Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Dec 28, 2010; 2(12): 455-462
Published online Dec 28, 2010. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v2.i12.455
Published online Dec 28, 2010. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v2.i12.455
Figure 1 Simple cyst showing no enhancement in the arterial (A), portal venous (B) and late phases (C).
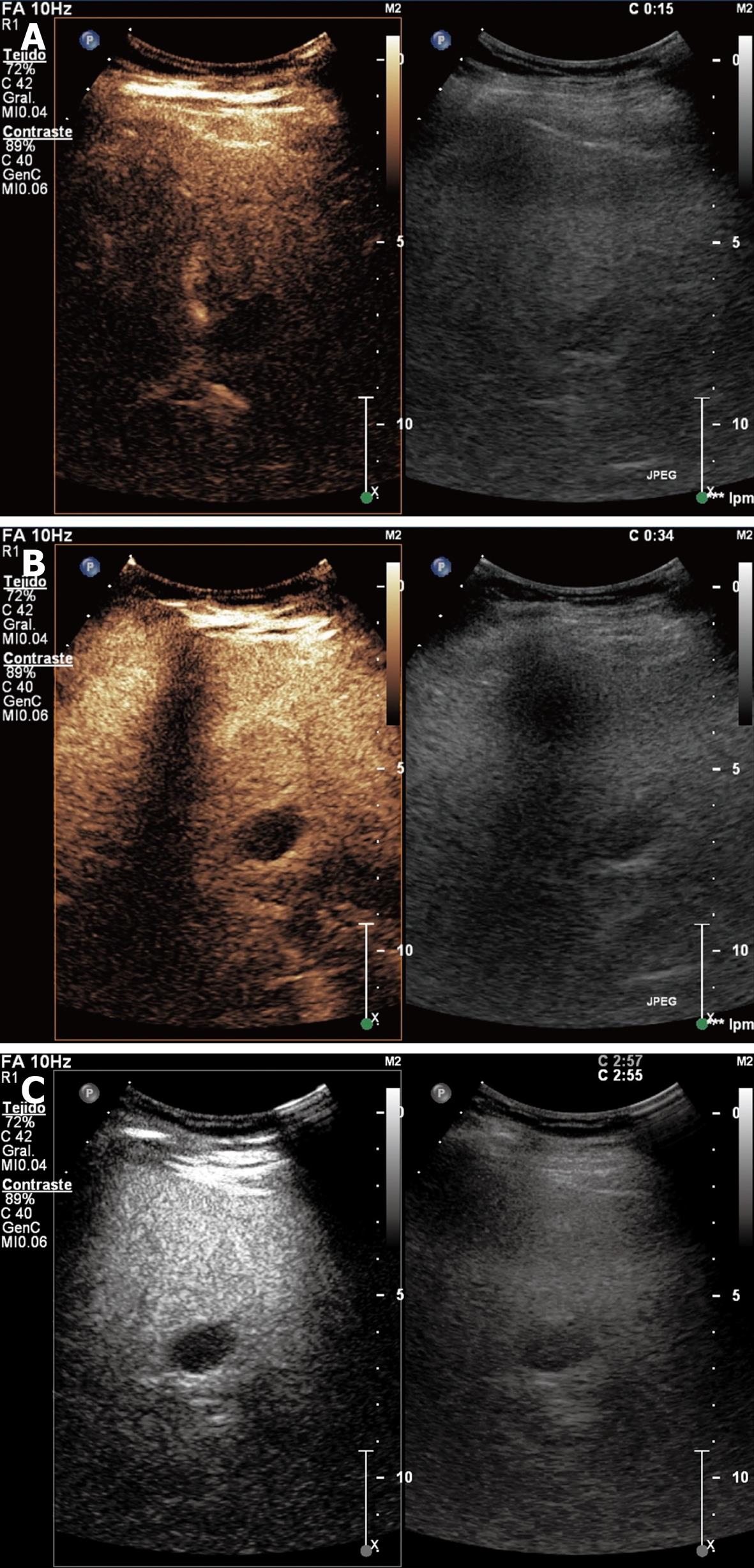
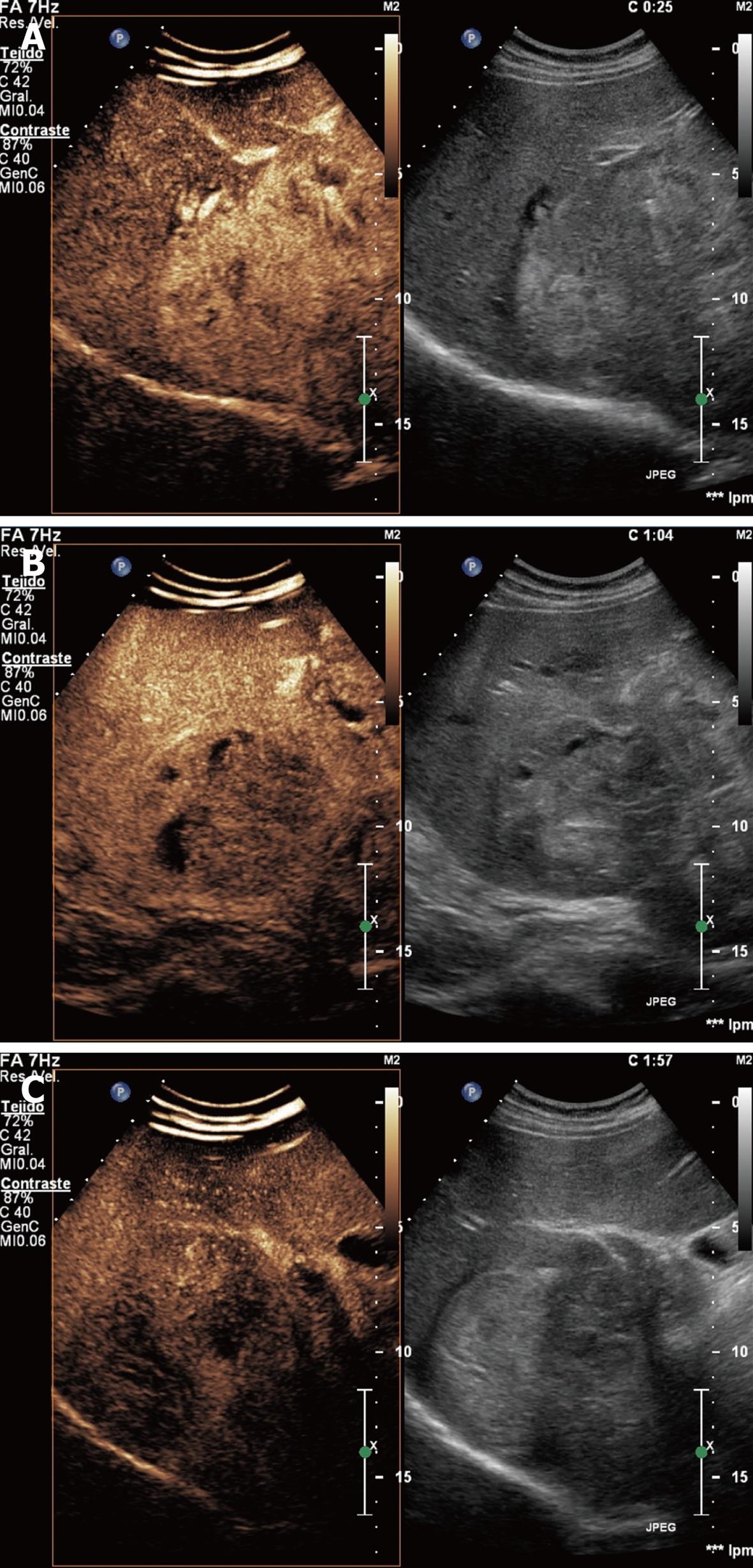
Figure 2 Hemangioma showing peripheral-nodular enhancement in arterial phase without central enhancement (A), partial centripetal filling in the portal venous phase (B), and complete enhancement in the late phase (C).
