©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Orthop. Feb 18, 2026; 17(2): 114984
Published online Feb 18, 2026. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v17.i2.114984
Published online Feb 18, 2026. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v17.i2.114984
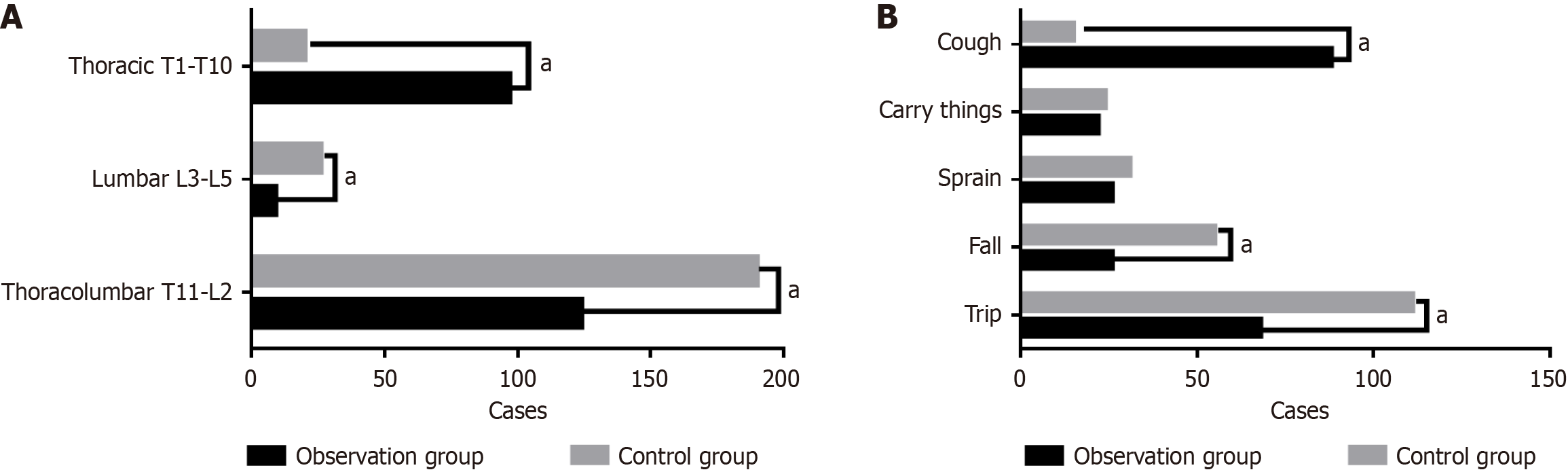
Figure 1 Comparison of fracture location and cause between the observation group and the control group.
A: Fracture location; B: Cause of fracture. The horizontal axis represents the type of fracture location/cause, and the vertical axis represents the number of cases. aP < 0.05. T: Thoracic vertebrae; L: Lumbar vertebrae.
