©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Jun 1, 2023; 14(3): 46-70
Published online Jun 1, 2023. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v14.i3.46
Published online Jun 1, 2023. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v14.i3.46
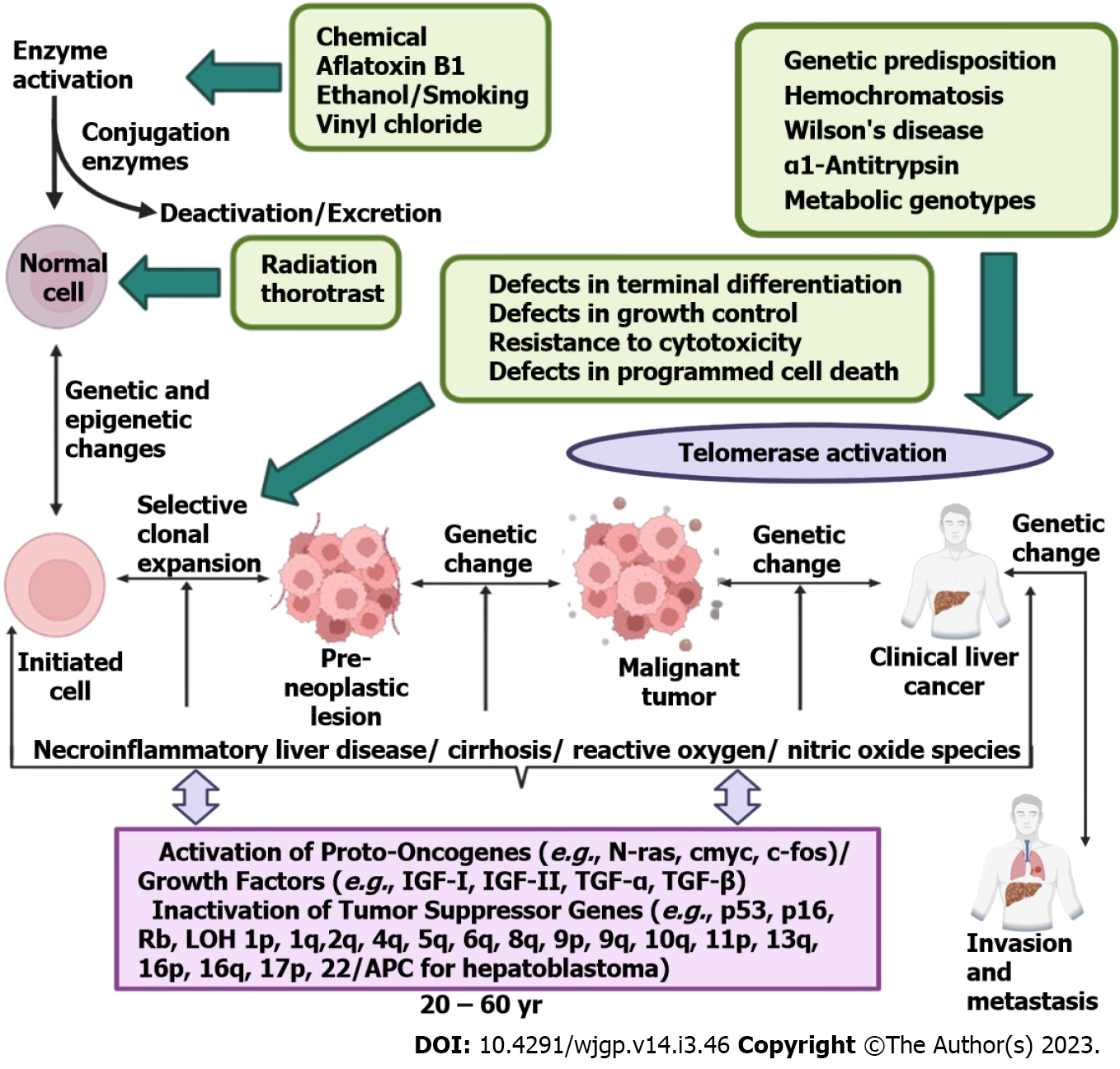
Figure 1 Etiological factors of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Aflatoxin B1, vinyl chloride, smoking, ethanol, and many such factors leads to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Genetic predisposition, hemochromatosis and metabolic genotypes could also be the reason for the initiation of the HCC. There are many stages in the development of HCC including formation of pre-neoplastic lesion and malignant tumour (Created with BioRender.com). IGF: Insulin-like growth factor; TGF-α: Tumour growth factor-α; TGF-β: Tumour growth factor-β.
