Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Respirol. Mar 28, 2015; 5(1): 40-46
Published online Mar 28, 2015. doi: 10.5320/wjr.v5.i1.40
Published online Mar 28, 2015. doi: 10.5320/wjr.v5.i1.40
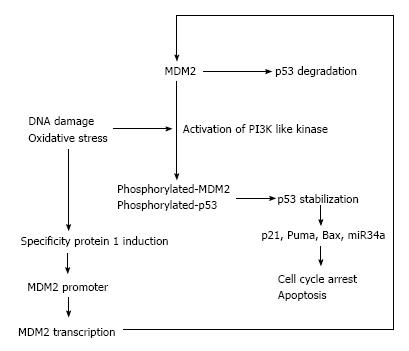
Figure 1 Schematic illustration of regulation and pathway of p53.
Genotoxic stress or oxidative stress induce phosphorylation of mouse double minute 2 homolog (MDM2) and p53 protein and activate p53 pathway, which induce cell cycle arrest and/or apoptosis. Puma: P53 up-regulated modulator of apoptosis; Bax: Bcl-2-associated X protein.
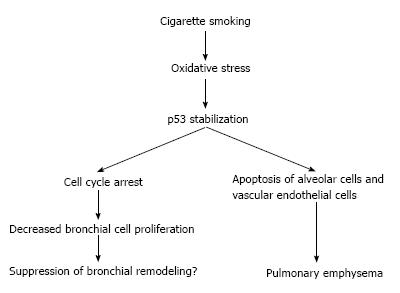
Figure 2 The hypothetical role of p53 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Oxidative stress from smoking activates the p53 pathway and thereby induces pulmonary emphysema through apoptosis of alveolar cells and vascular endothelial cells. The p53 pathway could be involved in bronchial remodeling.
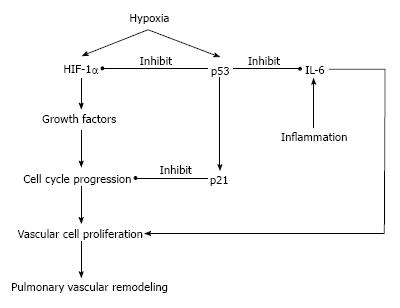
Figure 3 Possible mechanistic roles of p53 in pulmonary hypertension.
Hypoxia induces vascular proliferation via hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) activation, which may be negatively regulated by p53 activation and also influence vascular remodeling induced by interleukin 6 (IL-6).
- Citation: Mizuno S, Bogaard HJ, Ishizaki T, Toga H. Role of p53 in lung tissue remodeling. World J Respirol 2015; 5(1): 40-46
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6255/full/v5/i1/40.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5320/wjr.v5.i1.40