©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Orthop. Sep 18, 2025; 16(9): 108629
Published online Sep 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i9.108629
Published online Sep 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i9.108629
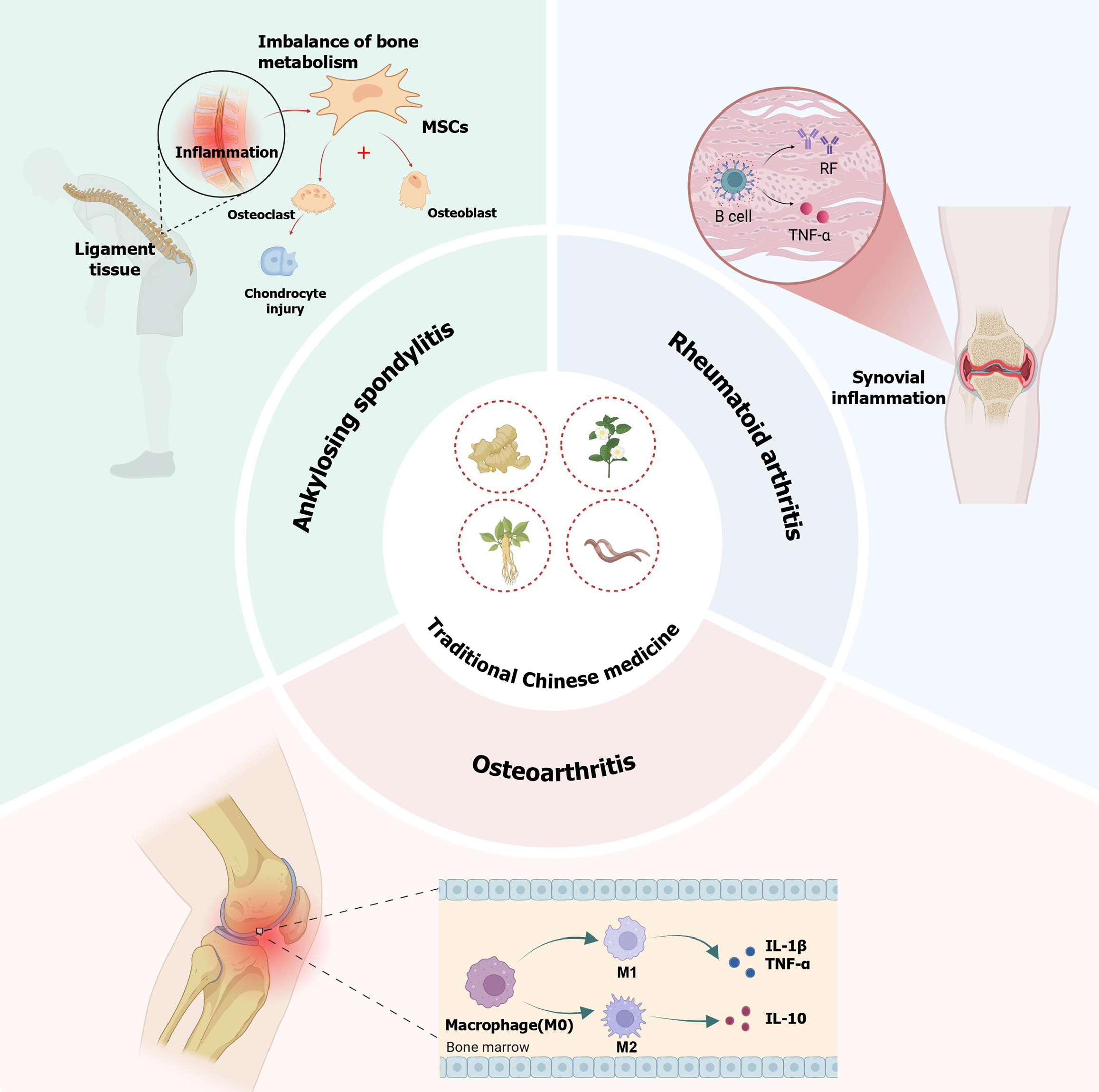
Figure 1 A summary of the important pathogenesis and pathological characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis and osteoarthritis and the therapeutic effect of traditional Chinese medicine.
MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells; RF: Rheumatoid factor; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α; IL: Interleukin.