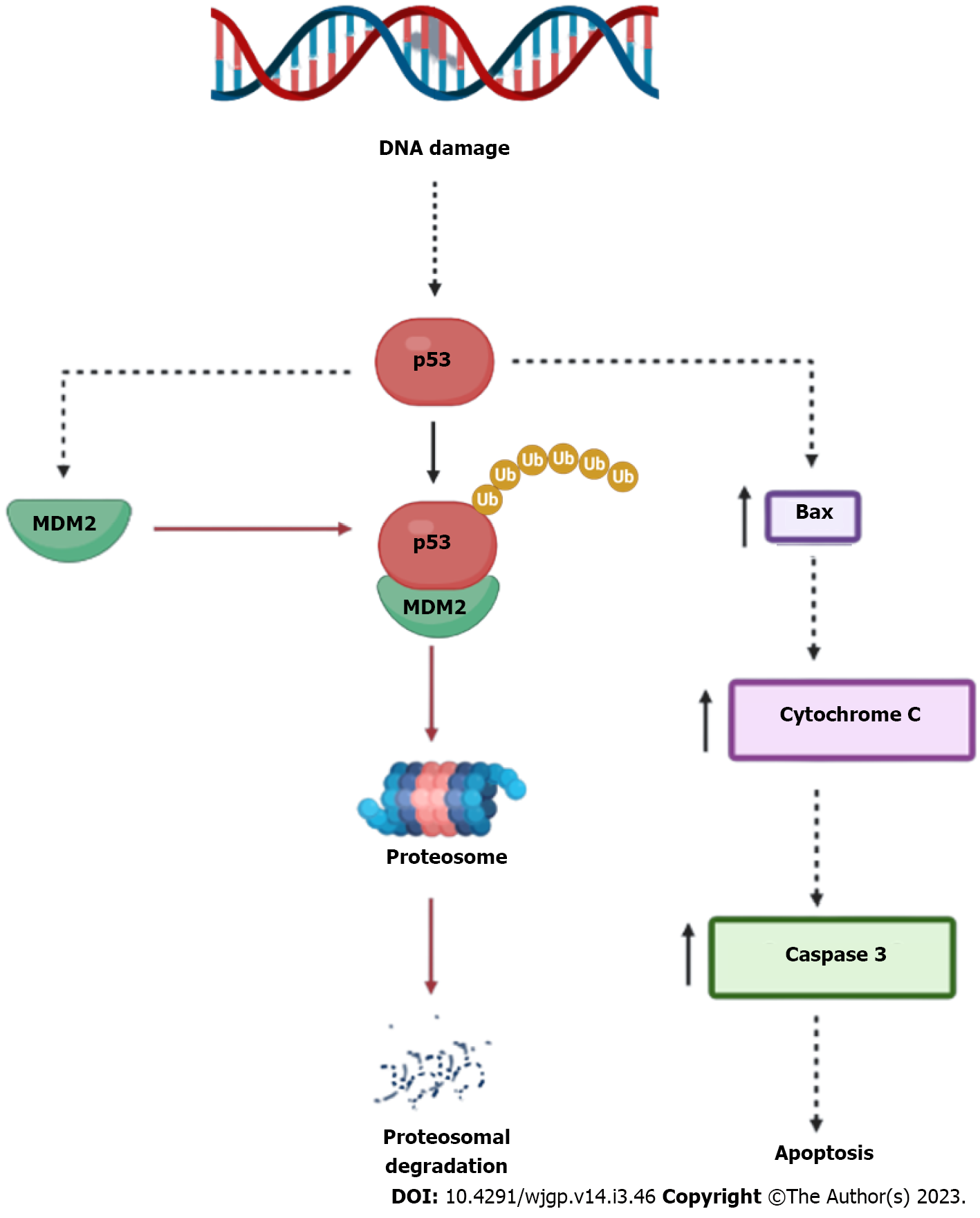
Figure 2 Regulation of p53.
p53 is a tumour suppressor protein which leads to increase in the apoptosis markers like Bax, cytochrome C and caspase 3. As murine double minute 2 complexes with p53 it leads to ubiquitination of p53 and proteasomal degradation takes place (Created with BioRender.com). MDM2: Murine double minute 2.
