Published online May 6, 2016. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v7.i2.283
Peer-review started: July 27, 2015
First decision: August 25, 2015
Revised: January 15, 2016
Accepted: January 27, 2016
Article in press: January 29, 2016
Published online: May 6, 2016
Processing time: 271 Days and 10.9 Hours
AIM: To investigate the utility of intestinal disaccharide analysis during esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) in children, we performed a systematic review of studies examining disaccharide activity.
METHODS: All full-length articles published in English during 1966-2014 were included if: (1) participants had small intestinal biopsy evaluation of disaccharide activity; (2) levels of lactase, sucrase, maltase or palatinase were reported; and (3) age of participants was under 18 years.
RESULTS: Thirty articles examining 34753 disaccharide assays fulfilled the specific search, inclusion, and exclusion criteria. All of the studies were observational in design and 57% (17) were prospective. Sixteen studies were conducted in the United States and 9 European studies were identified. The biggest study enrolled about 30, 314 procedures and 13 studies investigated fewer than 50 procedures. Eleven studies examined Caucasian subjects, 3 studies examined Asian subjects, and 6 examined African subjects. Only one Hispanic subject was included. In studies reporting disaccharide deficiency, the overall proportion of lactase deficiency was 39.2%, sucrase deficiency was 9.0%, maltase deficiency was 12.6% and palatinase deficiency was 9.1%. The prevalence of duodenal inflammatory changes ranged from 6% to 24% for non-specific histological lesions (e.g., duodenitis). Sixteen studies examined the association of histologic findings with disaccharide activities, and 12 studies reported an inverse association between degree of histologic inflammation and disaccharide levels.
CONCLUSION: We reviewed 30 studies including 34753 biopsy specimens with disaccharide analysis from children undergoing EGD. Our findings advocate a large study is to further illuminate the importance of EGD with disaccharide analysis in children.
Core tip: Intestinal disaccharide analysis of duodenal biopsy specimens are often obtained during esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) in children. In our review examining 34753 disaccharide assays the overall proportion of lactase deficiency was 39.2%, sucrase deficiency was 9.0%, maltase deficiency was 12.6% and palatinase deficiency was 9.1% in children. The impact of EGD with disaccharide analysis on treatment plans, quality of life, improvement of gastrointestinal symptoms, and cost-effectiveness has not been well studied. There is also little published data on Hispanic children undergoing EGD with disaccharide analysis.
- Citation: Daileda T, Baek P, Sutter ME, Thakkar K. Disaccharidase activity in children undergoing esophagogastroduodenoscopy: A systematic review. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 2016; 7(2): 283-293
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5349/full/v7/i2/283.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4292/wjgpt.v7.i2.283
Intestinal disaccharide analysis of duodenal biopsy specimens are often obtained during esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) in children. Options for disaccharide evaluation include stool analysis, hydrogen breath tests, and sugar tolerance testing. However, the “gold-standard” to accomplish a diagnosis of disaccharide deficiency is a small intestinal biopsy and enzyme assay[1,2]. The four enzyme complexes commonly assessed for disaccharide hydrolysis (disaccharidases) are lactase, sucrase, maltase and palatinase. In pediatrics, disaccharide deficiency has a wide clinical presentation with symptoms possibly including diarrhea, bloating, flatulence, abdominal pain, borborygmi, and failure to thrive. Therefore, it can be challenging to select patients undergoing EGD to complete the additional disaccharide evaluation which generally requires at least two additional duodenal biopsy specimens.
Many clinical investigators have attempted to characterize the prevalence of disaccharide deficiency and explore disaccharide activity in select pediatric populations. However, for most children with non-specific symptoms, clinical guidelines do not clearly express indications for disaccharide measurement during diagnostic EGD. Clear indications for disaccharide analysis might include chronic diarrhea and failure to thrive of unclear etiology. However, in patients with other clinical features such as abdominal pain, bloating, or gastroesophageal reflux it is not clear when disaccharide analysis should be pursued. For example, the diagnosis of functional gastrointestinal disease usually is made without evaluations of disaccharide activity, although symptoms from carbohydrate intolerance can overlap.
We completed a systematic review of the medical literature to appraise the evidence regarding intestinal disaccharide activity reported in duodenal biopsy specimens from children undergoing EGD. We sought to review the effect of ethnicity, underlying conditions, presenting symptoms, histological findings, and region of origin on disaccharide activities in children. Finally, we searched for studies examining clinical outcomes (treatment changes, quality of life, impact on gastrointestinal symptoms, cost-effectiveness) following EGD with disaccharide analysis.
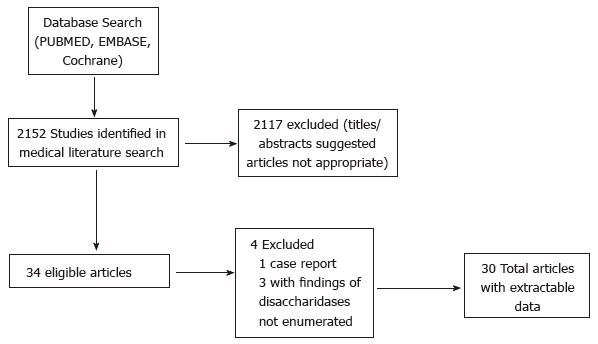
A query of the medical literature was performed for clinical studies examining subjects undergoing EGD with small intestinal biopsy evaluation of disaccharide activity using MEDLINE (1966-March 2014), EMBASE (1995-March 2014), and the Cochrane Database (March 2014). Manuscripts were identified with the Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) and free text terms Disaccharidases/analysis, Duodenum/enzymology, Disaccharidases/deficiency, Disaccharidases/metabolism, Intestinal Mucosa/enzymology (all MeSH heading and free text terms). PubMed was utilized to query MEDLINE and the limits were applied to restrict the search to manuscripts written in the English language and including subjects under 18 years. Bibliographies of manuscripts that met inclusion criteria were reviewed for pertinent articles (Figure 1).