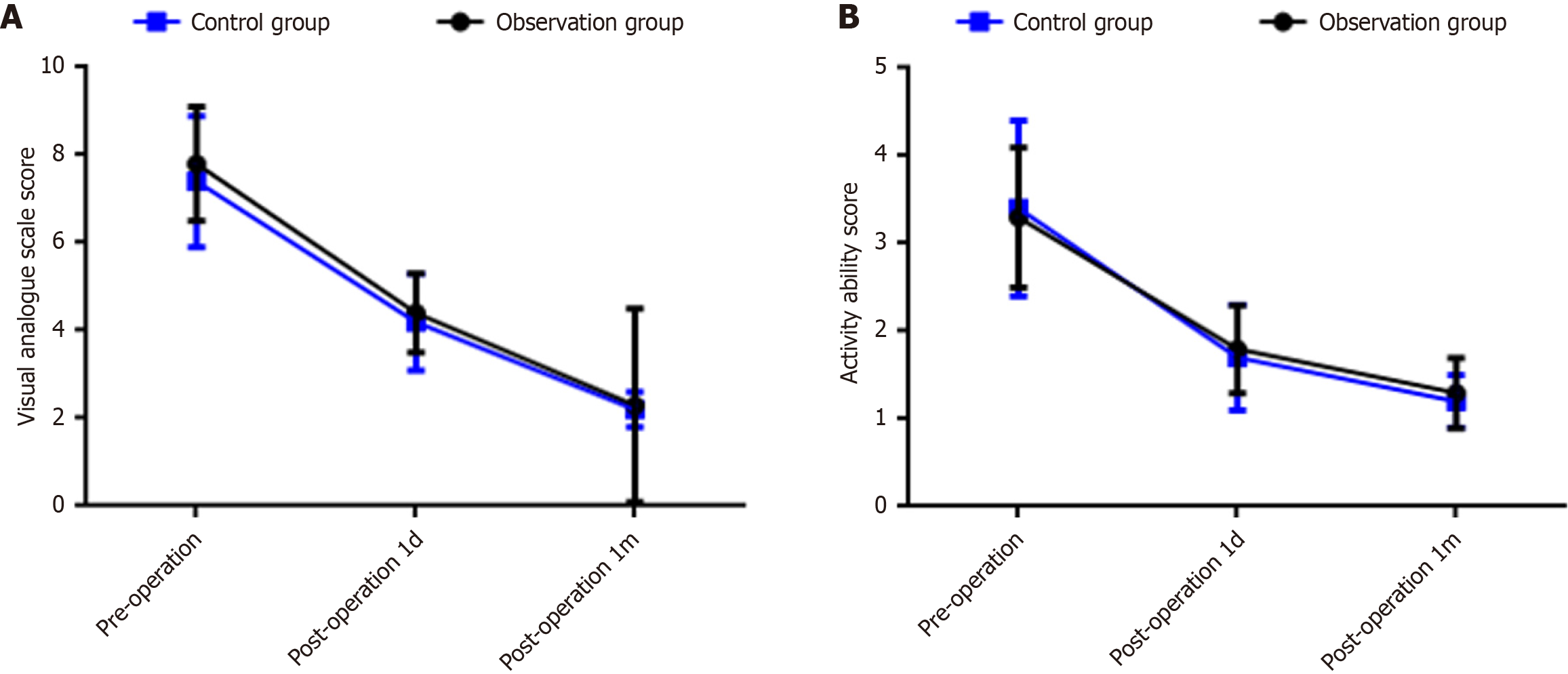
Figure 2 Comparison of visual analogue scale scores and activity ability scores between the observation group and the control group before surgery, 1 day after surgery, and 1 month after surgery.
B: Activity ability score. The horizontal axis represents the time point (pre-operation, 1 day post-operation, 1 month post-operation), and the vertical axis represents the score value). 1d: 1 day; 1m: 1 month.
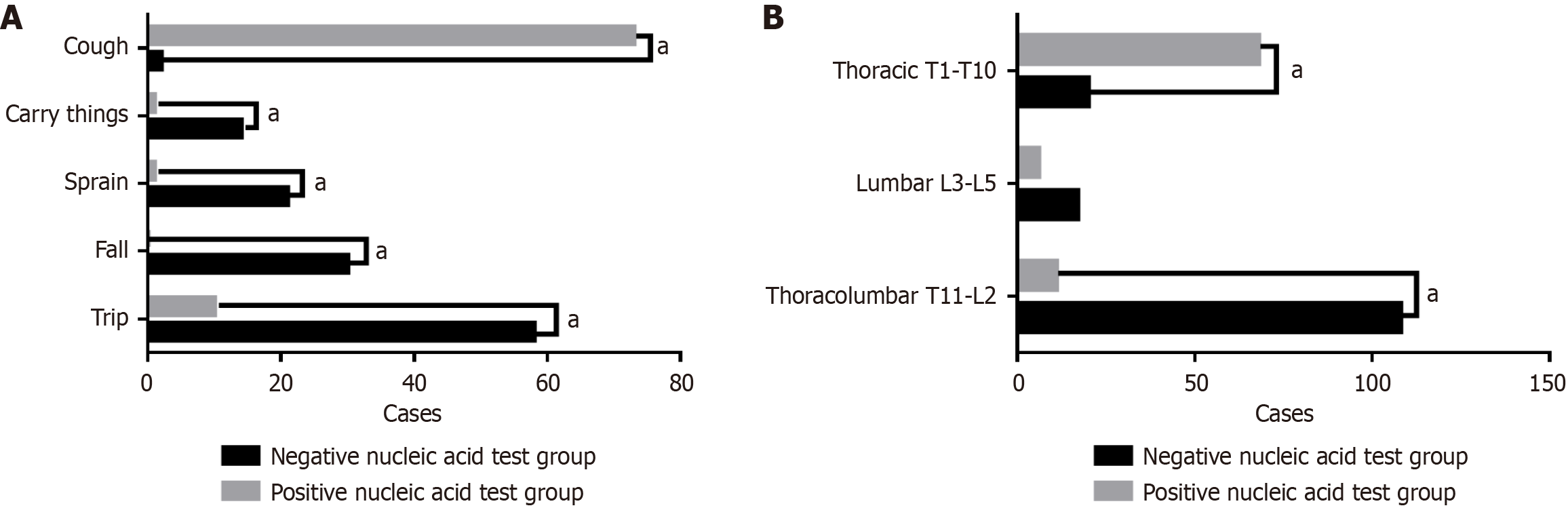
Figure 3 Comparison of different nucleic acid test.