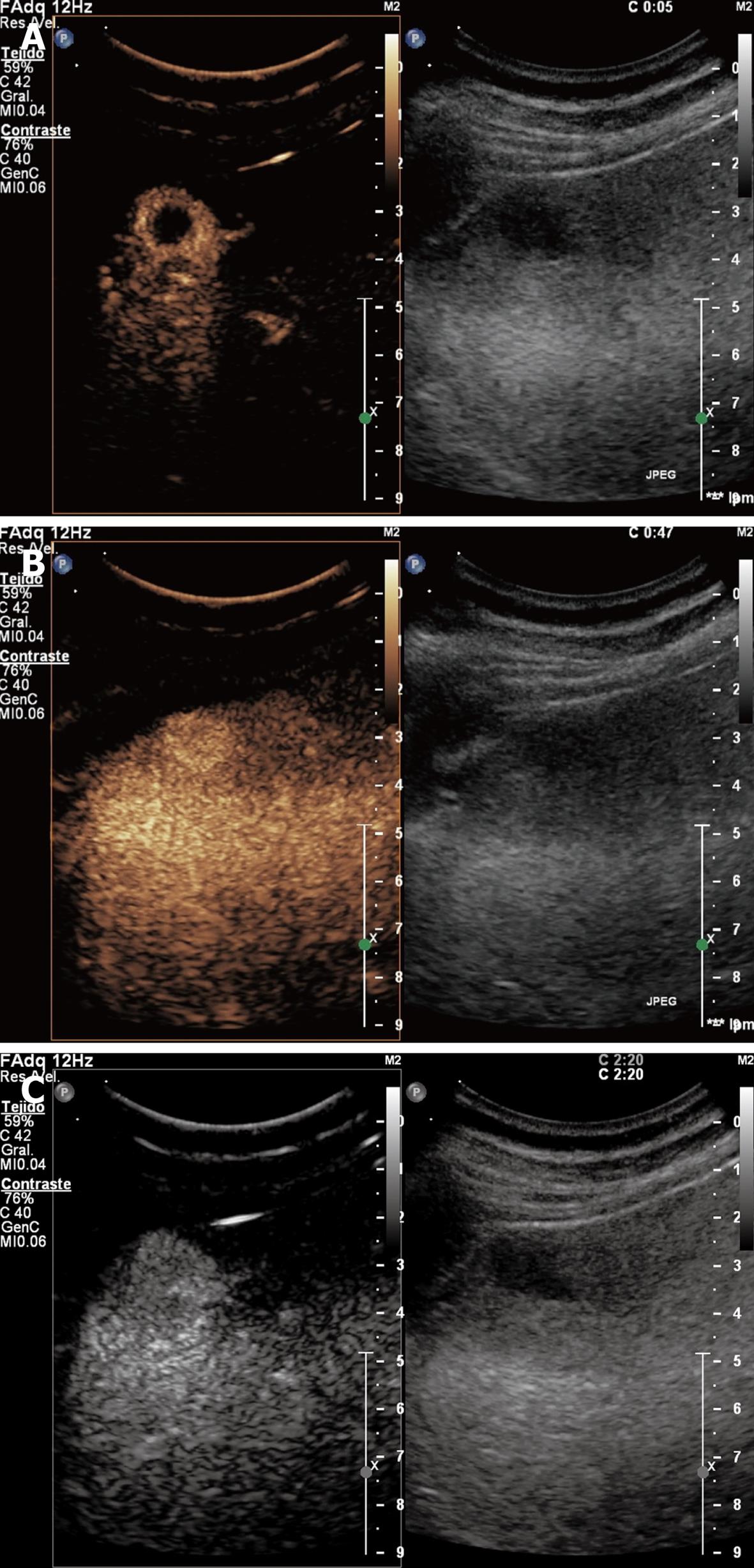
Figure 3 Focal nodular hyperplasia showing hyper-enhancement in arterial phase with complete and early centrifugal filling (A), in portal venous phase (B), and hyper/iso-enhancement in late phase (C).