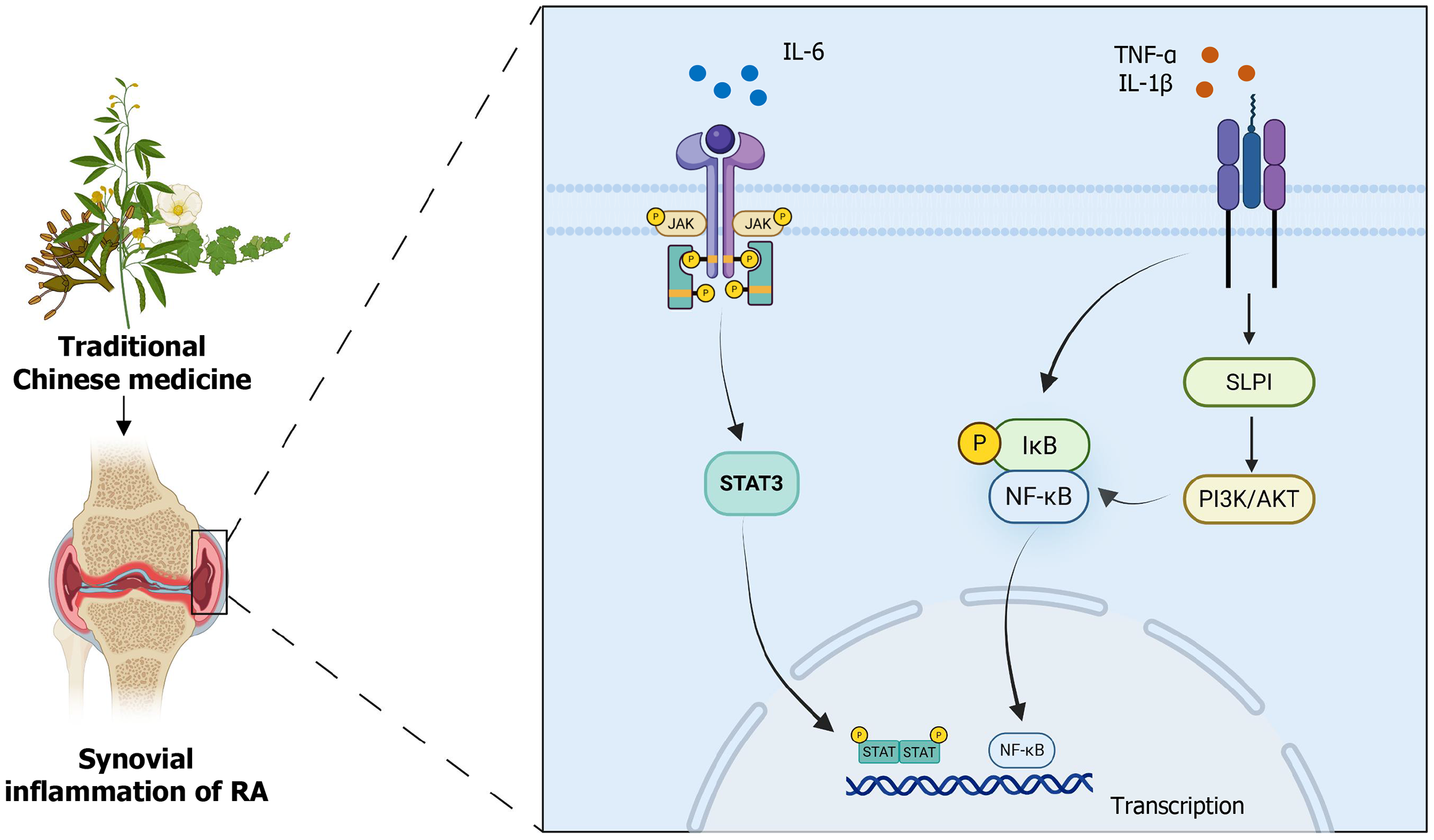
Figure 2 Traditional Chinese medicine reduce the synovial inflammation of rheumatoid arthritis through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B, Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathways.
RA: Rheumatoid arthritis; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α; IL: Interleukin; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; IκB: IkappaB; SLPI: Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor; PI3K/AKT: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.
