©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Radiol. Nov 28, 2015; 7(11): 415-420
Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v7.i11.415
Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v7.i11.415
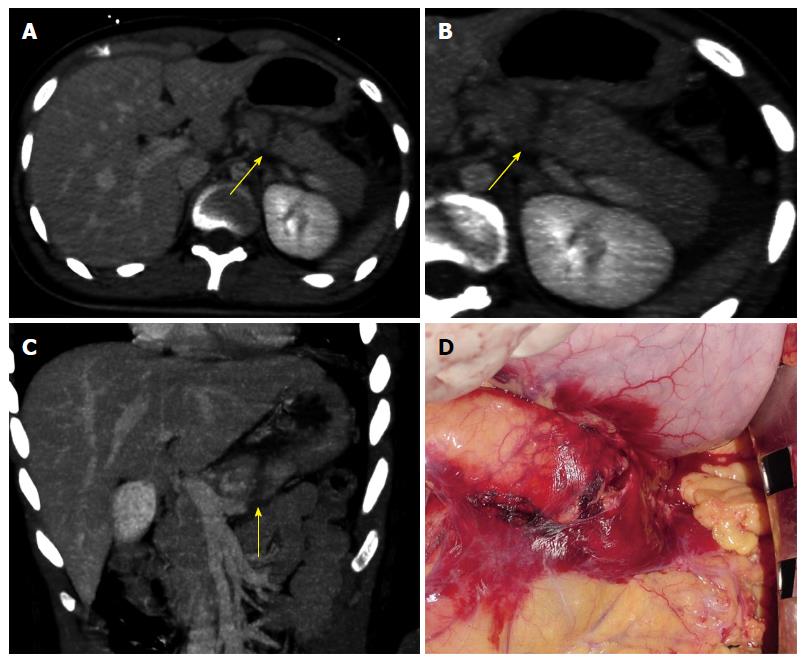
Figure 1 Computed tomography and intra-operative findings of pancreatic parenchymal fracture.
A: CT image on axial plan showing a complete laceration of the pancreatic body appearing as a low-attenuation line oriented perpendicular to the long axis of the pancreas (arrow); B: CT image on axial plan showing a complete laceration of the pancreatic body appearing as a low-attenuation line oriented perpendicular to the long axis of the pancreas (arrow); C: CT image on coronal plan showing a complete laceration of the pancreatic body appearing as a low-attenuation line oriented perpendicular to the long axis of the pancreas (arrow); D: Intra-operative finding confirming the CT diagnosis of post-traumatic laceration of the pancreas. CT: Computed tomography.
- Citation: Moschetta M, Telegrafo M, Malagnino V, Mappa L, Ianora AAS, Dabbicco D, Margari A, Angelelli G. Pancreatic trauma: The role of computed tomography for guiding therapeutic approach. World J Radiol 2015; 7(11): 415-420
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v7/i11/415.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v7.i11.415