©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Radiol. Jan 28, 2026; 18(1): 115503
Published online Jan 28, 2026. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v18.i1.115503
Published online Jan 28, 2026. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v18.i1.115503
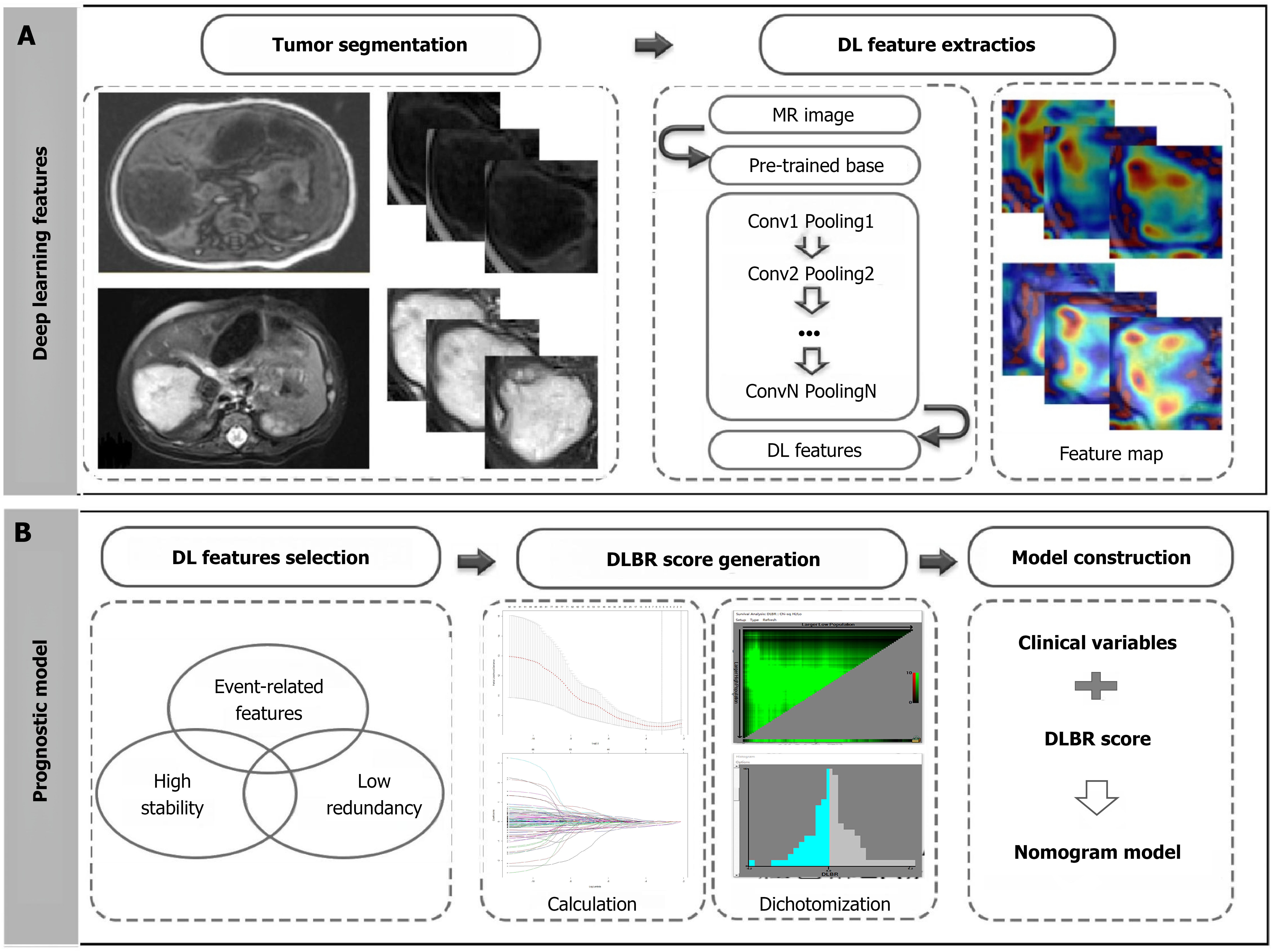
Figure 1 Flowchart of deep learning features extraction, and deep learning-based radiomics score generation and related prognostic models construction for predicting event-free survival in hepatoblastoma patients receiving surgical resection.