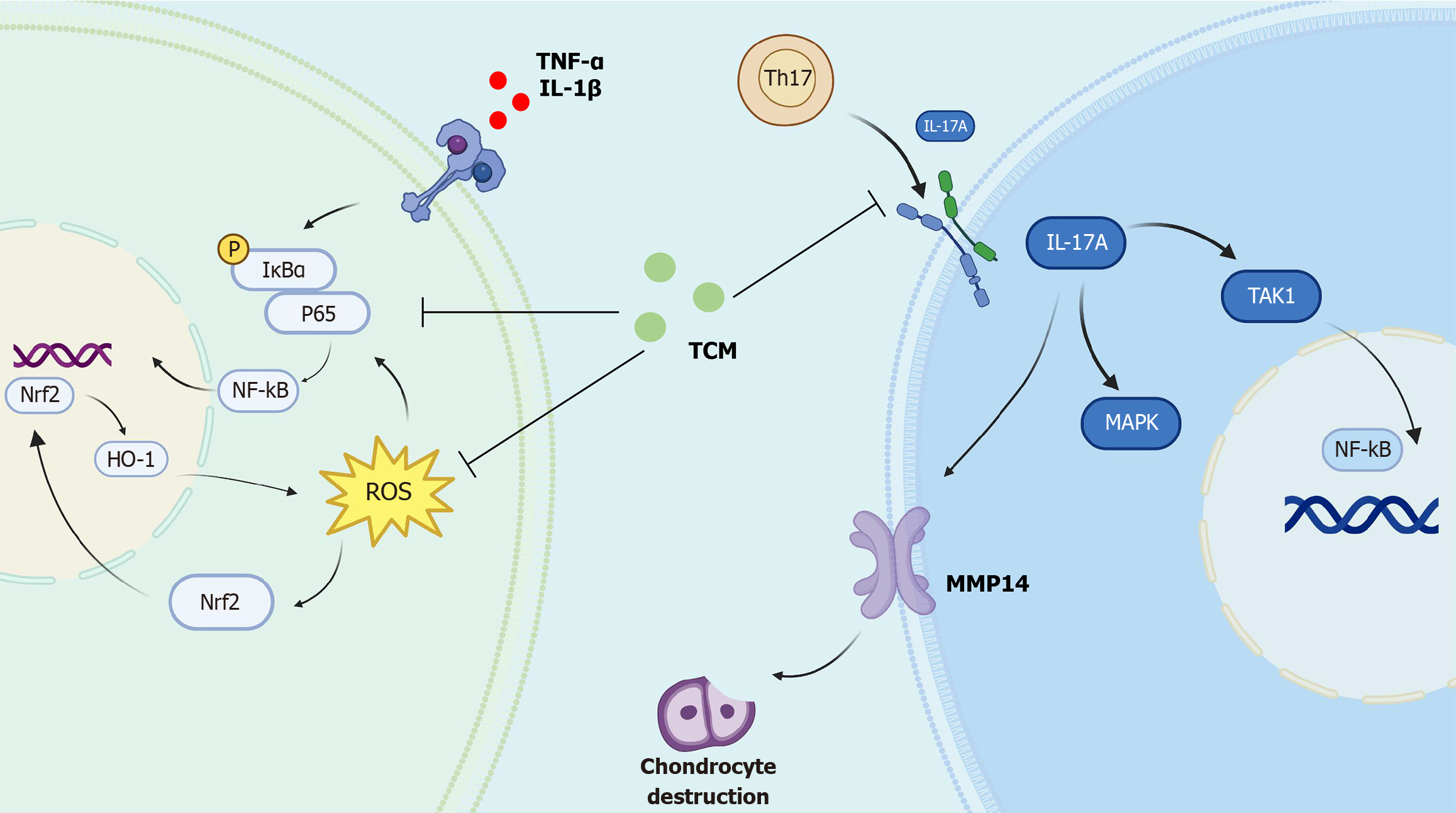
Figure 3 Traditional Chinese medicine alleviate inflammatory bone destruction in ankylosing spondylitis through nuclear factor erythroid/reactive oxygen species/nuclear factor kappa B axis and interleukin-17A signaling pathway.
TH17: T helper-17; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α; IL: Interleukin; IκBα: IkappaB α; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TCM: Traditional Chinese medicine; MMP14: Matrix metalloproteinase 14; TAK1: Transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase.