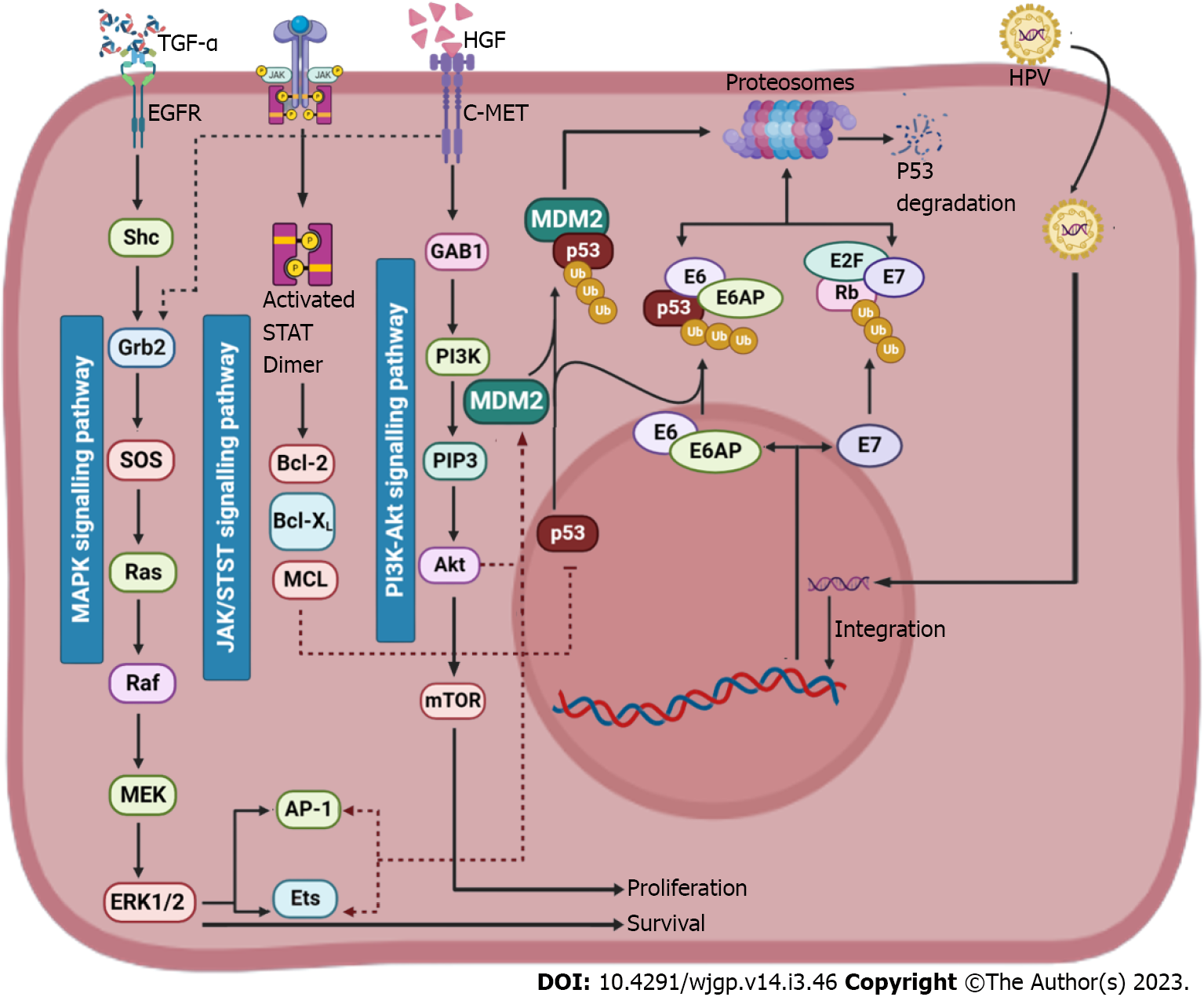
Figure 3 Role of p53 in pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Murine double minute 2 (MDM2) suppresses the tumour suppressing activity of p53 by formation of a MDM2-p53 complex. The activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and PI3K-Akt signalling pathway activates the production of MDM2 and the activation of JAK/STAT signalling pathway suppresses the p53 protein (Created with BioRender.com). TGF: Tumour growth factor; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; HPV: Human papillomavirus; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinases; MDM2: Murine double minute 2; MEK: Mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinas; ERK1/2: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; mTOR: Mechanistic target of rapamycin; AP-1: Activating protein-1; MCL: Medial collateral ligament.
- Citation: Choudhary HB, Mandlik SK, Mandlik DS. Role of p53 suppression in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2023; 14(3): 46-70
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v14/i3/46.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v14.i3.46