A: Comparison of causes of fractures between subgroups with different nucleic acid test results; B: Comparison of fracture locations between subgroups with different nucleic acid test results. The horizontal axis represents the type of fracture cause/Location, and the vertical axis represents the number of cases. aP < 0.05. T: Thoracic vertebrae; L: Lumbar vertebrae.
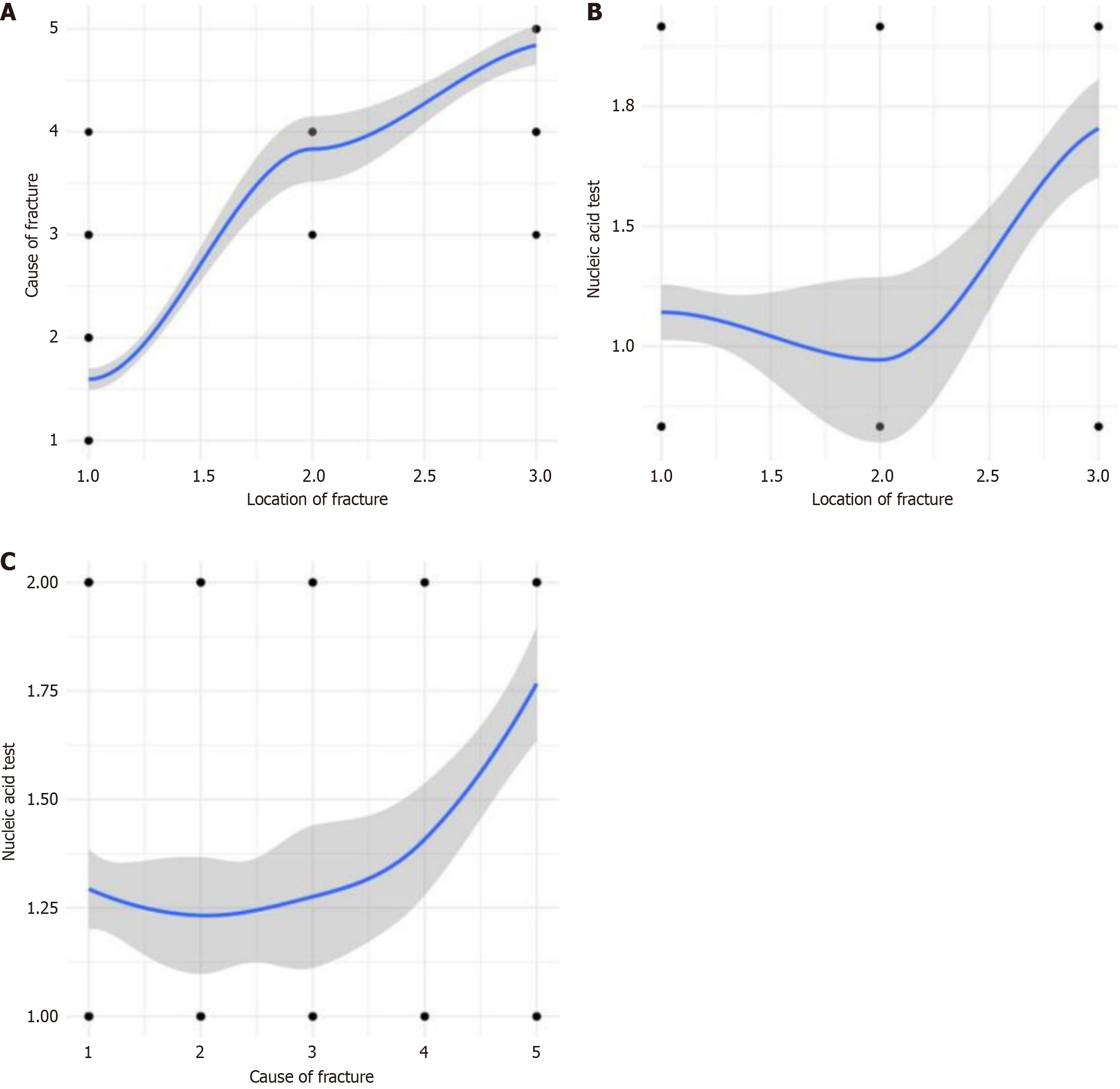
Figure 4 Correlation analysis chart.
