©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. Dec 5, 2025; 16(4): 109177
Published online Dec 5, 2025. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v16.i4.109177
Published online Dec 5, 2025. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v16.i4.109177
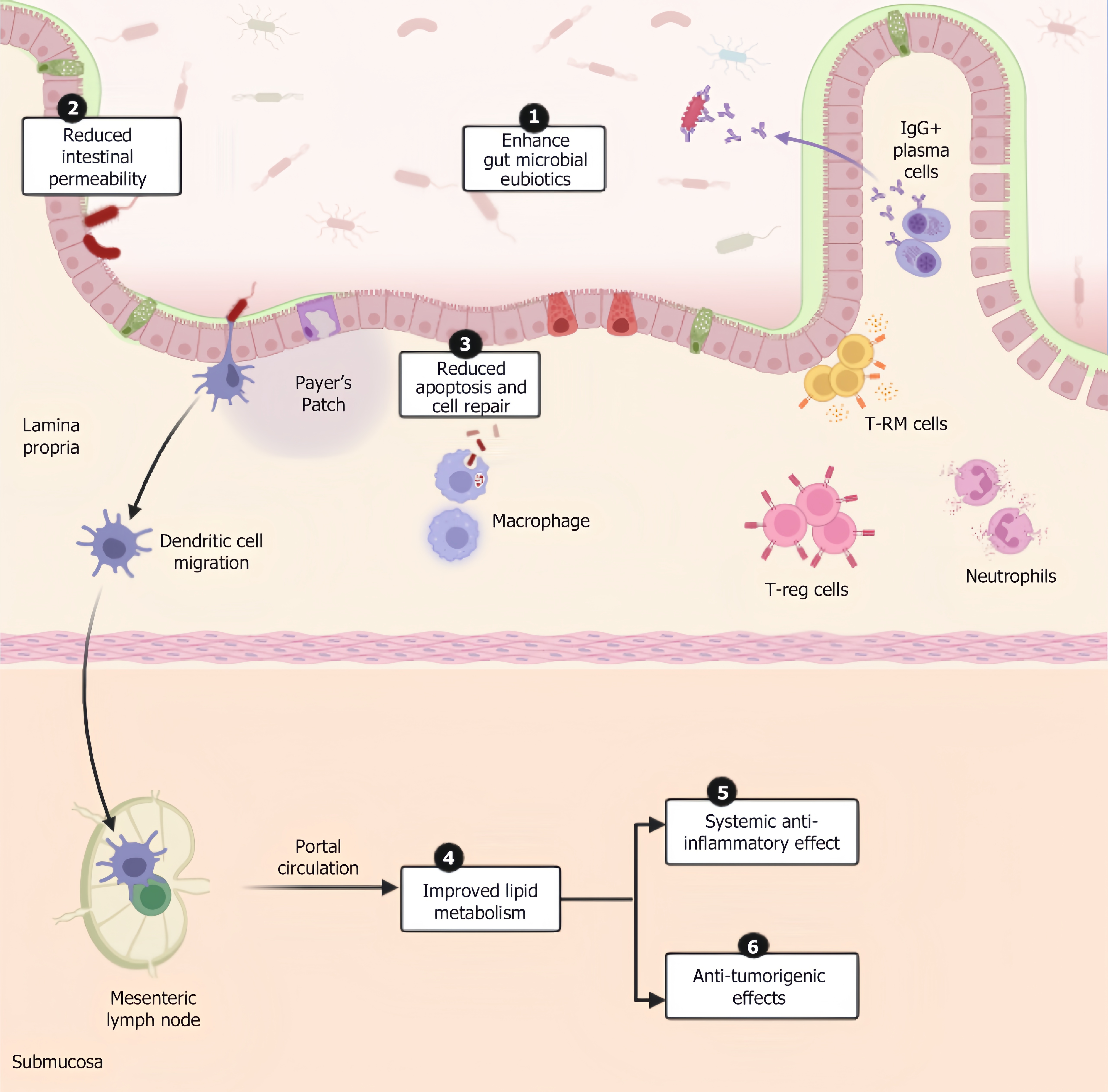
Figure 1 Mechanism of action of postbiotics.
This includes (1) Enhancement of gut eubiosis, favouring commensal species while suppressing pathogenic strains; (2) Strengthening intestinal integrity by upregulation of occludins, tight junctions etc.; (3) Enhanced epithelial regeneration and mucosal healing promotes cell repair and reduces apoptosis; (4) Improved transit of lipid metabolites with enhanced processing at liver resulting in reduced pro-inflammatory lipid mediators; (5) Modulation of immune cells reduces excessive inflammation; and (6) Reduction of chronic inflammation and regulation of metabolism lowers the risk of malignant transformation. IgG: Immunoglobulin G; T-RM: Resident memory T.
- Citation: Jeyaraman N, Jeyaraman M, Mariappan T, Nallakumarasamy A, Subramanian P, T P, Vetrivel VN. Harnessing postbiotics for liver health: Emerging perspectives. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 2025; 16(4): 109177
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5349/full/v16/i4/109177.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4292/wjgpt.v16.i4.109177