A: Flowchart of deep learning features extraction; B: Related prognostic models construction. DL: Deep learning; MR: Magnetic resonance; DLBR: Deep learning-based radiomics.
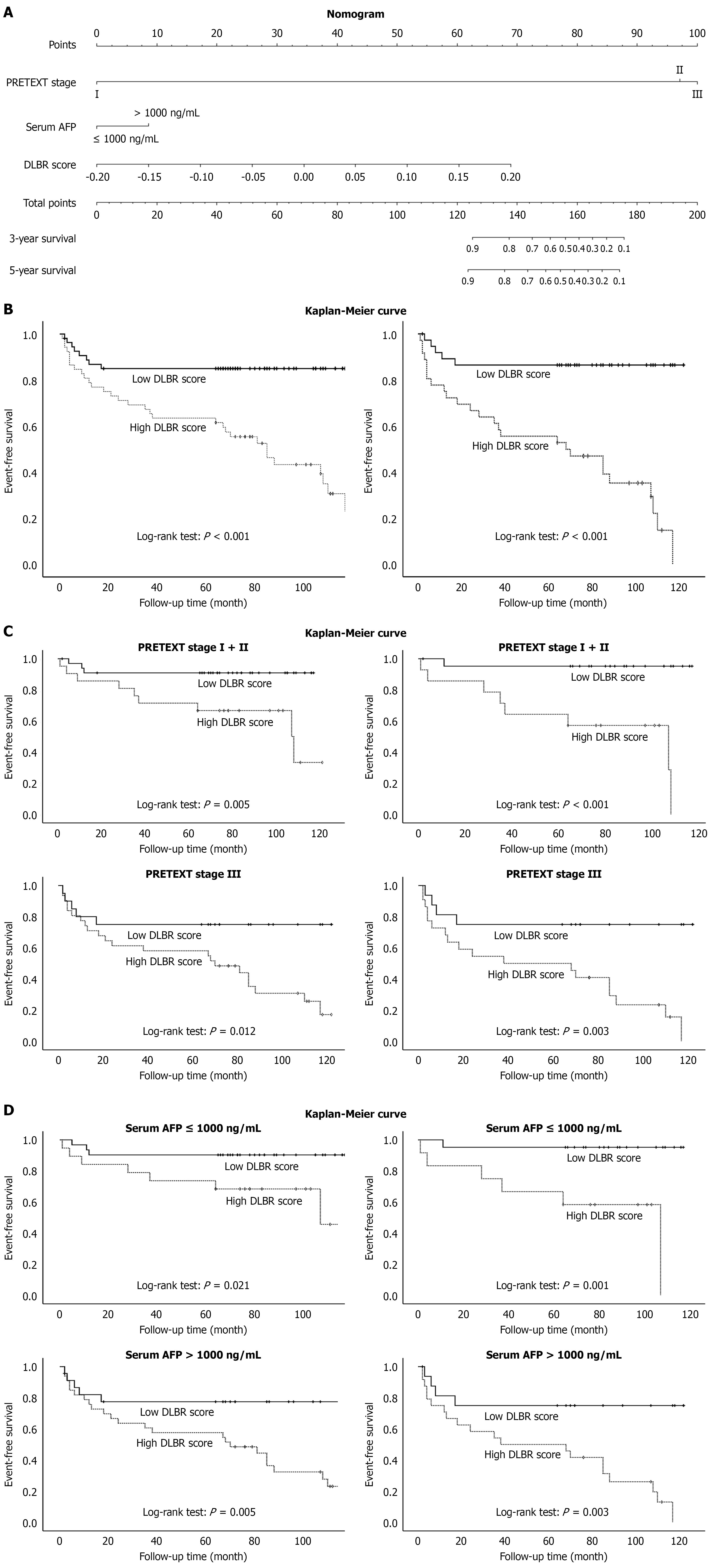
Figure 2 Nomogram and Kaplan-Meier plots of deep learning-based radiomics score for event-free survival in hepatoblastoma patients receiving surgical resection.
A: Nomogram developed by significant clinical variables and deep learning-based radiomics score to predict event risks in the training cohort; B-D: Kaplan-Meier plots of deep learning-based radiomics score (B), and stratified by 2017 PRE-Treatment EXTent of tumor stage (C) and serum alpha-fetoprotein concentration (D) on event-free survival compared by log-rank tests in the training (left) and testing (right) cohorts, respectively. PRETEXT: 2017 PRE-Treatment EXTent of tumor; AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; DLBR: Deep learning-based radiomics.
