©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Sep 28, 2011; 3(9): 215-223
Published online Sep 28, 2011. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v3.i9.215
Published online Sep 28, 2011. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v3.i9.215
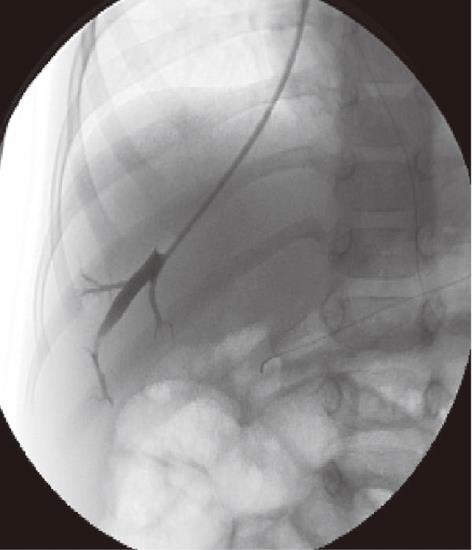
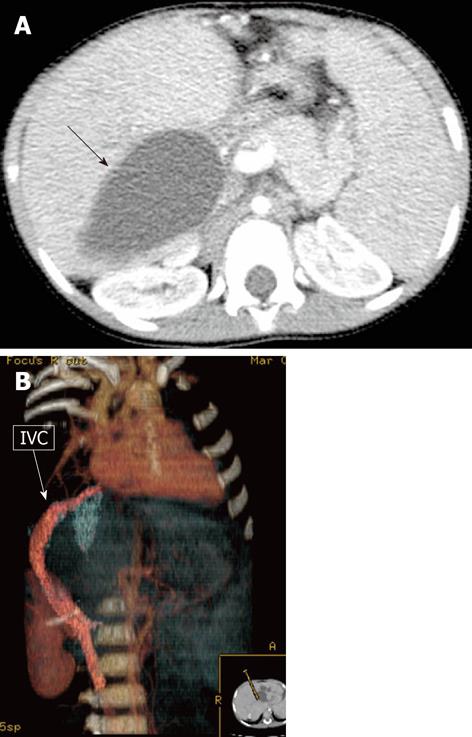
Figure 1 A 3-year-old male child post-Kasai.
Fluoroscopic image of normal wedged venogram, hepatic venous pressure gradient 15.5 mmHg.
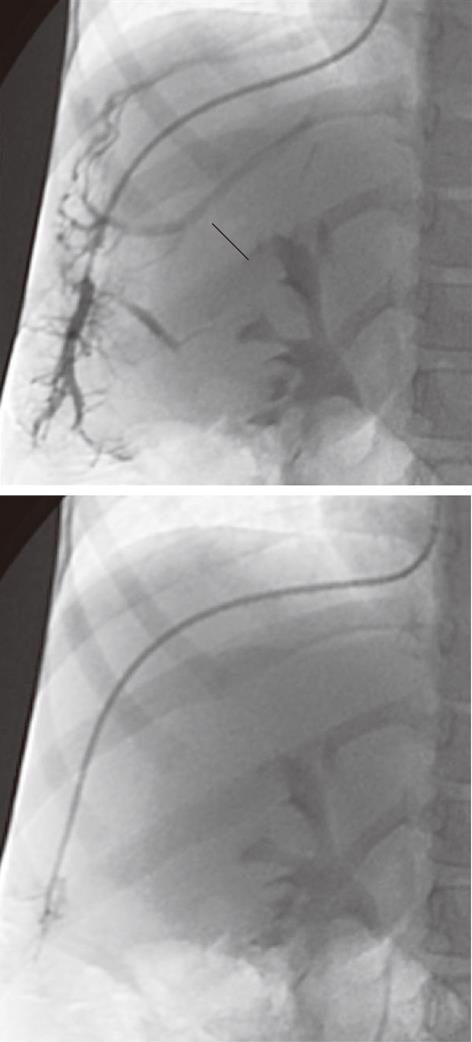
Figure 2 A 5-year-old female child post-Kasai.
Fluoroscopic image. A: Wedged venogram showing multiple peripheral venovenous communications (arrows); B: 5F occlusion balloon catheter advanced distally in the hepatic vein, no venous communications visualized; Wedged (occluded) hepatic vein pressure obtained, hepatic venous pressure gradient 15 mmHg.
