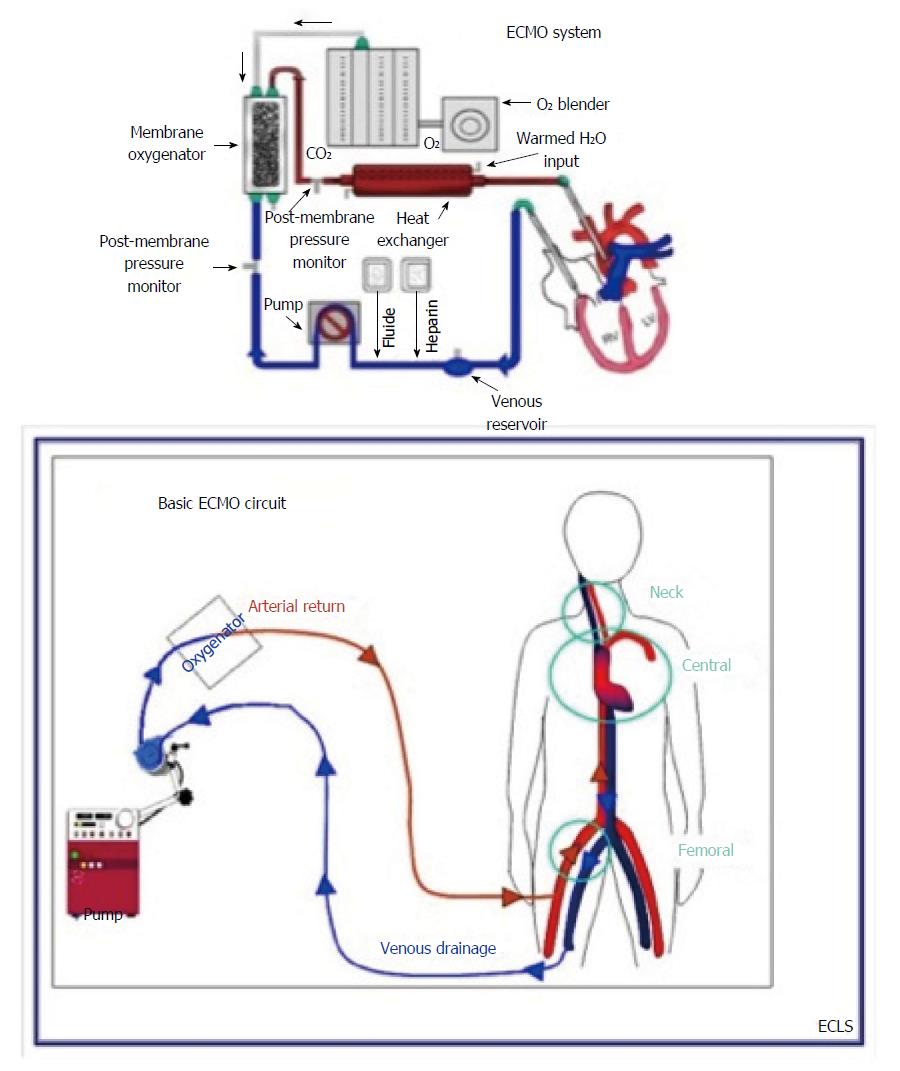
Figure 2 Schematic illustrating the components of an extracorporeal membrane oxygenation circuit: centrifugal pump, membrane oxygenator, inflow and outflow cannulas or cannula, and tubing with the potential to add ports for hemodialysis or ultrafiltration[9].
ECMO: Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
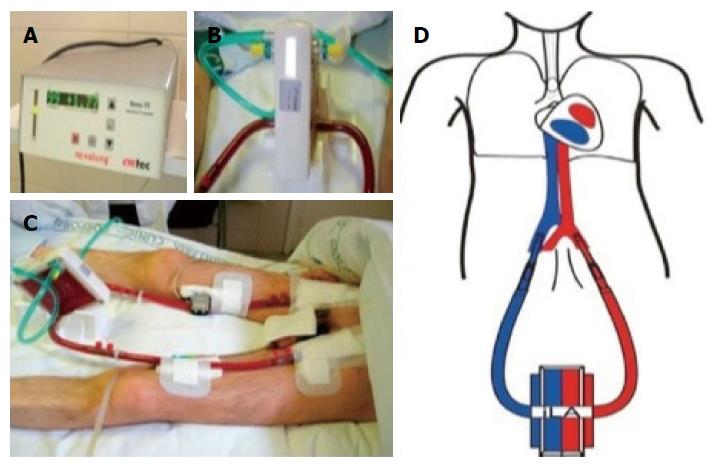
Figure 3 Extracorporeal lung assist, Interventional Lung Assist, or the NovaLung® System.
A: Flow measure across the system, in this case 1.77 L of blood per minute; B: Arterial and venous lines, oxygen inflow, and extracorporeal membrane made of polymethylpentene which provides gas exchange by simple diffusion; C: Exchange membrane and arterial and venous cannulations; D: AV cannulation diagram for extracorporeal lung assist, note the absence of a pump[32].
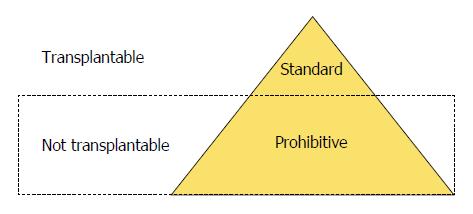
Figure 4 Only 15%-20% of donor organs meet standard criteria for lung transplant.
-
Citation: Bennett SC, Beal EW, Dumond CA, Preston T, Ralston J, Pope-Harman A, Black S, Hayes Jr D, Whitson BA. Mechanical circulatory support in lung transplantation: Cardiopulmonary bypass, extracorporeal life support, and
ex-vivo lung perfusion. World J Respirol 2015; 5(2): 78-92 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6255/full/v5/i2/78.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5320/wjr.v5.i2.78