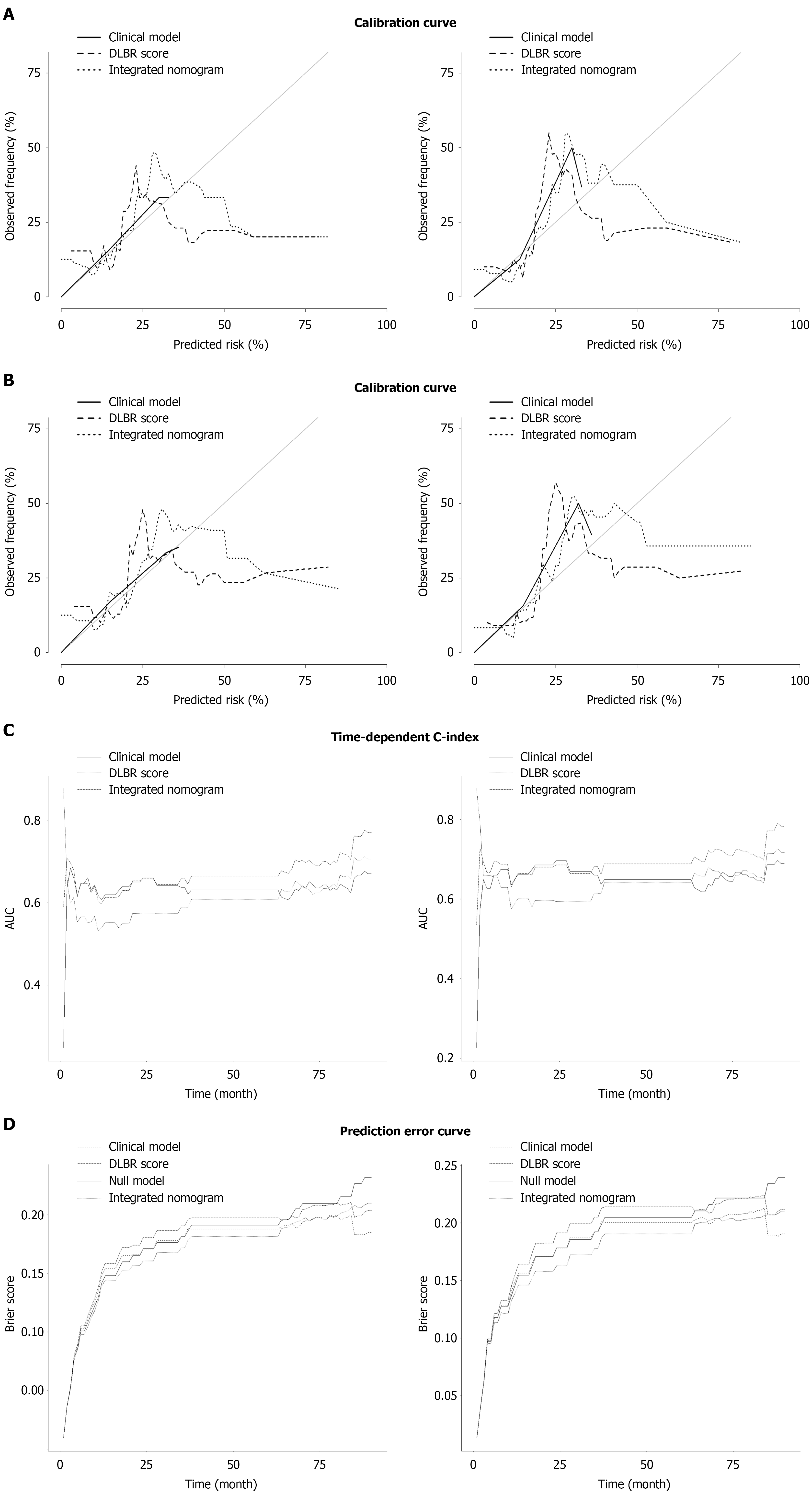
Figure 3 The calibration and discrimination performance of deep learning-based radiomics score for event-free survival in hepato
- Citation: Yang YH, Li Y. Magnetic resonance imaging-based deep-learning radiomics score for survival prediction and risk stratification in pediatric hepatoblastoma receiving surgical resection. World J Radiol 2026; 18(1): 115503
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v18/i1/115503.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v18.i1.115503