Manuscripts were chosen if they examined disaccharide levels after EGD in pediatric patients. The specific inclusion criteria for the studies were: (1) participants had small intestinal biopsy evaluation of disaccharide activity; (2) levels of lactase, sucrase, maltase or palatinase were reported; and (3) age of participants was under 18 years. The exclusion criteria were: (1) subjects over 18 years of age; and (2) omission of specific results (activity levels or deficiency) of disaccharide analysis of intestinal biopsy.
The specific data exported from each study included: The year and country of enrollment, sample size, ethnicity, underlying conditions, study design, presenting symptoms, disaccharide activity level, and histology reports. Included manuscripts were reviewed for examination of the following elements: (1) relationship of clinical symptoms with diagnostic yield; (2) relationship of the particulars regarding abdominal pain (severity, site) with specific pathology; (3) patient outcomes (quality of life, improvement of symptoms); or cost-effectiveness; and (4) patient-centered clinical outcomes (quality of life, symptom abatement), or cost-effectiveness. Several specific quality measures were searched for in each study: Whether (1) the participants were enrolled consecutively; (2) the clinical outcomes was measured precisely; and (3) confounding factors were recognized and adjusted for.
We computed prevalence estimates by combining data from studies that achieved the inclusion criteria and calculating sample-size - weighted mean values. We calculated pooled means for disaccharide levels using the weighted means equation. Our findings are included in tabular format.
Overall retrieval was 2152 manuscripts based on the search criteria described in the Methods (Figure 1). We reviewed all the titles and abstracts from the overall retrieval and 30 studies met both the inclusion and the exclusion criteria (Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3). The included articles were all observational or cohort studies and the majority were prospective (17). The studies were completed between 1966 and 2012. 77% of the studies (n = 23) occurred in European or American subjects. 11 studies examined Caucasian subjects, 3 studies examined Asian subjects, 6 examined African subjects, and one study examined Native Americans. Hispanic subjects were only included in one study which had only one Hispanic subject[3]. Only one study did not report histologic features of participating subjects[4]. The studies did not examined resource utilization, cost-effectiveness, or quality of life related to disaccharide analysis after EGD. The biggest study included about 30000 endoscopies and 10 studies included fewer than 100 endoscopies.
| Ref. | Histology association between histology and disaccharidase activity | Other underlying condition | Sample size, % male | Age range, mean | Ethnicity | Lactase (μmol/min per gram) | Sucrase (μmol/min per gram)mean | Maltase(μmol/min per gram)mean | Palatinase (μmol/min per gram)mean |
| Disaccharidase values in iron-deficient infants (1981) Lanzkowsky et al[35] United States | No abnormalities | Severe nutritional iron deficiency anemia | 10 (5 biopsied), sex not reported | 8-30 mo, 14.9 mo | Not reported | Initial: 10 Post-iron treatment: 40 | Initial: 140 Post-iron treatment: 230 | Initial: 190 Post-iron treatment: 400 | Not reported |
| Diamine oxidase and disaccharidase activities in small intestinal biopsies of children (1984) Forget et al[24] Belgium | No abnormalities | Bronchitis, vomiting, chronic diarrhea, failure to thrive | 18, 61% | 0.2-6 yr, 2.32 yr | Not reported | 1.78 (measured in U/g wet weight) | 4.34 (measured in U/g wet weight) | 15.48 (measured in U/g wet weight) | Not reported |
| Dissacharidase deficiency in children with immunologic deficits (1970) Dubois et al[30] United States | Villous atrophy in two patients with idiopathic acquired hypogammaglobulinemia. No abnormalities in all other patients; Association not reported | Congenital hypogammaglobulinemia; Idiopathic acquired hypogammaglobulinemia; Isolated IgA deficiency; Thymic Dysplasia, Thymic alymphoplasia | 18, 77.80% | 3 mo-16 yr, 8.72 yr | Caucasian | 14.2 (21 biopsies) | 40.1 (20 biopsies) | 150 (20 biopsies) | Not reported |
| Histologic findings are not correlated with disaccharidase activities in infants with protracted diarrhea (1991) Shulman et al[5] United States | Mucosal inflammation; No association | Diarrhea of approximately 2 wk, mild to severe malnutrition | 21, sex not reported | 1.0-6.0 mo, 2.5 ± 1.5 mo | Not reported | 17.1 | 71.1 | 224.3 | Not reported |
| Intestinal disaccharidase deficiency in children with coeliac disease (1966) Arthur et al[22] United Kingdom | Mucosal inflammation and increased cells in lamina propria; Association not reported | Coeliac disease, post-gastroenteritis, monosaccharide intolerance, and pancreatic hypoplasia | 22, 50% Normal: 6 Celiac disease: 12 Miscellaneous conditions: 4 | 7 mo-10.58 yr, 2.84 yr | Not reported | 3.17 (measured in U/g wet weight) | 3.42 (measured in U/g wet weight) | 9.98 (measured in U/g wet weight) | 1.34 (measured in U/g wet weight) |
| Lactose absorption and mucosal disaccharidases in covalescent pellagra and kwashiorkor children (1971) Prinsloo et al[26] South Africa | No abnormalities | Kwashiorkor, classical pellagra without oedema | 22, 68.18% | 15 mo-12 yr, 8.758 yr | Bantu | 5.28 | 50.4 | 173.5 | Not reported |