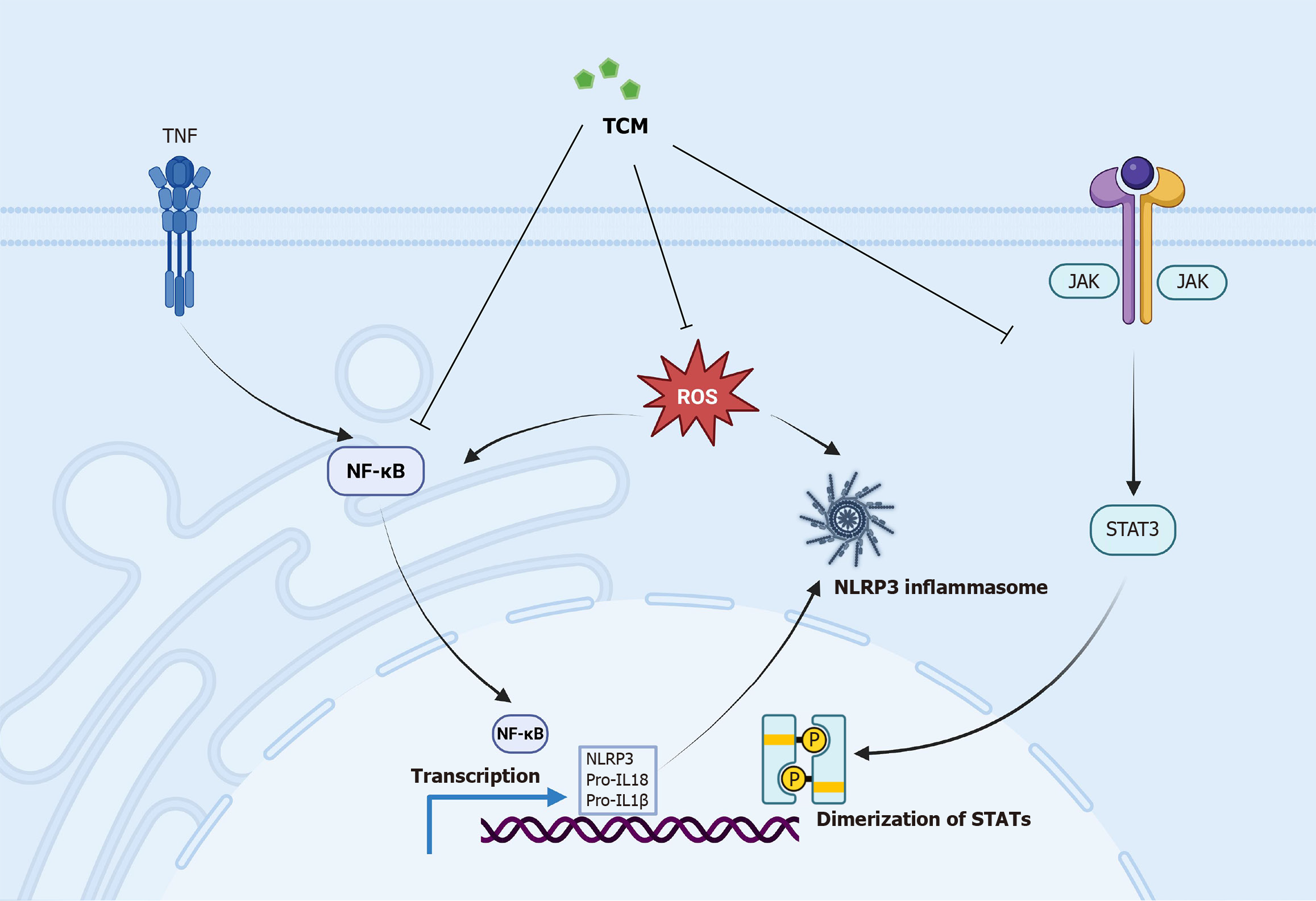
Figure 4 Traditional Chinese medicine suppress osteoarthritis-related inflammation by inhibiting the Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, nuclear factor kappa B, reactive oxygen speciesand NOD-like receptor 3 inflammatory signaling pathways.
TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TCM: Traditional Chinese medicine; IL: Interleukin; NLRP3: NOD-like receptor 3; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; JAK: Janus kinase.
- Citation: Lu JS, Yang M, Han ZG, Song CY, Sarbay N, Wang KY. Therapeutic potential of traditional Chinese medicine for inflammatory bone diseases: Elucidating molecular mechanisms and insights. World J Orthop 2025; 16(9): 108629
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v16/i9/108629.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v16.i9.108629