©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Nov 15, 2014; 5(4): 416-426
Published online Nov 15, 2014. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v5.i4.416
Published online Nov 15, 2014. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v5.i4.416
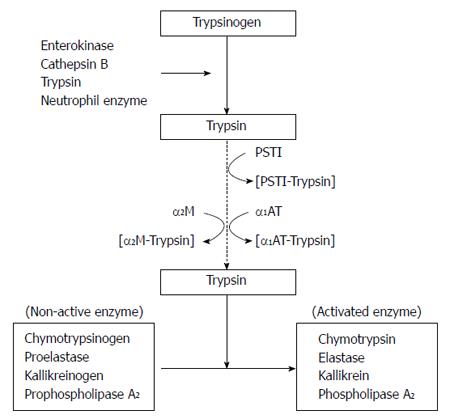
Figure 1 Suppression mechanisms for pancreatic enzyme activation.
PSTI: Pancreatic secretory trypsin inhibitor; α2M: α2-macroglobulin; α1AT: α1-antitrypsin.
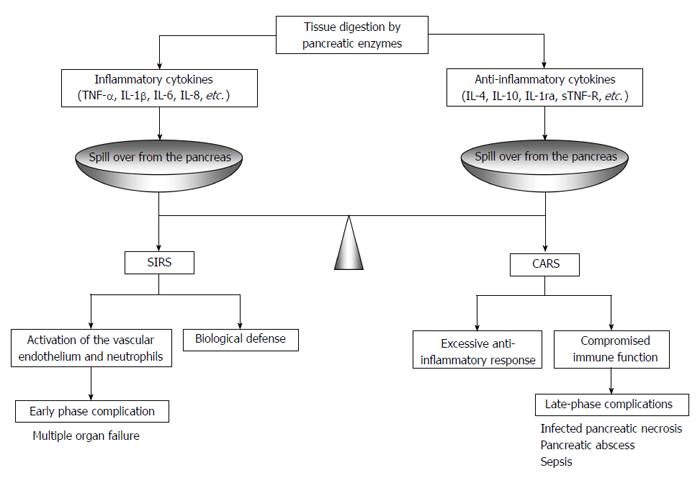
Figure 2 Compensatory anti-inflammatory response syndrome and systemic inflammatory response syndrome during acute pancreatitis.
TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; sTNF-R: Soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor; CARS: Compensatory anti-inflammatory response syndrome; SIRS: Systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
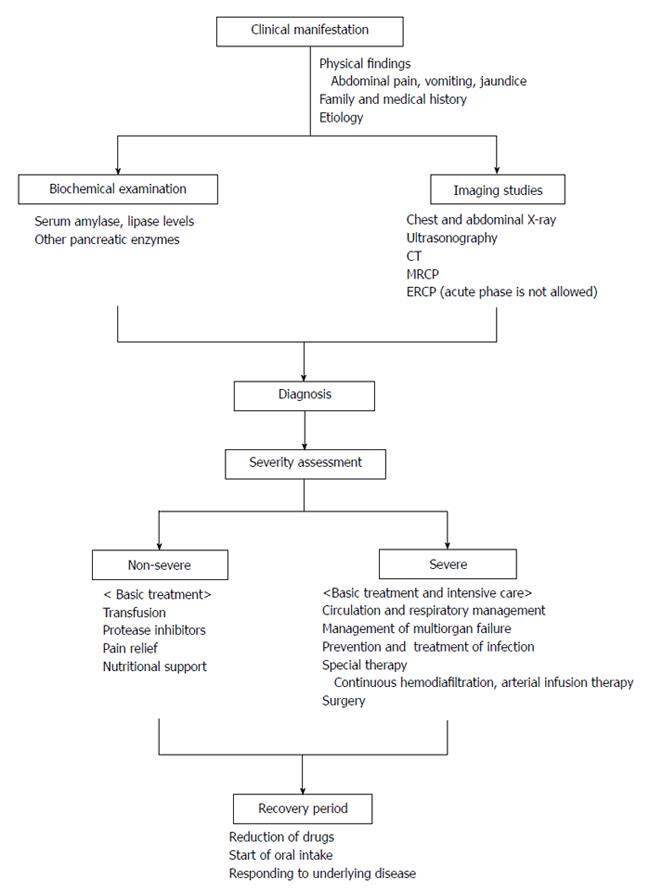
Figure 3 Clinical diagnosis of acute pancreatitis.
CT: Computed tomography; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; MRCP: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography.
- Citation: Suzuki M, Sai JK, Shimizu T. Acute pancreatitis in children and adolescents. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2014; 5(4): 416-426
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v5/i4/416.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v5.i4.416