| Intestinal disaccharidase and alkaline phosphatase activity in giadiasis (1984) Welsh et al[7] United States | Villous atrophy in two patients; No association | Giardiasis, diarrhea of 2 wk to 12 mo duration | 23, 43% | 11 mo-14 yr, 3.39 yr | Caucasian | 46 | 82 | 269 | Not reported |
| Moderate and severe protein energy malnutrition in childhood: Effects on jejunal mucosal morphology and disaccharidase activites (1983) Römer et al[25] Venezuela | Villous atrophy; Association not reported | Degrees of Malnutrition: I Degree (10%-24% deficit), II Degree (25%-39% deficit), III Degree (over 40% deficit), marasmic kwashiorkor | 33, 60.60% | 0.7-5.6 yr Mean not reported | Not reported | 11.4 | 59 | 191.5 | Not reported |
| Disaccharidase activities in jejunal fluid (1983) Aramayo et al[12] United Kingdom | Villous atrophy and parasitic infection; Association present for lactase, sucrase, and maltase | STVA, unspecified gastrointestinal symptoms | 29, sex not reported | 10 mo-14 yr, 5.9 yr | Not reported | 3.67 (measured in U/g wet weight) (approximated from figure) | 6.39 (measured in U/g wet weight) (approximated from figure) | 23 (measured in U/g wet weight) (approximated from figure) | Not reported |
| Reinvestigation of lactose intolerant children: lack of correlation between continuing lactose intolerance and small intestinal morphology, disaccharidase activity, and lactose tolerance tests (1977) Harrison et al[8] United Kingdom | Mucosal inflammation and villous atrophy; No association | Secondary lactose intolerance | 30, 69% | 2-38 mo, 10.4 mo | Not reported | 2.3 (data from 4 patients) (measured in U/g wet weight) | 4.4 (data from 4 patients) (measured in U/g wet weight) | 16.4 (data from 4 patients) (measured in U/g wet weight) | Not reported |
| Disaccharidases in coeliac disease (1983) Horvath et al[6] Hungary | Villous atrophy; No association | Confirmed and suspected coeliac disease | 30, sex not reported | 8 mo-10 yr, 2.4 yr | Not reported | 2.1 (measured in U/g wet weight) | Not reported | 16 (measured in U/g wet weight) | Not reported |
| Quantitative assay of disaccharidase activities of small intestinal mucosal biopsy specimens in infancy and childhood (1965) Townley et al[23] United States | Villous atrophy; Association not reported | Urinary tract infection, cystic fibrosis, diabetes mellitus, hepatosplenomegaly, hypoproteinemia, protein-losing enteropathy, anemia, celiac disease | 36, 58.30% | 1/12-16 11/12 yr, 3.62 yr | Not reported | 1.91 (measured in U/g wet weight) | 3.6 (measured in U/g wet weight) | 13.2 (measured in U/g wet weight) | 4.03 (measured in U/g wet weight) |
| Disaccharidase activities in dyspeptic children: Biochemical and molecular investigations of maltase-glucoamylase activity (2002) Karnsakul et al[3] United States | No abnormalities | Dyspepsia, abdominal pain, reflux, vomiting | 44, 66.70% | 0.5-18 yr, 9.5 yr | 37 Caucasian (84%) 1 Hispanic (2%) 2 African (5%) | 7.01 (data from 12 patients) | 19.2 (data from 11 patients) | 92.66 (data from 8 patients) | Not reported |
| Ref. | Histology; association between histology and disaccharidase activity | Other underlying condition | Sample size, % male | Age range, mean | Ethnicity | Lactase (μmol/min per gram) mean | Sucrase (μmol/min per gram) mean | Maltase (μmol/min per gram) mean | Palatinase (μmol/min per gram) mean |
| Disaccharidase deficiency in pediatric patients with celiac disease and intact villi (2011) Mones et al[21] United States | Increased lymphocytes and crypt hypertrophy; Association not reported | Celiac disease | 51 CD: 25, 54% Control: 26, 50% | Ranges not reported, CD: 11.3 yr Control: 12.3 yr | Not reported | 11.6 | 34.1 | 104.7 | 7.25 |
| Disaccharidase activities, jeujunal morphology, and carbohydrate tolerance in children with chronic diarrhea (1985) Calvin et al[14] United States | Villous atrophy; Association present for lactase, sucrase, and maltase | Chronic Diarrhea | 88, sex not reported | 1-16 yr, 25 mo | Not reported | 23.7 | 56.3 | 214.6 | Not reported |
| Brush border enzyme activities in relation to histological lesion in pediatric celiac disease (2008) Prasad et al[16] India | Villous atrophy; Association present for lactase, sucrase, and maltase | GERD, celiac disease | GERD: 29, 62.09% CD: 71, 60.56% | CD: 15 mo-14 yr, 6.0 yr Control: 18 mo-14 yr, 6.2 yr | North Indian | 15.7 | 30.7 | 62.3 | Not reported |
| Activity of duodenal disaccharidases in relation to normal and abnormal mucosal morphology (1990) Langman et al[15] Australia | Mucosal inflammation and villous atrophy; Association present for lactase, sucrase, and maltase | Suspected celiac disease, giardiasis, diarrhea, weight loss, abdominal pain, low folate concentrations | 100, 41% | 7-76 yr, Four patients under 15 yr, data is from all pts including adults 39 yr | 98 Caucasian (98%) 1 African (1%) 1 Indian (1%) | 5.7 | 16 | 28.5 | Not reported |
| Glucoamylase and dissacharidase activities in normal subjectsand in patients with mucosal injury of the small intestine (1980) Lebenthal et al[29] United States | Villous atrophy; Association present for lactase, sucrase, maltase, and palatinase | Chronic diarrhea, failure to thrive | 124, sex not reported | 1 mo-18 yr, mean not reported | Not reported | 19.7 | 42.4 | 141 | 10.8 |
