©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Radiol. Jul 28, 2016; 8(7): 693-699
Published online Jul 28, 2016. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i7.693
Published online Jul 28, 2016. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i7.693
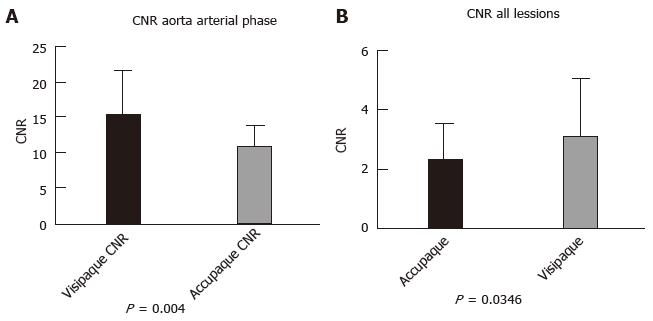
Figure 1 Schematic representation of the results of comparison of contrast-to-noise ratio of (A) aorta and (B) all focal lesions to liver parenchyma between iohexol 350 and iodixanol 270 group.
CNR: Contrast-to-noise ratio.
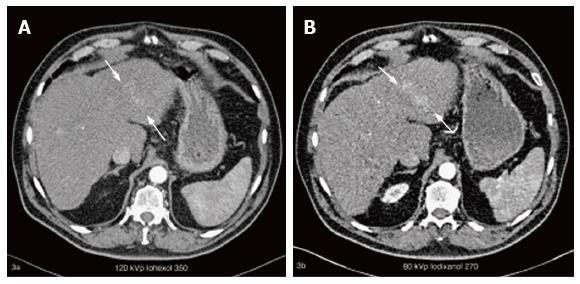
Figure 2 A 74-year-old patient with cirrhosis and known hepatocellular carcinoma who underwent 4 phase liver computed tomography twice in the duration of the study for clinical indications.
Axial CT images of the arterial phase acquisition with the iohexol 350 protocol (A) and with the iodixanol 270 protocol (B), show a hypervascular tumour of the left liver lobe (white arrows in A and B) which is more evident with the iodixanol 270 protocol. The CNR ratios for this lesion were 0.36 and 2.32 for iohexol 350 and iodixanol 270 protocol respectively. CNR: Contrast-to-noise ratio; CT: Computed tomography.
- Citation: Botsikas D, Barnaure I, Terraz S, Becker CD, Kalovidouri A, Montet X. Value of liver computed tomography with iodixanol 270, 80 kVp and iterative reconstruction. World J Radiol 2016; 8(7): 693-699
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v8/i7/693.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v8.i7.693