©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Radiol. Oct 28, 2017; 9(10): 389-399
Published online Oct 28, 2017. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v9.i10.389
Published online Oct 28, 2017. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v9.i10.389
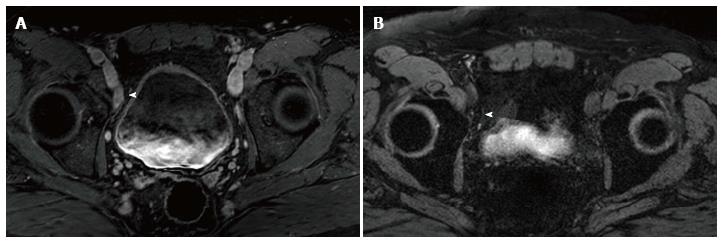
Figure 1 Selected imaged from a ferumoxytol enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in a 59-year-old man who underwent transrectal ultrasonography prostate biopsy for elevated PSA (10.
8 ng/mL) which showed Gleason 3 + 4 disease of 4 cores. A: Initial prostate multiparametric T1 weighted post gadolinium magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed a 1.8 cm × 0.9 cm right external iliac chain lymph node that was suspicious base on size criteria (arrowhead); B: 24 h post injection of ferumoxytol (7.5 Fe/kg dose), T2* weighted MRI showed decreased signal intensity within the node (arrowhead), consistent with uptake of ferumoxytol. This was considered a benign lymph node based on these results. The patient underwent computed tomography guided biopsy for confirmation and the node was negative for malignancy.
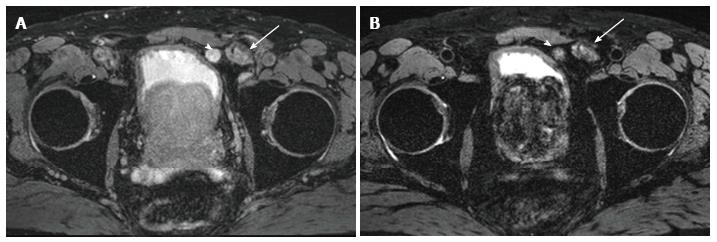
Figure 2 Selected images from a ferumoxytol enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in a 65 years old man status post magnetic resonance imaging/ultrasound fusion guided prostate biopsy revealing 3 + 3 prostate cancer and PSA 16.
6 ng/mL. A: Baseline T2* weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed a rounded lymph node anterior to the bladder (arrowhead) that measured 1.5 cm and was hyperintense. Lobular mass like lesion (arrow) lateral to the suspicious lymph node corresponds to hernia mesh; B: 24 h post injection of ferumoxytol (7.5 Fe/kg dose) enhanced MRI shows persistent heterogeneous hyperintensity within the node (arrowhead). The lack of ferumoxytol uptake within the node was suspicious for malignant involvement. Pathology revealed castleman's disease (false positive). Arrow again indicates hernia mesh.
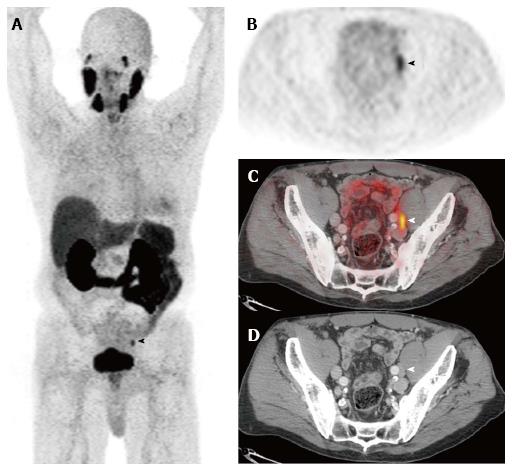
Figure 3 Prostate specific membrane antigen.
Selected images from a [68Ga]PSMA-11-PET/CT study performed prior to therapy in a man with biopsy-proven Gleason 9 prostate adenocarcinoma, a serum PSA of 11.6 ng/mL, and a clinical tumor stage of cT2b. The anterior maximum intensity projection (MIP) image (A) and the axial PET (B), fusion (C), and CT (D) images through the pelvis demonstrate focal activity in a left external iliac lymph node. This appearance is highly suspicious for a lymph node metastasis. Images courtesy of Tom Hope, MD, University of California San Francisco, Department of Radiology. PSMA: Prostate specific membrane antigen; PET/CT: Positron emission tomography/computed tomography.
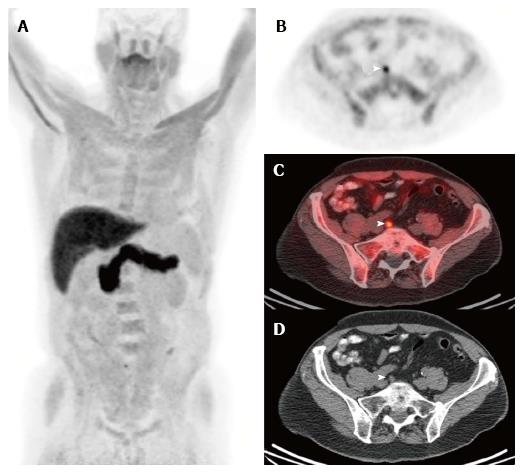
Figure 4 Fluciclovine.
Selected images from a (18F)fluciclovine-positron emission tomography/computed tomography study performed in a man who underwent prostatectomy for Gleason 8 prostate adenocarcinoma 11 years ago. He developed biochemical recurrence with a serum PSA of 0.8 ng/mL and a PSA doubling time of 14 mo at the time of the (18F)fluciclovine-PET/CT study. The anterior maximum intensity projection (MIP) image (A) and the axial PET (B), fusion (C), and CT (D) images near the level of the pelvic inlet demonstrate focal activity in a subcentimeter right common iliac lymph node. This appearance is highly suspicious for a lymph node metastasis. Images courtesy of Ephraim Parent MD, PhD, and David Schuster, MD, Emory University, Department of Radiology. PET/CT: Positron emission tomography/computed tomography.
- Citation: Zarzour JG, Galgano S, McConathy J, Thomas JV, Rais-Bahrami S. Lymph node imaging in initial staging of prostate cancer: An overview and update. World J Radiol 2017; 9(10): 389-399
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v9/i10/389.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v9.i10.389