| Disaccharidase activity in infants and comparison based on symptoms and histological changes (2007) Tori et al[11] United States | Villous atrophy; Association present for lactase, sucrase, maltase, and palatinase | Diarrhea, failure to thrive | 131, 57% | 20 d-364 d, 180 d | 111 Caucasian (85%) 14 African (11%) | 29.2 | 42.1 | 138.2 | 10 |
| Correlation of Lactase activity, lactose tolerance and milk consumption in different age groups (1975) Lebenthal et al[10] United Kingdom | No abnormalities | Failure to thrive with no organic cause, irritable colon syndrome | 160 sex not reported | 6 wk-50 yr, mean not reported | 6 Other (4%) Caucasian | 29.8 | 56.2 | 189.6 | 15.5 |
| Intestinal Disaccharidase activity in patients with autism (2011) Kushak et al[20] United States | Mucosal inflammation (6%); Association present for lactase. | Autism (abdominal pain, flatulence, constipation, vomiting, weight loss, food allergy, suspected GERD) | 199, 82.40% | 22 mo-28 yr, 5.75 yr | 195 Caucasian (98%) 2 Asian (1%) 2 Indian (1%) | 14.7 | 45.6 | 209.2 | Not reported |
| Ref. | Histology; association between histology and disaccharidase activity | Underlying condition/symptoms | Sample size, % male | Age range, mean | Ethnicity | Lactase (μmol/min per gram) mean | Sucrase (μmol/min per gram) mean | Maltase (μmol/min per gram) mean | Palatinase (μmol/min per gram) mean |
| Ethnic differences in intestinal disaccharidase values in children in Finland (2000) Kolho et al[28] Finland | No abnormalities | Abdominal pain, vomiting, suspected celiac disease, suspected inflammatory bowel disease, asthma, constipation, diarrhea, feeding problems, anemia, other | 223, 55.20% | Finnish: 0.2-18 yr, median: 8.0 yr African: 1-13 yr, median: 5.0 yr Other: 4.5-15 yr, median: 12 yr | 188 Finnish (84%) 27 African (12%) 8 other (4%) | 23.4 | 48.1 | 186.3 | Not reported |
| Intestinal lactase, sucrase, and alkaline phosphatase in 373 patients with coeliac disease (1984) O’Grady et al[17] Ireland | Mucosal inflammation; Association present for lactase and sucrase | Celiac disease | 230 sex not reported | 1-18 yr, Mean not reported | Not reported | 14.05 (data from 45 patients) | 33.9 (data from 45 patients) | Not reported | Not reported |
| Disaccharidase activities in children: Normal values and comparison based on symptoms and histological changes (1999) Gupta et al[9] United States | Villous atrophy; Association present for lactase, sucrase, maltase, and palatinase | Group 1: Recurrent abdominal pain, vomiting, gastroesophageal reflux, hematemesis, failure to thrive Group 2: All had diarrhea (included patients with celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, parasitic infestation, and congenital sucrase-isomaltase deficiency) | 232, 47.80% | 0.08-17 yr 5.9 yr | Not reported | 18.3 | 37.9 | 169.1 | 12.7 |
| Disaccharidase activities in small intestinal mucosa in patients with cystic fibrosis (1978) Antonowicz et al[19] United States | Villous atrophy; Association present for lactase | Cystic fibrosis Chronic diarrhea, failure to thrive, abdominal pain, vomiting, crying baby, other | 240 sex not reported | Range and mean not reported | Caucasian | 31.1 | 64 | 241 | 19.8 |
| Disaccharidase activites in Belgian children: Reference intervals and comparison with non- Belgian Caucasian children (2003) Blomme et al[13] Belgium | Mucosal inflammation and villous atrophy; Association present for lactase, sucrase, and maltase | 185 60.50% | Belgian: 0.1-12 yr, Median: 1.3 yr Caucasian: 0.2-8 yr, Median: 1.3 yr | 151 Belgian (82%) 34 non-Belgian Caucasian (18%) | (median values) Group A: 40 (6-122) Group B: 28 Group C: 7 Non-Belgian: 33 (5-70) | (median values) Group A: 69 (18-184) Group B: 54 Group C: 25 Non-Belgian: 63 (10-125) | (median values) Group A: 208 Group B: 181 Group C: 96 Non-Belgian: 186 | Not reported | |
| Intestinal Disaccharidase Activites in Relation to Age, Race, and Mucosal Damage (1978) Welsh et al[7] United States | No abnormalities | Mucosal damage | 399 sex not reported | 1 mo-93 yr, mean not reported | 339 Caucasian (85%) 53 African (13%) | 35.9 | 76.5 | 262.2 | 26.6 |
| “Normal” disaccharidase levels in children (1988) Barnes et al[34] Australia | No abnormalities | Failure to thrive, chronic diarrhea, short stature, family history of celiac disease, iron deficiency anemia, food hypersensitivity | 580 sex not reported | 0-12 yr, mean not reported | 7 Native American (2%) Not reported | 3.9 (measured in U/g wet weight) | 6.4 (measured in U/g wet weight) | 19.1 (measured in U/g wet weight) | Not reported |
| Human intestinal disaccharidase activities: Correlations with age, biopsy technique, and degree of villus atrophy (1991) Heitlinger et al[18] United States | Mucosal inflammation and villous atrophy; Association present for lactase and maltase | Not reported | 798 sex not reported | 0-18 yr, Mean not reported | Not reported | 23.3 | 52.5 | 145.8 | 11.6 |
| Frequency of sucrase deficiency in mucosal biopsies (2012) Nichols et al[4] United States | Not reported | Not reported | 27875 % male not reported | 0-93.5 yr, 11 yr | Not reported | 21.8 | 56.5 | 167.6 | 11.3 |
The largest study examined 30314 biopsy specimens. A sum of 4439 subjects were participants in the remaining 29 studies. In studies reporting specific disaccharide deficiency, the overall proportion of lactase deficiency was 39.2%, sucrase deficiency was 9.0%, maltase deficiency was 12.6% and palatinase deficiency was 9.1%.