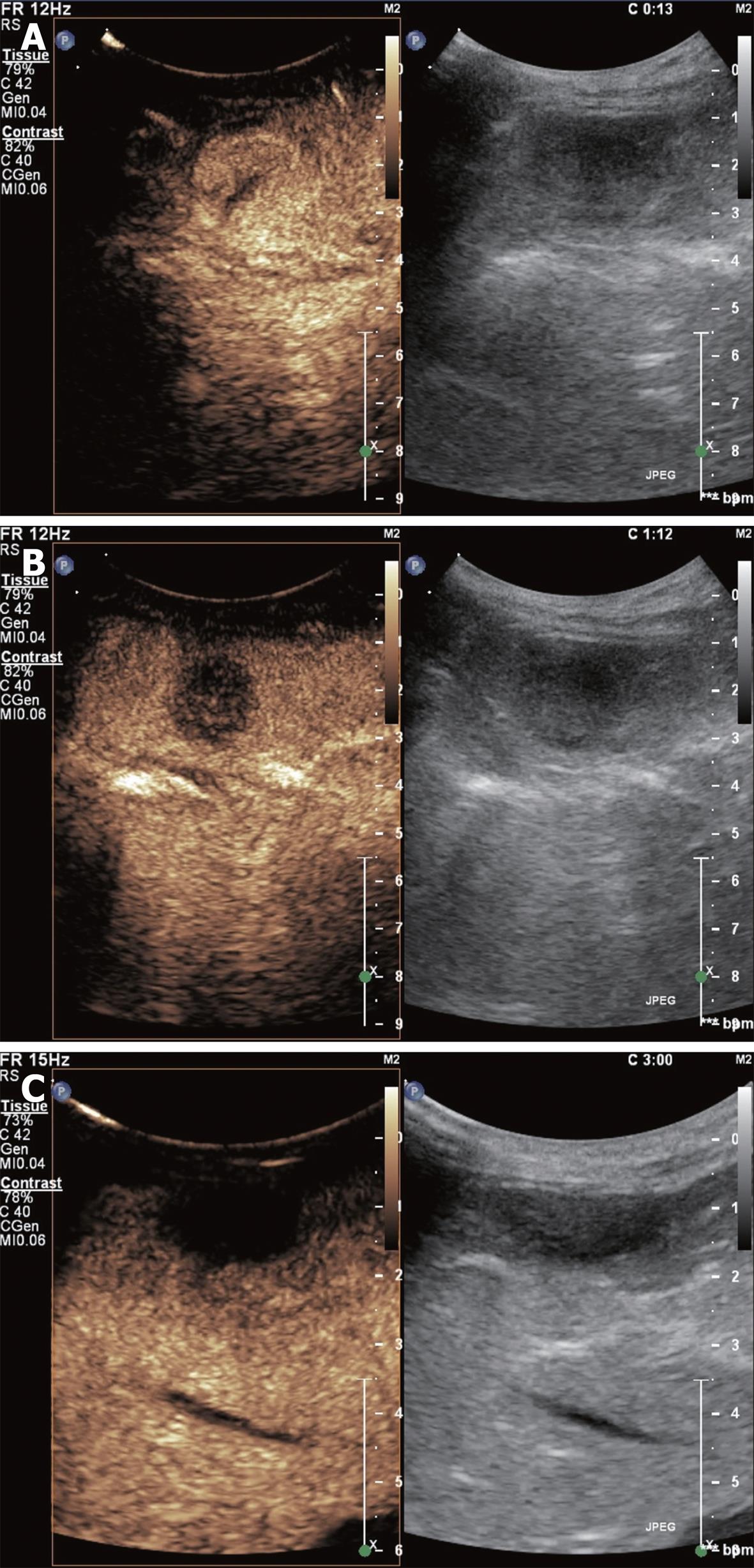
Figure 4 Focal fatty sparing demonstrating an iso-enhancement in the arterial (A), portal (B) and late phases (C).