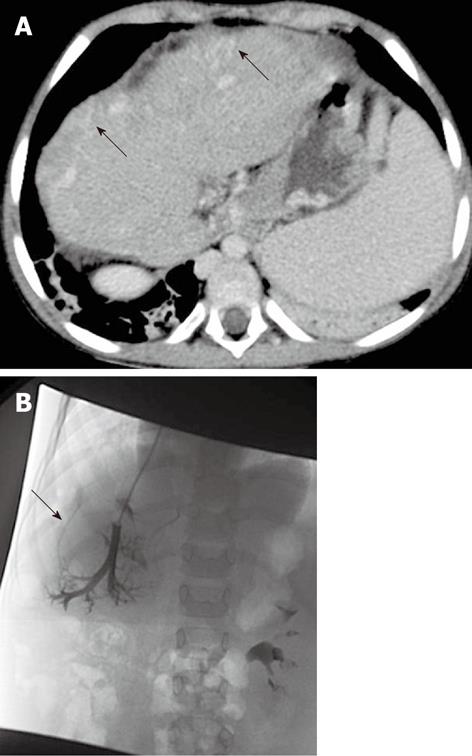
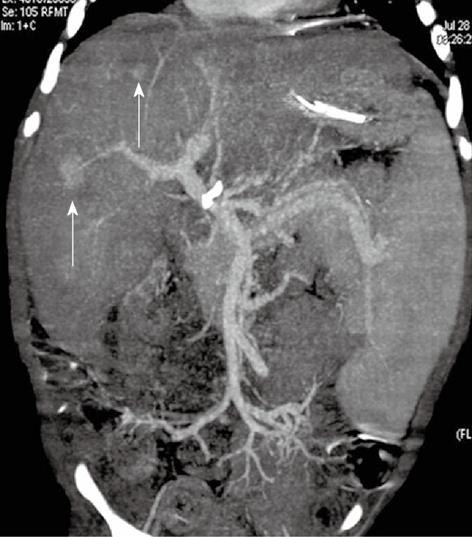
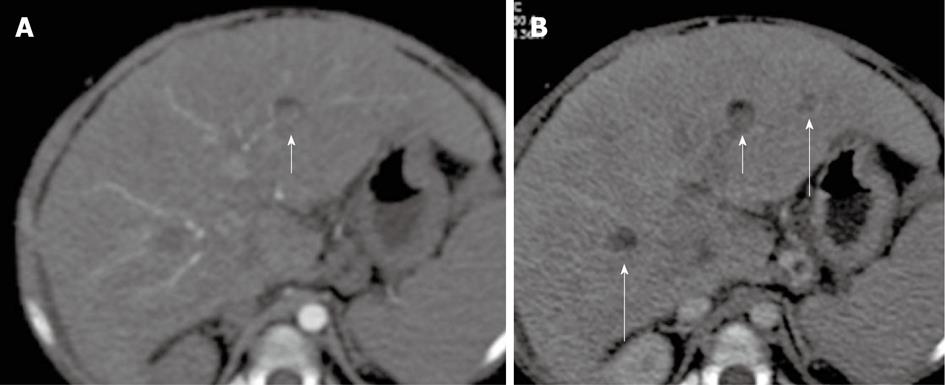
Figure 3 A 5-year-old female child post-Kasai.
A: Multi-detector computed tomography shows peripheral venous-venous communications (arrows). Of note: Azygos vein dilatation secondary to retro-hepatic interruption of inferior vena cava; B: Fluoroscopic image: wedged venogram confirms peripheral venovenous communications (arrow).