Twenty-nine studies included histological analysis. Among histologic findings, eight studies reported no histopathologic abnormalities and 21 studies reported abnormal histopathology. Subjects classified as “abnormal” usually had varying amounts of villous atrophy or histological mucosal inflammation. The occurrence of duodenal inflammatory changes ranged findings ranged from 6% to 24% for non-specific histological gastrointestinal inflammatory lesions such as duodenitis. The prevalence of villous atrophy ranged from 8.7% to 100%. Sixteen studies examined the association of histologic findings with disaccharide activities. Four studies reported no clear association between histopathology findings and disaccharide activity[5-8]. However, 12 studies reported some degree of inverse association between degree of histologic inflammation and disaccharide levels. Among these 12 studies, 3 studies reported an association between all disaccharide levels and histologic findings[9-11]. Five studies reported correlation between lactase, sucrose, and malatase and histoligc inflammation[12-16]. O’Grady et al[17] study reported association between lactase and sucrose with histology inflammation. Heitlinger et al[18] reported an inverse correlation with lactase and maltase with inflammatory changes. Finally, two studies reported a correlation with lactase only[19,20].
Seven studies specifically examined patients with celiac disease and enumerated the results accordingly[6,14,16,17,21-23]. These studies examined a total of 269 EGDs in 224 patients were performed with celiac disease. Among these 269 procedures, 181 had significant microscopic inflammation/villious atrophy and 88 patients had no significant inflammation. Six studies reported mean disaccharide levels and found that mean lactase levels were 6.9 μmol/min per gram protein in patients with significant inflammation and 20.69 6.9 μmol/min per gram protein in patients without significant histologic changes. Mean sucrase levels were 18.3 6.9 μmol/min per gram protein in patients with significant inflammation and 45.14 6.9 μmol/min per gram protein in patients without significant histologic changes. Mean maltase levels were reported in 5 studies, 6.9 μmol/min per gram protein in patients with significant inflammation and 102.4 6.9 μmol/min per gram protein in patients without significant histologic changes. Mean palatinase levels were reported in 2 studies 3.44 6.9 μmol/min per gram protein in patients with significant inflammation and 8.27 6.9 μmol/min per gram protein in patients without significant histologic changes. Among 4 studies reporting the proportion of subjects with lactase deficiency, lactase deficiency was found in 54/61 (88.5%) patients with untreated celiac disease as compared to 8/51 (15.7%) patients with treated celiac disease. Among 3 studies reporting the proportion of subjects with maltase deficiency, maltase deficiency was found in 54/61 (88.5%) patients with untreated celiac disease as compared to 2/6 (33.3%) patients with treated celiac disease. Among 3 studies reporting the proportion of subjects with sucrase deficiency, sucrase deficiency was found in 27/76 (35.5%) patients with untreated celiac disease as compared to patients with 2/6 (33.3%) treated celiac disease. Among 2 studies reporting the proportion of subjects with palatinase deficiency, palatinase deficiency was found in 27/31 (87.1%) patients with untreated celiac disease as compared to 2/6 (33.3%) patients with treated celiac disease.
Five studies specifically examined patients with chronic diarrhea and enumerated the results accordingly[5,9,14,23,24]. These studies examined a total of 214 patients were performed with chronic diarrhea undergoing EGD. All studies reported mean disch levels and found that mean lactase levels were 27.5 μmol/min per gram protein in patients with normal histology, 15.3 μmol/min per gram protein in patients with mild inflammatory changes, 8.7 μmol/min per gram protein in patients with moderate/severe inflammation. Mean sucrase levels were 59.7 μmol/min per gram protein in patients with normal histology, 44.2 μmol/min per gram protein in patients with mild inflammatory changes, 27.3 μmol/min per gram protein in patients with moderate/severe inflammation. Mean maltase levels were 201.5 μmol/min per gram protein in patients with normal histology, 177.2 μmol/min per gram protein in patients with mild inflammatory changes, 110.3 μmol/min per gram protein in patients with moderate/severe inflammation. Two study reported palatinase levels and found mean palatinase levels were 12.1 μmol/min per gram protein in patients with normal histology, 5.8 μmol/min per gram protein in patients with mild inflammatory changes, 3.0 μmol/min per gram protein in patients with moderate/severe inflammation[9,23]. Among two studies reporting the proportion of subjects with lactase deficiency in subjects with chronic diarrhea, lactase deficiency was found in 73/190 (38.4%)[9,14]. One study reported sucrose deficiency in subjects with chronic diarrhea and found 10/88 (11.4%)[14].