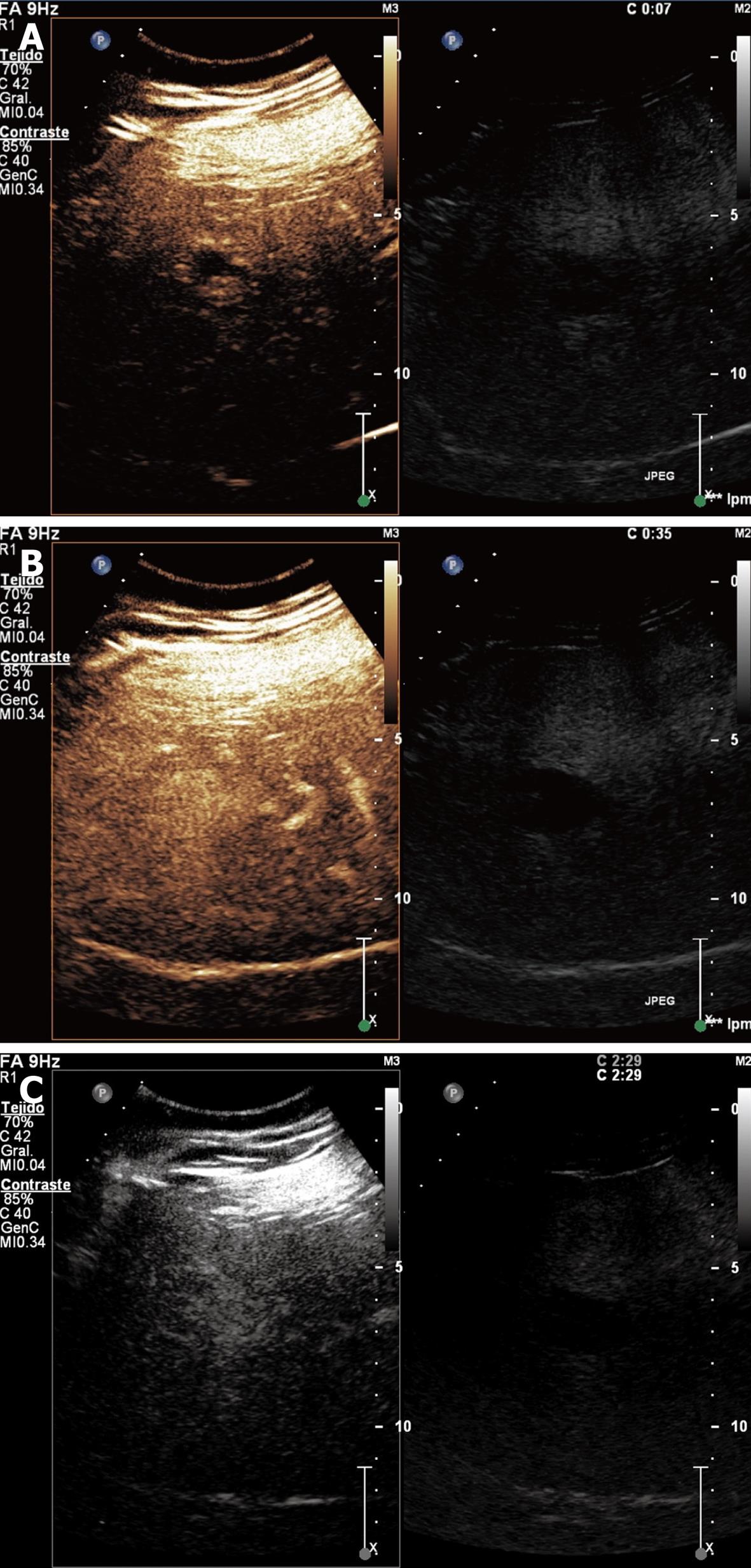
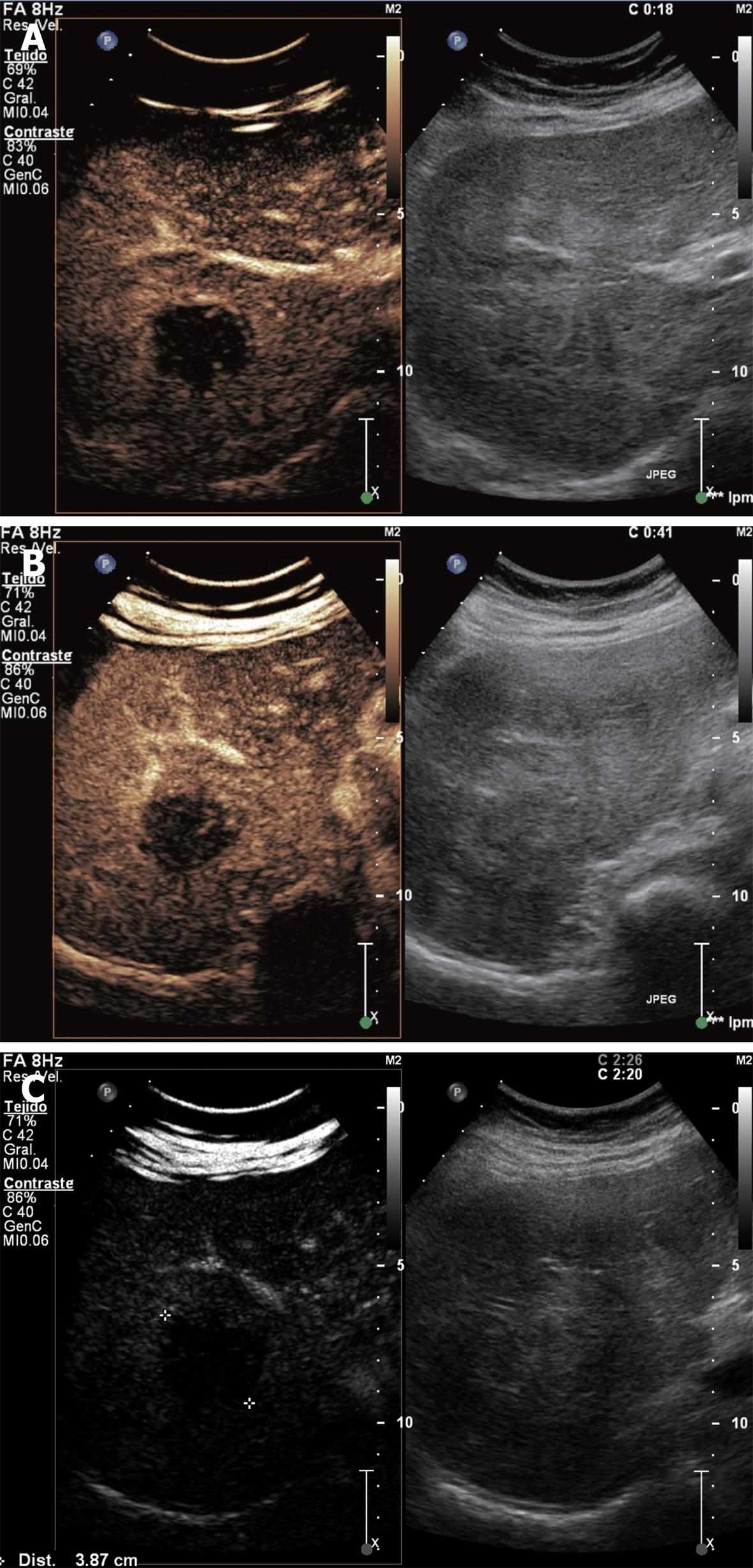
Figure 5 Hepatocellular carcinoma showing hyper-enhancing in arterial phase with necrotic non-enhancing areas (A), iso-enhancement in portal venous phase with necrotic non-enhancing areas (B), and hypo/iso-enhancing in late phase (C).