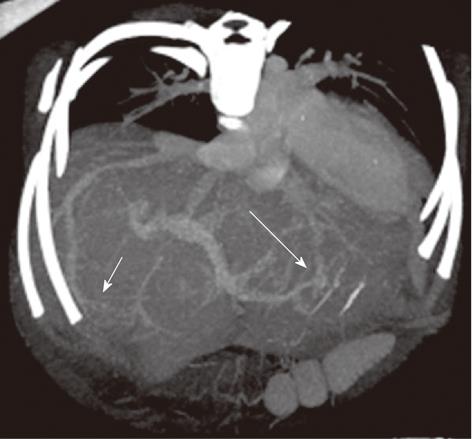
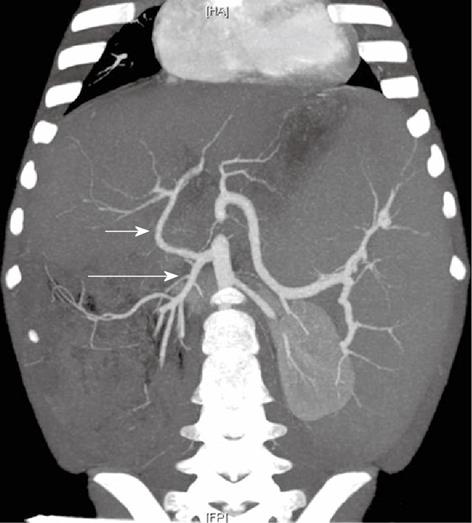
Figure 4 A 9-mo-old boy post-Kasai.
Multi-detector computed tomography: Paraxial multi intensity projection reconstruction shows peripheral venous-venous communication (short arrow) and portal venous shunts (long arrow).
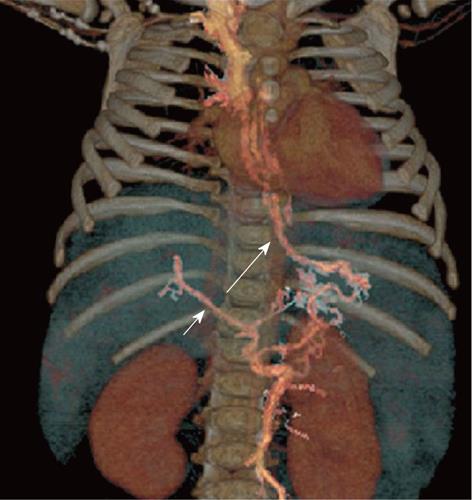
Figure 5 A 2-year-old female child post-Kasai.
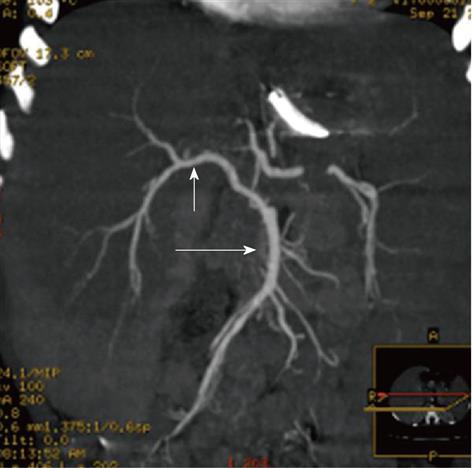
Multi-detector computed tomography: Multiple Intensity Projection reconstruction, right hepatic artery (short arrow) off from superior mesenteric artery (long arrow).
Figure 6 A 5-year-old female child post-Kasai.
Multi-detector computed tomography: Multiple Intensity Projection reconstruction, common hepatic artery (short arrow) arising from superior mesenteric artery (long arrow). Of note: large splenomegaly.
Figure 7 A 15-mo-old male child post-Kasai.
Multi-detector computed tomography: Multiple Intensity Projection reconstruction. Good caliper of main portal vein, significant splenomegaly. Two hepatic hypervascular nodules coexist (arrows).
Figure 8 A 8-mo-old female child post-Kasai.
Multi-detector computed tomography: volume rendering reconstruction shows small main portal vein (short arrow), patent coronary vein (long arrow) with filling of esophageal varices.
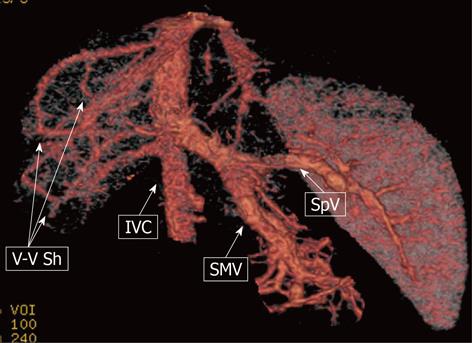
Figure 9 A 9-mo-old male child.