Two studies examining 7 patients reported disaccharide activities in subjects with failure to thrive[23,24]. All studies reported mean disaccharide levels and found that mean lactase levels were 1.97 μmol/min per gram protein, mean sucrase levels were 4.6 μmol/min per gram protein, mean maltase levels were 15.5 μmol/min per gram protein. All 7 patients had pan disaccharide deficiency.
Two studies examining 14 patients reported disaccharide activities in subjects with kwashiorkor[25,26]. All studies reported mean disaccharide levels and found that mean lactase levels were 6.4 μmol/min per gram protein, mean sucrase levels were 52.9 μmol/min per gram protein, mean maltase levels were 190.9 μmol/min per gram protein. One article reported the specific proportion of disaccharide deficient patients and found 8/10 (80%) were lactase deficient, 2/10 were sucrose deficient, and 3/10 were maltase deficient[26].
Three studies compared disaccharide activity across ethnic populations[13,27,28]. One study performed in the United States found that lactase deficiency is rare in Caucasian children as compared to native American and African populations as all 117 Caucasian children under age 5 had normal lactase levels[27]. Another study from Finland found that the mean activities of lactase, sucrose, and maltase were significantly higher in Finnish children as compared to African children[28]. The study further found that 31% (59/188) of Finnish children had low lactase as compared to 67% (18/27) of African children. The final study was performed in Belgium and compared Belgian children to non-Belgian Caucasian children and found that median values for lactase levels were lower in non-Belgian children (33 μmol/L per gram) as compared to Belgian children (40 μmol/L per gram) (P = 0.02).
Eleven studies examined Caucasian subjects, but only 4 focused on Caucasian subjects and enumerated results accordingly. Among these 4 studies, a total of 441 patients were included with variable underlying conditions including failure to thrive, irritable bowel syndrome, cystic fibrosis, immunologic deficits and giardiasis[7,19,29,30]. All 4 studies reported the proportion of lactase deficiency in subgroup populations and the overall prevalence was 43/162 (26.5%). Two studies report the proportion of sucrose and maltase deficiency and sucrose deficiency was reported in 12/39 (30.8%) and maltase deficiency was reported in 16/39 (41.0%). Combined mean disaccharide levels from studies examining Caucasian populations were: 30.6 μmol/L per gram for lactase, 61.0 μmol/L per gram for sucrose, 204.0 μmol/L per gram for maltase and 16.7 μmol/L per gram for palatinase. When stratified by histologic inflammation, Caucasian patients with normal histology had mean levels of 31.8 μmol/L per gram for lactase, 61.4 sucrase, 204.8 for maltase, and 16.8 for palatinase. Those with mild inflammation had levels of 17.9 lactase, 62.0 sucrase, 219.5 maltase, 17.3 for palatinase. Moderate severe inflammation was associated with levels of 7.3 lactase, 39.1 sucrase, 125.5 maltase, 11.3 palatinase.
One study focused on 100 Indian subjects with celiac or GERD and did not report the proportion of disaccharide deficiency in the cohort[16]. Overall levels were reported at 15.7 for lactase, 30.7 sucrase, 62.2 for maltase. When stratified by histologic inflammation, Caucasian patients with normal histology had mean levels of 23.3 μmol/L per gram for lactase, 39.9 sucrase, 72.8 for maltase. Those with mild inflammation had levels of 18.4 lactase, 28.7 sucrase, 64.3 maltase. Moderate severe inflammation was associated with levels of 11.0 lactase, 25.3 sucrase, 55.7 maltase.
Prinsloo et al[26] reported disaccharide levels in an exclusively African cohort of 22 subjects with kwashiorkor or pellagra. The proportion of patients who had disaccharide deficiency was only reported for lactase with 7/10 subjects with kwashiorkor and 10/10 for pellagra for an overall prevalence of 17/20 (85%). For kwashiorkor, the levels were 8.4 for lactase, 50.1 for sucrose, 185.7 for maltase, 67.9 for palatinase. For pellagra, the levels were 2.73 lactase, 50.7 sucrase, 163.4 maltase and 70.0 for palatinase. Combined levels were 5.3 lactase, 50.4 sucrase, 173.5 maltase, 69.1 for palatinase.
Three studies examined Asian subjects, 6 examined African subjects, and one study examined Native Americans. Studies focused on specific ethnic populations.
The largest study reported findings in 30314 samples received over a 5 year period in a reference laboratory[4]. This study found that the most common deficiency was lactase occurring in 8963 (32%), followed by pandisaccharide deficiency in 2347 (8%). Congential sucrose-isomaltase deficiency was extremely rare, occurring in just 0.1% of the samples.
Only one study examined management changes as a result of intestinal disaccharide analysis[9]. Gupta et al[9] conducted a questionnaire to evaluate the usefulness of diet changes in patients with lactase deficiency and found that 81.5% (22/27) of patients responded to dietary modification.
Our systematic review of 30 studies of intestinal disaccharide analysis, including over 30000 samples, found that lactase deficiency was most common (39.2%), followed by maltase deficiency (12.6%), palatinase deficiency (9.1%), and sucrase deficiency (9.0%). Histopathology was reported in most studies and the primary findings included duodenal inflammation (6% to 24%) or villious atropy (9% to 100%). A large multi-center study including 30314 disaccharide analysis was performed in 2012, however, this study did not include information on the underlying conditions, histology, or ethnicity of its subjects.