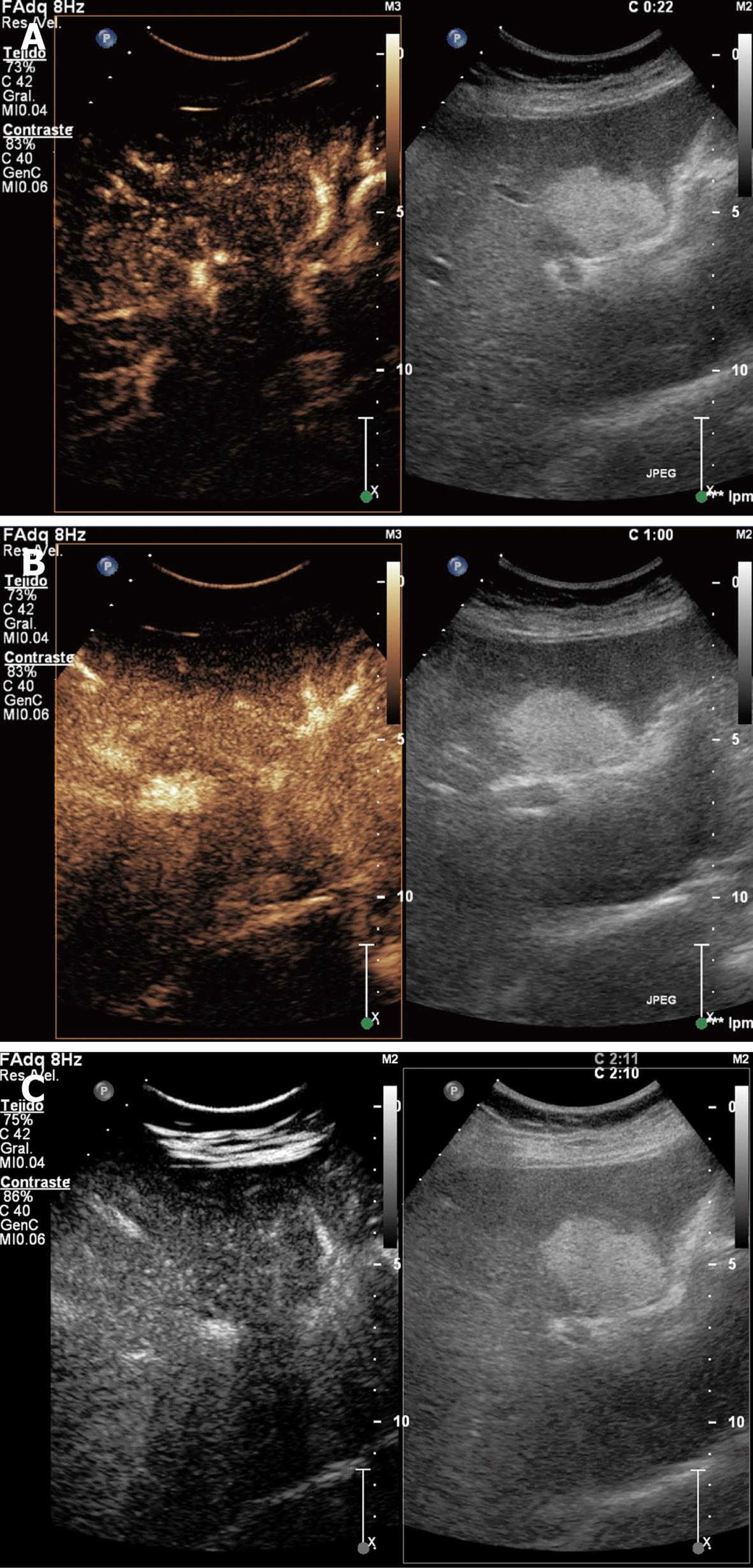
Figure 6 Hypervascular metastases showing hyper-enhancement in arterial phase (A), hypo-enhancement in portal venous phase (B), and hypo/non-enhancement in late phase (C).
Figure 7 Hypovascular metastases showing rim enhancement with central hypo-enhancement in arterial phase (A), hypo-enhancement in portal venous phase (B), and hypo/non-enhancement in late phase (C)
- Citation: Molins IG, Font JMF, Álvaro JC, Navarro JLL, Gil MF, Rodríguez CMF. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound in diagnosis and characterization of focal hepatic lesions. World J Radiol 2010; 2(12): 455-462
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v2/i12/455.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v2.i12.455