Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Radiol. Nov 28, 2016; 8(11): 895-901
Published online Nov 28, 2016. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i11.895
Published online Nov 28, 2016. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i11.895
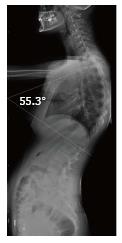
Figure 1 Illustration of Cobb angle in lateral radiography (Patient no: 17).
Cobb angle: 55.3°.
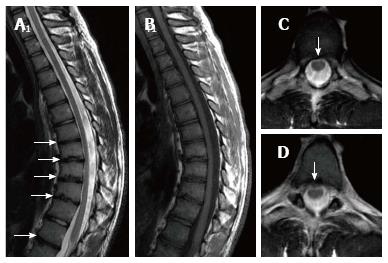
Figure 2 Seventeen years old patient with typical Scheuermann’s disease (Patient no: 9).
Sagittal plane (A) T2 weighted (B) T1 weighted (C and D) axial plane T2 weighted magnetic resonance imaging A and B: Kyphosis with apex facing to T9 vertebra (Cobb angle 61.7°), irregularities more evident in central part of T6-T12 endplates (white arrows) and disc degeneration are shown at these levels; C and D: Syrinx in medulla spinalis at thoracic 9-10 levels (black arrows).
Figure 3 Nineteen years old male patient with typical Scheuermann’s disease (Patient no: 8).
Sagittal plane (A) T2 weighted (B) T1 weighted (C and D) axial plane T2 weighted magnetic resonance imaging A and B: Kyphosis with apex facing to T9, irregularities in T7-L1 endplates and disc degeneration at these levels (except for T11-12) (white arrows) are shown; C and D: Bulging is demonstrated at thoracic 8-9 and 10-11 levels (white arrows).
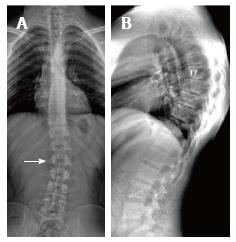
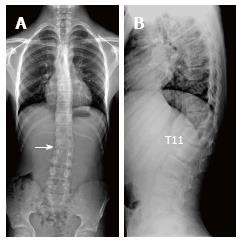
Figure 4 Twenty-three years old male patient with typical Scheuermann’s disease (Patient no: 7).
A: A scoliosis radiography demonstrating scoliosis with opening facing to right (white arrow) in lumbar axis; B. Lateral radiography of kyphosis with apex facing to T7 vertebra in thoracic spinal axis (Cobb angle 60.1°) and irregularities in thoracic endplates are shown.
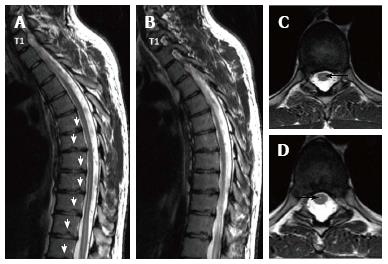
Figure 5 Twenty three years old male patient with typical Scheuermann’s disease (Patient no: 7).
(A and B) Thoracic sagittal plane (C and D) axial plane T2 weighted magnetic resonance imaging. A and B: Irregularities in endplates (white arrows), degenerations in discs slight syringomyelia in spinal cords are shown; C and D: Hyperintensity due to syrinx (black arrows) in spinal cord and diffused bulging are shown.
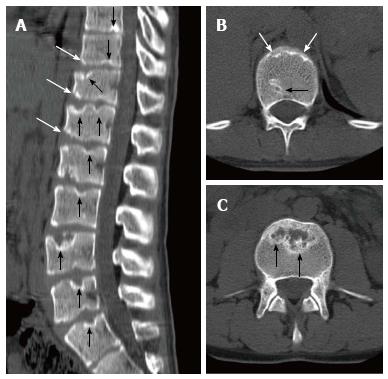
Figure 6 Eighteen years old male patient with atypical Scheuermann’s disease (Patient no: 3).
(A) Sagittal reformatted (B and C) axial plane computerized tomography. A: Evident irregularities and Schmorl nodules in thoracic, lumbar and sacral endplate surfaces (black arrows), anterior wedging in vertebra corpuses (white arrows) are shown; B and C: Endplate irregularities in axial plane CT images (white arrows) and Schmorl nodules (black arrows) are shown.
Figure 7 Eighteen years old male patient with atypical Scheuermann’s disease (Patient no: 3).
Sagittal plane (A) T2 weighted (B) T1 weighted (C and D) axial plane T2 weighted magnetic resonance imaging A and B: Thoracic 7-8, T9-L2 endplate irregularities, Schmorl nodules (white arrows) and degeneration signals in discs are shown; C and D: Posterior central protrusion (white arrow) and diffused bulging are shown.
Figure 8 Fourteen years old male patient with atypical Scheuermann’s disease (Patient no: 6).
A: Slight scoliosis with opening facing towards right in lumbar axis is shown in a scoliosis radiography (white arrow); B: Kyphosis with apex facing towards T11 level, and successive thoracic and lumbar endplate irregularities are demonstrated in a lateral radiography.
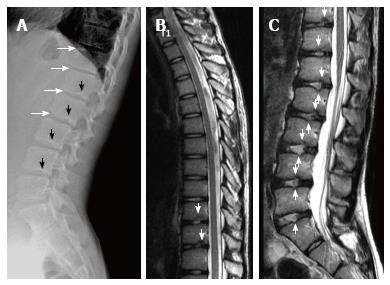
Figure 9 Fourteen years old male patient with atypical Scheuermann’s disease (Patient no: 6).
(A) Thoracic (B) lumbar sagittal plane T2 weighted magnetic resonance imaging A: Elevated kyphosis at lower thoracic level, endplate irregularities and disc degenerations starting at T5 level (white arrows) and syringomyelia on thoracic spinal cord (black arrow) are demonstrated; B: Evident degenerative irregularities and disc degenerations (white arrows) in lower thoracic and upper lumbar endplates are shown.
Figure 10 Fourteen years old male patient with atypical Scheuermann’s disease (Patient no: 16).
(A) Lateral radiography (B) Thoracic and (C) Lumbar sagittal plane T2 weighted magnetic resonance imaging. A: Anterior wedging in corpuses of lower thoracic and upper lumbar vertebrae (white arrows), and lower thoracic and lumbar endplate irregularities (black arrows) are shown; B and C: Lower thoracic and lumbar endplate irregularities (white arrows) and disc degenerations are demonstrated.
- Citation: Gokce E, Beyhan M. Radiological imaging findings of scheuermann disease. World J Radiol 2016; 8(11): 895-901
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v8/i11/895.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v8.i11.895