Multi-detector computed tomography: volume rendering reconstruction shows the superior mesenteric vein (SMV) and the splenic vein (SpV) joining to form a short common trunk that directly enters into the suprarenal inferior vena cava (IVC); Venous-venous intrahepatic shunting (V-V Sh) coexist.
Figure 10 A 12-mo-old female child post-Kasai.
A: Multi-detector computed tomography (MDCT), isolated large biliary cyst in the right lobe (arrow); B: MDCT, volume rendering reconstruction shows inferior vena cava (IVC) compressed and displaced by the large intrahepatic biliary cyst.
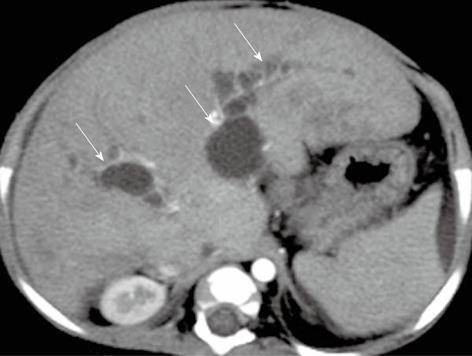
Figure 11 A 8-mo-old female child post-Kasai.
Multi-detector computed tomography shows multiple intrahepatic biliary cysts after Kasai operation (arrows).
Figure 12 A 5-mo-old female child post-Kasai.
Colangio magnetic resonance shows multiple intrahepatic biliary cysts (arrows).
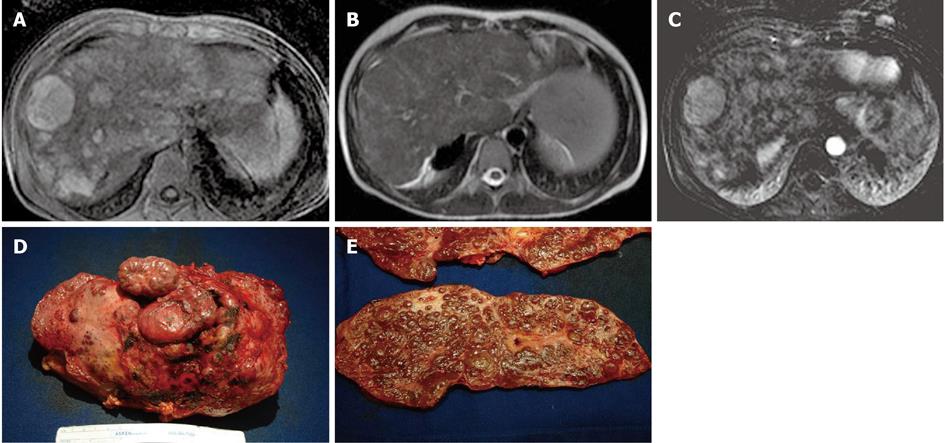
Figure 13 A 13-year-old male post-Kasai who underwent surgical spleno-renal shunt for gastrointestinal bleeding.
A: Axial T1 Fat Sat weighted acquisition shows multiple hyperintense nodules, the largest of these in S8; B: Axial T2 weighted acquisition: the nodules are isointense; C: Axial T1 Fat Sat weighted acquisition obtained with digital subtraction between the arterial phase and the unenhanced phase shows the vascular enhancement of the nodules; D: Explanted liver shows an irregular and multilobulated surface; E: Gross examination of sectioned liver confirms the presence of multiple regenerative nodular hyperplasia nodules.
Figure 14 A 20-mo-old female without previous Kasai operation.
Multi-detector computed tomography: In S3, nodule (short arrow) that shows in anterior portion a mild amount of fat. The nodule appears slightly hyperdense in arterial phase (A) and hypoattenuating in portal/venous phase; B: Regenerative nodule was found at liver explant. Of note: other hypoattenuating regenerative nodules in S6 and S3 (long arrows).
- Citation: Miraglia R, Caruso S, Maruzzelli L, Spada M, Riva S, Sciveres M, Luca A. MDCT, MR and interventional radiology in biliary atresia candidates for liver transplantation. World J Radiol 2011; 3(9): 215-223
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v3/i9/215.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v3.i9.215