A: Correlation analysis chart between cause of fracture and fracture location; B: Correlation analysis chart between nucleic acid test result and fracture location (thoracic vertebra); C: Correlation analysis chart between nucleic acid test result and cause of fracture. The horizontal axis represents fracture location/cause of fracture, and the vertical axis represents nucleic acid test result/cause of fracture/fracture location.
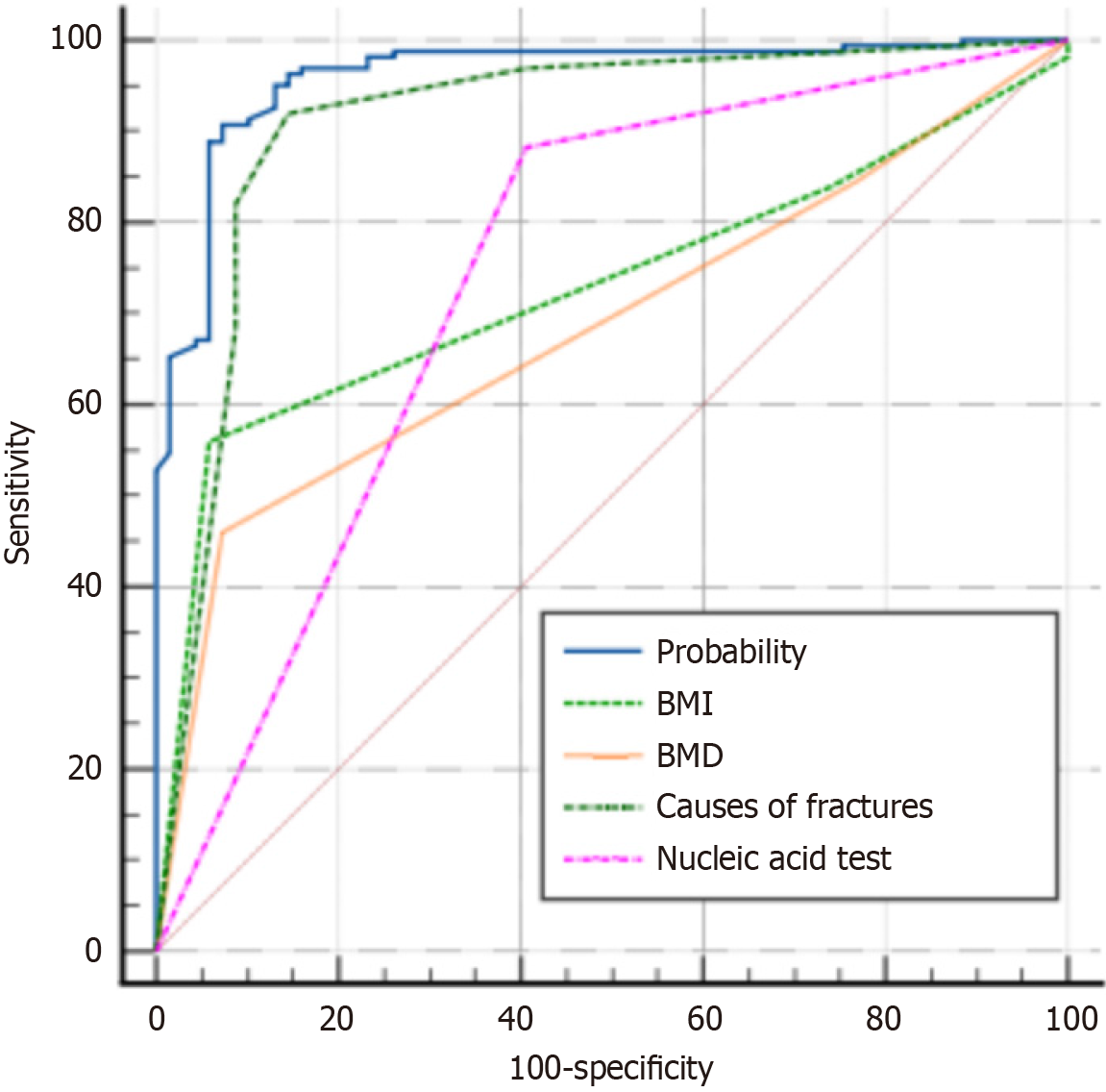
Figure 5 Receiver operating characteristic curve comparison of each influencing factor.
The horizontal axis represents 100 - specificity, and the vertical axis represents sensitivity. Different curves represent different influencing factors: Probability, body mass index, bone mineral density, causes of fractures, and nucleic acid test. BMI: Body mass index; BMD: Bone mineral density.