In the articles reviewed, many did not specifically enumerate the indication or underlying condition for the EGD with disaccharide analysis. The most common conditions examined included celiac disease, chronic diarrhea, and malnutrition. In clinical practice, chronic diarrhea and malnutrition are common indications for disaccharide analysis. However, generally enzyme levels are not routinely measured in patients with celiac disease, as intestinal function usually normalizes with a gluten free diet. The most common indications for EGD in children include abdominal pain, vomiting, and reflux symptoms[31,32]. However, subjects with abdominal pain, reflux symptoms or vomiting were specifically examined in just 2 studies. Karnsakul et al[3] examined 33 children with abdominal pain, 11 with vomiting, and with reflux. Overall, half of all enrolled children had low activity of one or more disaccharidases[3]. The study also found that vomiting was related to low lactase, but no other associations between symptoms and disaccharide levels were found. Prasad et al[16] enrolled 29 children with GERD symptoms and found normal disaccharide levels in this small cohort. Four remaining studies include patients with abdominal pain, vomiting, and reflux but did not specifically analyze the relationship between disaccharide activity and these indications for EGD.
The majority of studies (29/30) included analysis of histopathology. Histology is critical to examine because it can be a factor leading to differentiation of primary from secondary disaccharidase deficiencies. The majority of studies (12/16) examining the association between enzyme levels and histopathology found that inflammatory changes were associated with enzyme deficiencies. It has been argued that specimens should be considered unsatisfactory when all the enzymes assayed are low and the histology appears normal. However, four studies included in this review reported no clear association between histopathology findings and disaccharide activity. Additionally, data in adult patients suggests that the disaccharidase deficiency is not confined to patients with abnormal histology[33]. Therefore, we conclude that although enzymes levels are lower in the majority of patients with duodenal inflammation, enzyme levels may be affected even with normal histopathology.
While ethnicity was reported in many studies, only three studies compared disaccharide activity between ethnic cohorts. The primary finding was lower levels of disacharidase activity in children of African descent[27,28]. Although current studies includes over 30000 biopsy specimens, only 1 Hispanic subject was included.
Change in clinical management after EGD with disaccharide analysis was reported only in relation to dietary treatment low lactase levels. No studies explored management changes after the discovery of low sucrase, maltase or palatinase. Studies also did not report on the use of enzyme or dietary supplements.
Our review is limited somewhat by the heterogeneity and variability of the included studies. Our review of the current evidence also did not contain any clinical trials, and included primarily observational studies.
In summary, the present medical literature examining the utility of disaccharide analysis during EGD for children is limited primarily by inadequate investigation of clinical presentation to disaccharide levels. The prevalence and outcomes of disaccharide deficiency in pediatric patients with abdominal pain, reflux, vomiting has not been well-studied. Also, the majority of clinical outcomes after EGD with disaccharide analysis (e.g., patient management impact, quality of life improvement, symptom abatement, cost) are not well described in the current literature. Prior studies do not sufficiently include Hispanic subjects. However, our findings may have applicability to routine clinical practice. We recommend large studies examining the association between clinical factors and disaccharide levels with detailed elucidation of histopathology reports to illuminate the utility of disaccharide analysis in children undergoing EGD. Further investigation should include a large sample size and explore the value of specific management options after low disaccharide levels are discovered by small intestinal biopsies.
For children with non-specific symptoms, clinical guidelines and current data do not clearly express indications for disaccharide measurement during diagnostic esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD).
The impact of disaccharide measurement on clinical management and the cost-effectiveness of disaccharide assays are important areas of future research.
This study is the first to compile the medical literature examining the utility of disaccharide analysis during EGD for children and reveal significant gaps in the current clinical data on this subject.
This review directs future investigations to include a large sample size and explore the value of specific management options after low disaccharide levels are discovered by small intestinal biopsies.
Disaccharide: Class of sugars, such as maltose, lactose, and sucrose, having two linked monosaccharide units per molecule; EGD: Test to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and first part of the small intestine.
The report describes the usefulness of disaccharide analysis from children undergoing EGD. The quality of manuscript is very good.
