©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Jan 5, 2019; 10(1): 1-10
Published online Jan 5, 2019. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v10.i1.1
Published online Jan 5, 2019. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v10.i1.1
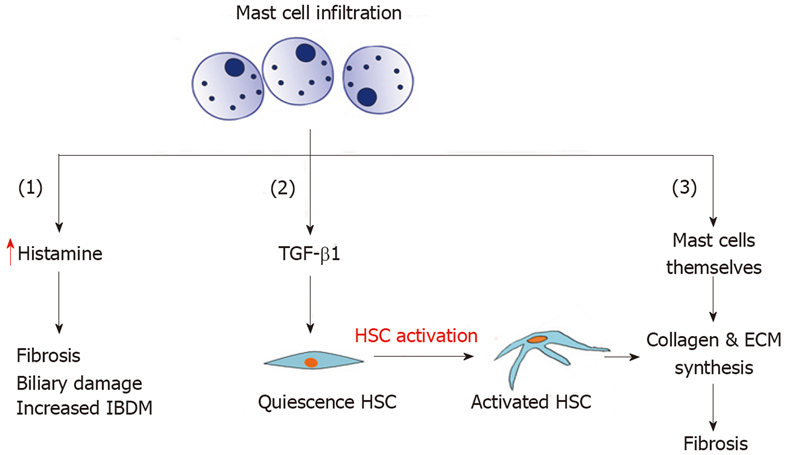
Figure 1 Mast cell infiltration and its role in biliary fibrosis.
HSC: Hepatic stellate cell; ECM: Extracellular matrix; IBDM: Intrahepatic bile duct mass; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor-beta 1.
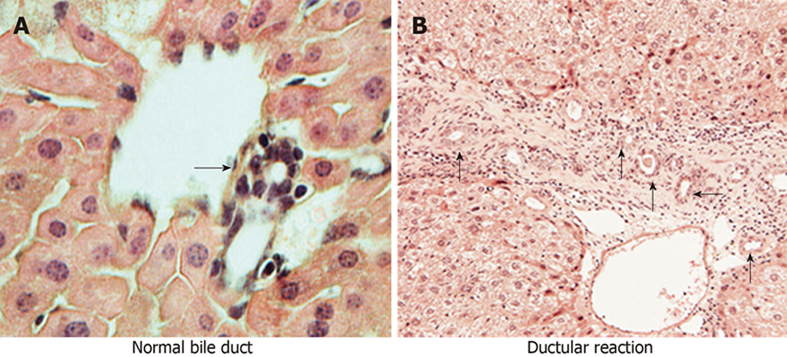
Figure 2 A bile duct consists of cholangiocytes in normal liver (A) and ductular reaction with reactive ductular cells in biliary diseases (B) (arrows indicate bile ducts).
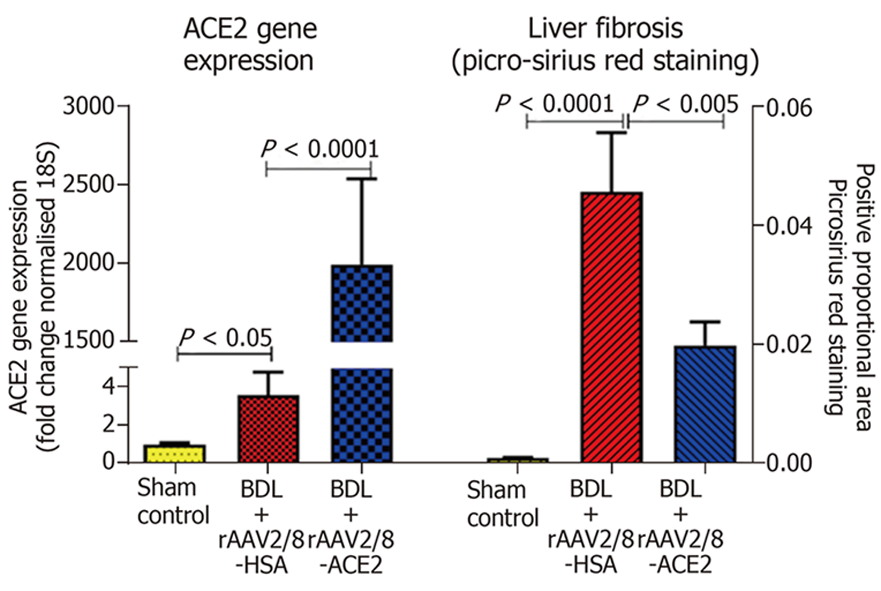
Figure 3 Hepatic ACE2 gene expression and fibrosis in a short-term model of biliary fibrosis with rAAV2/8-ACE2 therapy.
ACE2 gene expression was significantly increased in ACE2-treated mice with biliary fibrosis compared to BDL mice injected with a control human serum albumin vector (rAAV2/8-HSA). rAAV2/8-ACE2 gene therapy markedly reduced the liver fibrosis in BDL mice compared to mice injected with rAAV2/8-HSA.
- Citation: Rajapaksha IG, Angus PW, Herath CB. Current therapies and novel approaches for biliary diseases. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2019; 10(1): 1-10
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v10/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v10.i1.1