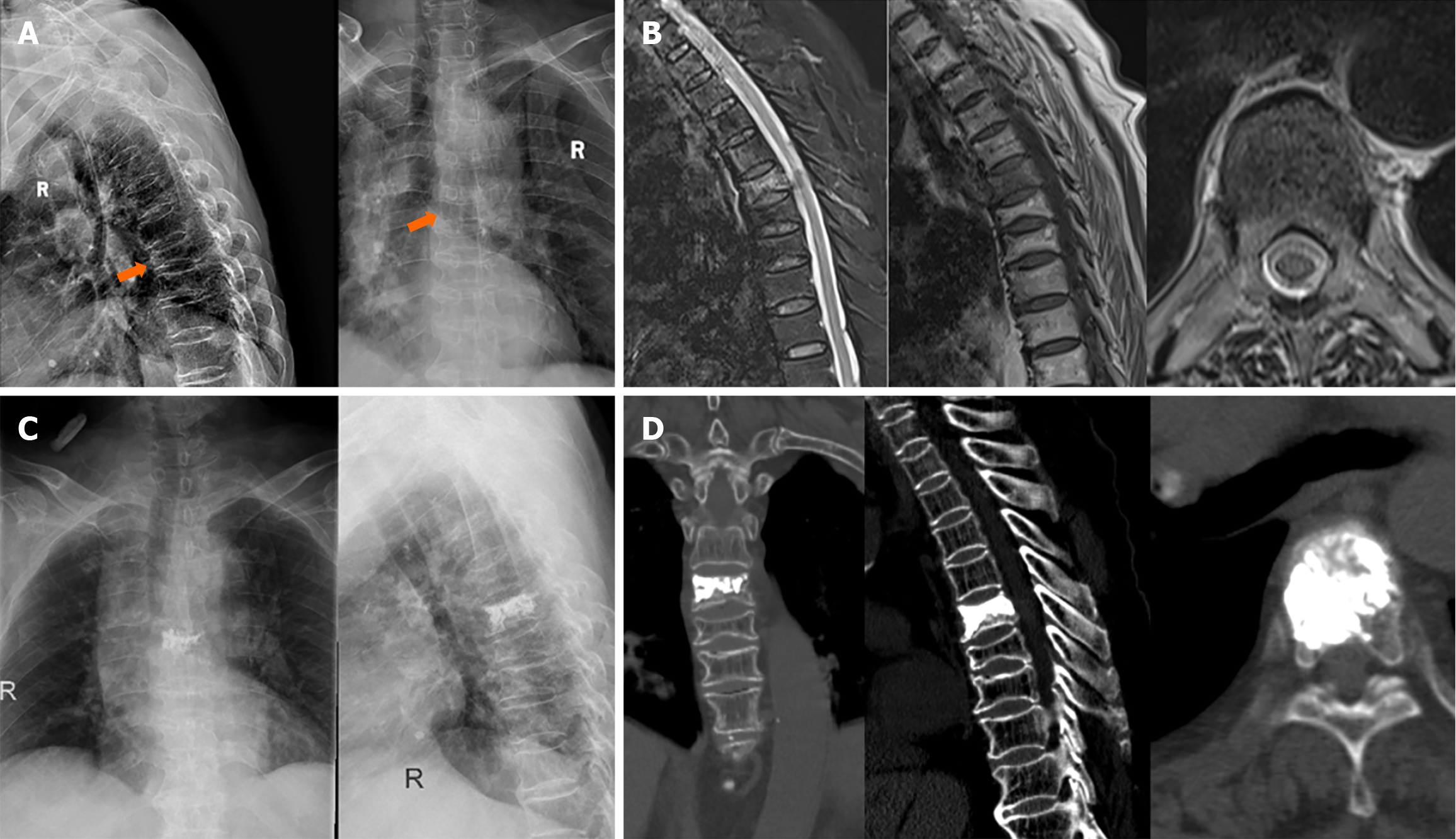
Figure 6 Imaging results.
A: Preoperative anteroposterior and lateral X-ray images of T6 fracture; B: Preoperative thoracic magnetic resonance imaging image; C: Anteroposterior and lateral X-ray images of the thoracic spine after T6 vertebroplasty; D: Thoracic computed tomography image after T6 vertebroplasty.
- Citation: Li YF, Wu CQ, Long Y, Yu QF, Xu W, Zhao JJ, Zhang XY, Li ZK. Risk factors for thoracic-osteoporotic thoracic vertebral compression fractures during the normalized prevention and control period of COVID-19. World J Orthop 2026; 17(2): 114984
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v17/i2/114984.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v17.i2.114984