| 1. | Robayo-Torres CC, Quezada-Calvillo R, Nichols BL. Disaccharide digestion: clinical and molecular aspects. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:276-287. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 77] [Cited by in RCA: 80] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Lee SH, Park YK, Cho SM, Kang JK, Lee DJ. Technical skills and training of upper gastrointestinal endoscopy for new beginners. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:759-785. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 32] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 3.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (11)] |
| 3. | Karnsakul W, Luginbuehl U, Hahn D, Sterchi E, Avery S, Sen P, Swallow D, Nichols B. Disaccharidase activities in dyspeptic children: biochemical and molecular investigations of maltase-glucoamylase activity. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2002;35:551-556. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 32] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Nichols BL, Adams B, Roach CM, Ma CX, Baker SS. Frequency of sucrase deficiency in mucosal biopsies. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012;55 Suppl 2:S28-S30. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Shulman RJ, Langston C, Lifschitz CH. Histologic findings are not correlated with disaccharidase activities in infants with protracted diarrhea. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1991;12:70-75. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Horváth K, Horn G, Bodánszky H, Tóth K, Váradi S. Disaccharidases in coeliac disease. Acta Paediatr Hung. 1983;24:131-136. [PubMed] |
| 7. | Welsh JD, Poley JR, Hensley J, Bhatia M. Intestinal disaccharidase and alkaline phosphatase activity in giardiasis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1984;3:37-40. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Harrison M, Walker-Smith JA. Reinvestigation of lactose intolerant children: lack of correlation between continuing lactose intolerance and small intestinal morphology, disaccharidase activity, and lactose tolerance tests. Gut. 1977;18:48-52. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 33] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Gupta SK, Chong SK, Fitzgerald JF. Disaccharidase activities in children: normal values and comparison based on symptoms and histologic changes. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1999;28:246-251. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 49] [Cited by in RCA: 38] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Lebenthal E, Lee PC. Glucoamylase and disaccharidase activities in normal subjects and in patients with mucosal injury of the small intestine. J Pediatr. 1980;97:389-393. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 58] [Cited by in RCA: 51] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Tori AJ, Carroll AE, Gupta SK. Disaccharidase activity in infants and comparison based on symptoms and histological changes. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007;45:194-198. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Aramayo LA, De Silva DG, Hughes CA, Brown GA, McNeish AS. Disaccharidase activities in jejunal fluid. Arch Dis Child. 1983;58:686-691. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Blomme B, Gerlo E, Hauser B, Vandenplas Y. Disaccharidase activities in Belgian children: reference intervals and comparison with non-Belgian Caucasian children. Acta Paediatr. 2003;92:806-810. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Calvin RT, Klish WJ, Nichols BL. Disaccharidase activities, jejunal morphology, and carbohydrate tolerance in children with chronic diarrhea. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1985;4:949-953. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Langman JM, Rowland R. Activity of duodenal disaccharidases in relation to normal and abnormal mucosal morphology. J Clin Pathol. 1990;43:537-540. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 29] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Prasad KK, Thapa BR, Nain CK, Sharma AK, Singh K. Brush border enzyme activities in relation to histological lesion in pediatric celiac disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;23:e348-e352. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | O’Grady JG, Stevens FM, Keane R, Cryan EM, Egan-Mitchell B, McNicholl B, McCarthy CF, Fottrell PF. Intestinal lactase, sucrase, and alkaline phosphatase in 373 patients with coeliac disease. J Clin Pathol. 1984;37:298-301. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Heitlinger LA, Rossi TM, Lee PC, Lebenthal E. Human intestinal disaccharidase activities: correlations with age, biopsy technique, and degree of villus atrophy. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1991;12:204-208. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 33] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Antonowicz I, Lebenthal E, Shwachman H. Disaccharidase activities in small intestinal mucosa in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr. 1978;92:214-219. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Kushak RI, Lauwers GY, Winter HS, Buie TM. Intestinal disaccharidase activity in patients with autism: effect of age, gender, and intestinal inflammation. Autism. 2011;15:285-294. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 21. | Mones RL, Yankah A, Duelfer D, Bustami R, Mercer G. Disaccharidase deficiency in pediatric patients with celiac disease and intact villi. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011;46:1429-1434. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Arthur AB. Intestinal disaccharidase deficiency in children with coeliac disease. Arch Dis Child. 1966;41:519-524. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Townley RR, Khaw KT, Shwachman H. Quantitative assay of disaccharidase activities of small intestinal mucosal biopsy specimens in infancy and childhood. Pediatrics. 1965;36:911-921. [PubMed] |
| 24. | Forget P, Grandfils C, van Cutsem JL, Dandrifosse G. Diamine oxidase and disaccharidase activities in small intestinal biopsies of children. Pediatr Res. 1984;18:647-649. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Römer H, Urbach R, Gomez MA, Lopez A, Perozo-Ruggeri G, Vegas ME. Moderate and severe protein energy malnutrition in childhood: effects on jejunal mucosal morphology and disaccharidase activities. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1983;2:459-464. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Prinsloo JG, Wittmann W, Kruger H, Freier E. Lactose absorption and mucosal disaccharidases in convalescent pellagra and kwashiorkor children. Arch Dis Child. 1971;46:474-478. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Welsh JD, Poley JR, Bhatia M, Stevenson DE. Intestinal disaccharidase activities in relation to age, race, and mucosal damage. Gastroenterology. 1978;75:847-855. [PubMed] |
| 28. | Kolho KL, Savilahti E. Ethnic differences in intestinal disaccharidase values in children in Finland. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2000;30:283-287. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Lebenthal E, Antonowicz I, Shwachman H. Correlation of lactase activity, lactose tolerance and milk consumption in different age groups. Am J Clin Nutr. 1975;28:595-600. [PubMed] |
| 30. | Dubois RS, Roy CC, Fulginiti VA, Merrill DA, Murray RL. Disaccharidase deficiency in children with immunologic deficits. J Pediatr. 1970;76:377-385. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 45] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Thakkar K, El-Serag HB, Mattek N, Gilger MA. Complications of pediatric EGD: a 4-year experience in PEDS-CORI. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;65:213-221. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 117] [Cited by in RCA: 130] [Article Influence: 6.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Gilger MA, Gold BD. Pediatric endoscopy: new information from the PEDS-CORI project. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2005;7:234-239. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 40] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Wilson IR, Oxner RB, Frampton CM, Tisch G, Chapman BA, Cook HB. Comparison of endoscopic forceps biopsies and capsule biopsies in determining disaccharidase activity in the duodenum. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991;37:527-530. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Barnes GL, Ford RP, Dawson S, Lawrance S. ‘Normal’ disaccharidase levels in children. Aust Paediatr J. 1988;24:31-33. [PubMed] |
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article which was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
P- Reviewer: Amornyotin S, Lee SH S- Editor: Ji FF L- Editor: A E- Editor: Wu HL