©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Orthop. Sep 18, 2025; 16(9): 110433
Published online Sep 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i9.110433
Published online Sep 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i9.110433
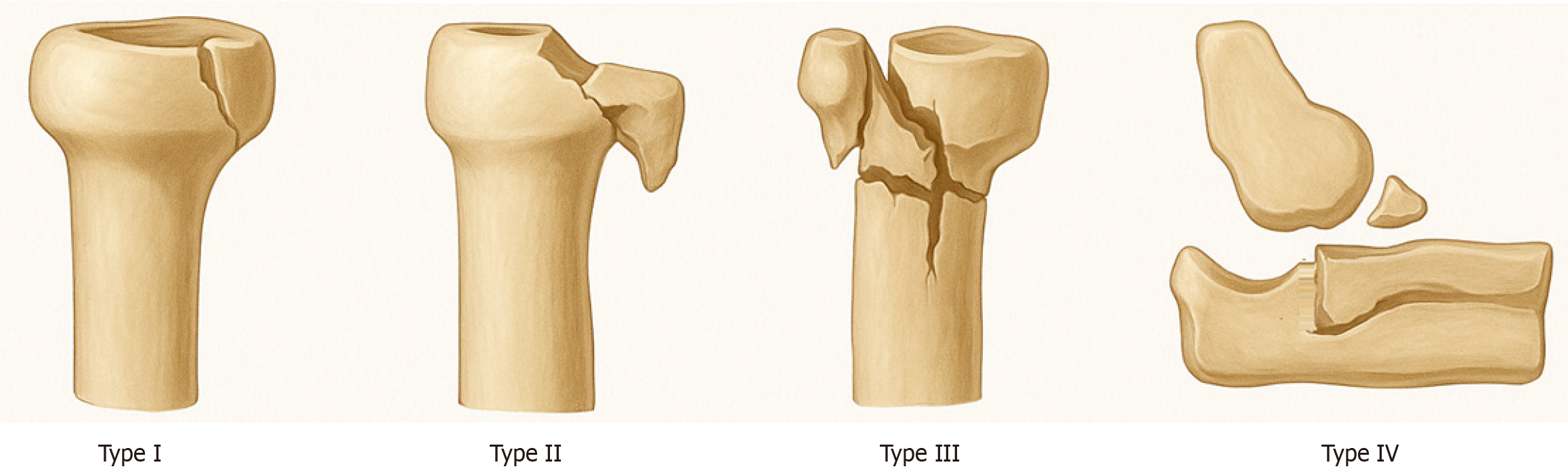
Figure 1 Mason-Johnston classification of radial head fractures.
Type I fractures are non-displaced or minimally displaced injuries of radial head (less than 2 mm) without mechanical block to motion; type II fractures are displaced by more than 2 mm, with potential blocking effect, but lack comminution; type III injuries are both comminuted and displaced; and type IV refers to radial head fractures occurring in the setting of elbow instability.
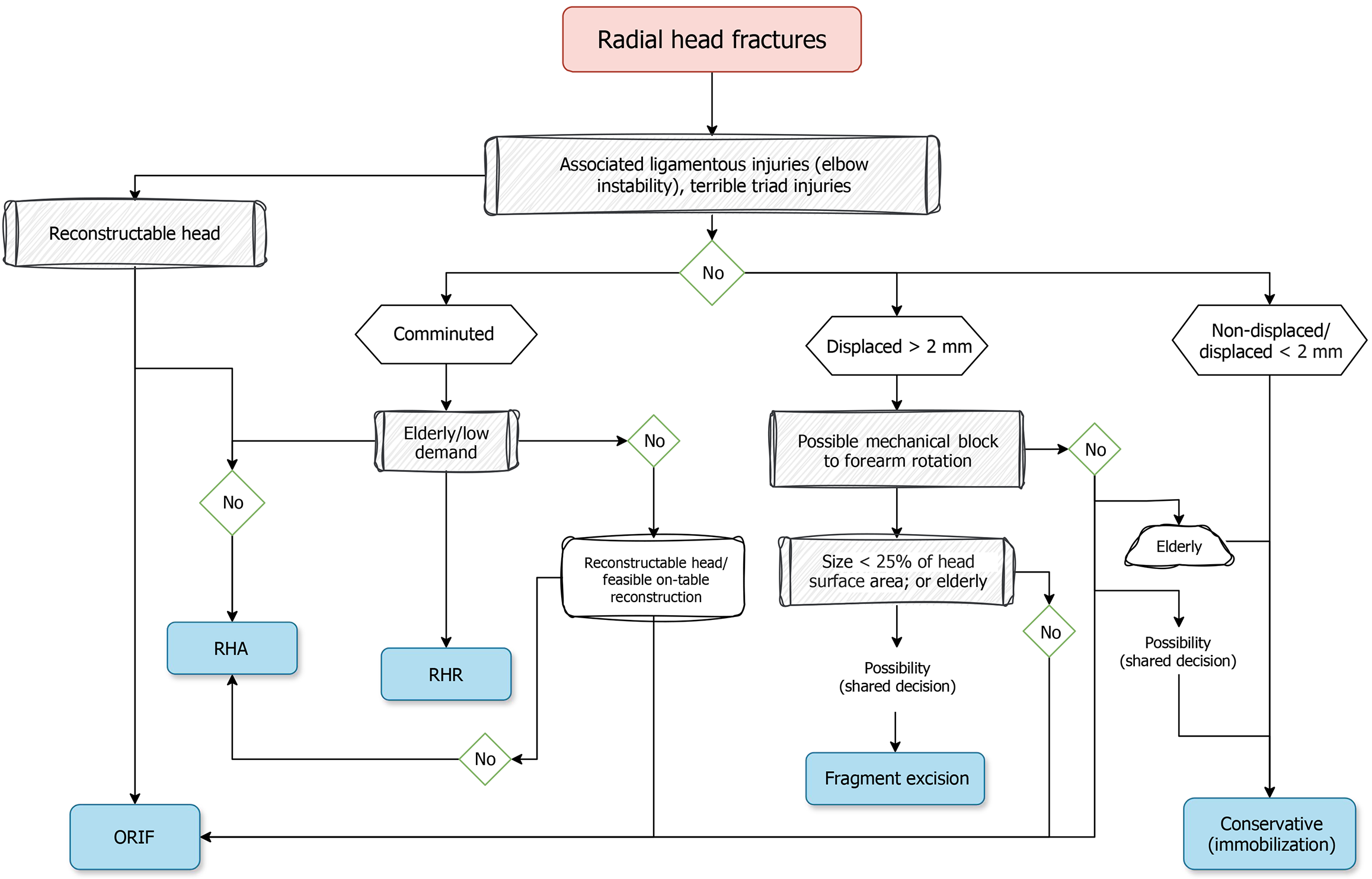
Figure 2 Simplified decision-making algorithm for Mason type III and IV radial head fractures.
Illustrating surgical selection among radial head arthroplasty, open reduction and internal fixation, and radial head resection based on fracture characteristics, reconstructability, ligament integrity, and patient demand level. ORIF: Open reduction and internal fixation; RHA: Radial head arthroplasty; RHR: Radial head resection.
- Citation: Elshahhat A, Almekoud M. Radial head arthroplasty: A pillar of stability in complex elbow fractures. World J Orthop 2025; 16(9): 110433
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v16/i9/110433.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v16.i9.110433