©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Radiol. Apr 28, 2025; 17(4): 105960
Published online Apr 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i4.105960
Published online Apr 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i4.105960
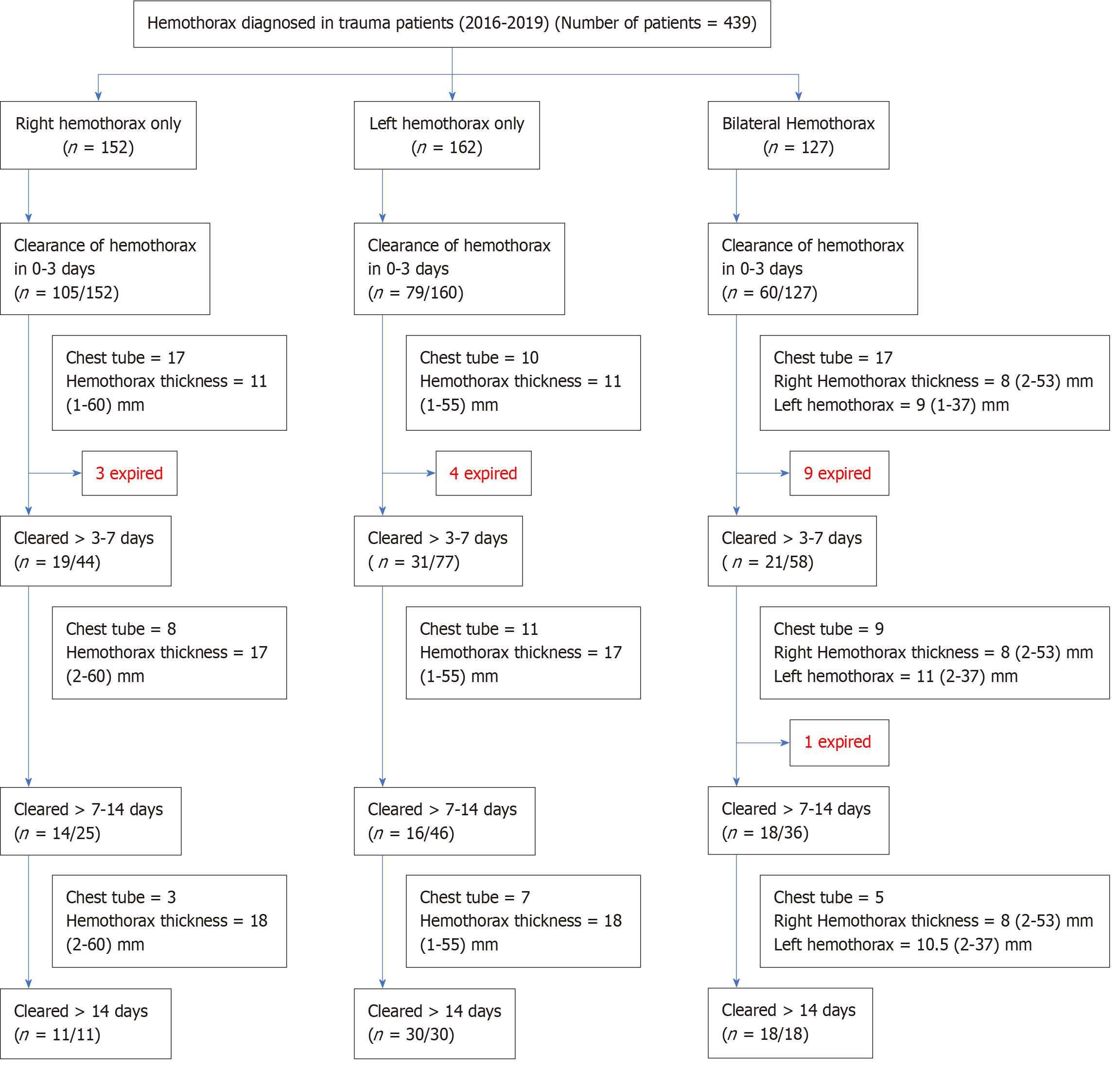
Figure 1
Flowchart of hemothorax management: Classification based on laterality, clearance time, and outcomes.
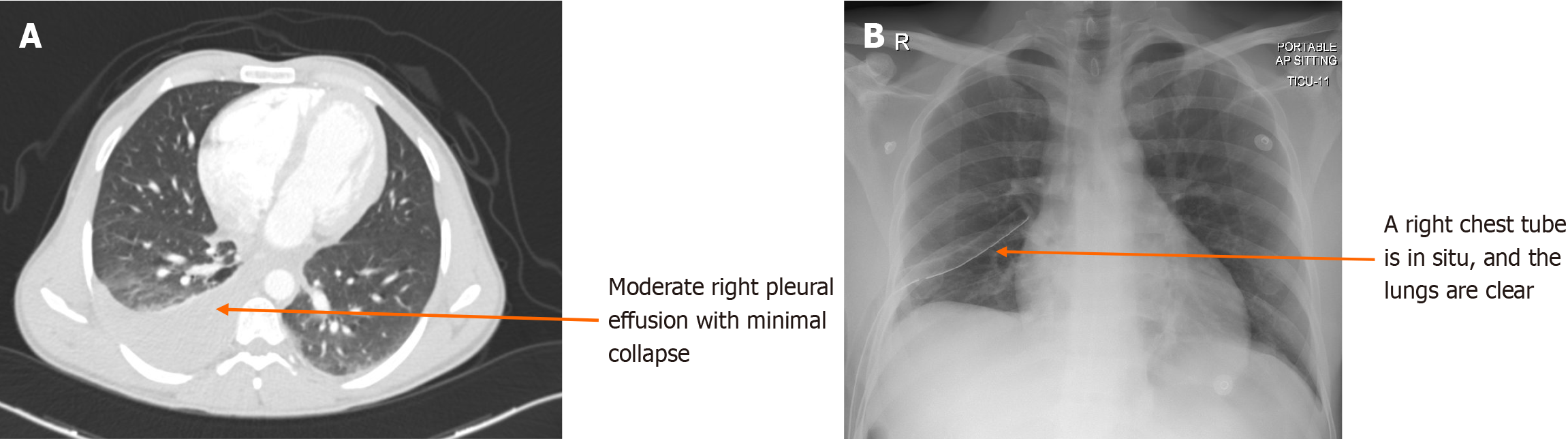
Figure 2 Image of hemothorax and chest tube.
A: Initial computed tomography (CT) scan of a polytrauma patient with right hemothorax; B: Chest X-ray post-CT scan-chest tube was inserted with a resolution of hemothorax.
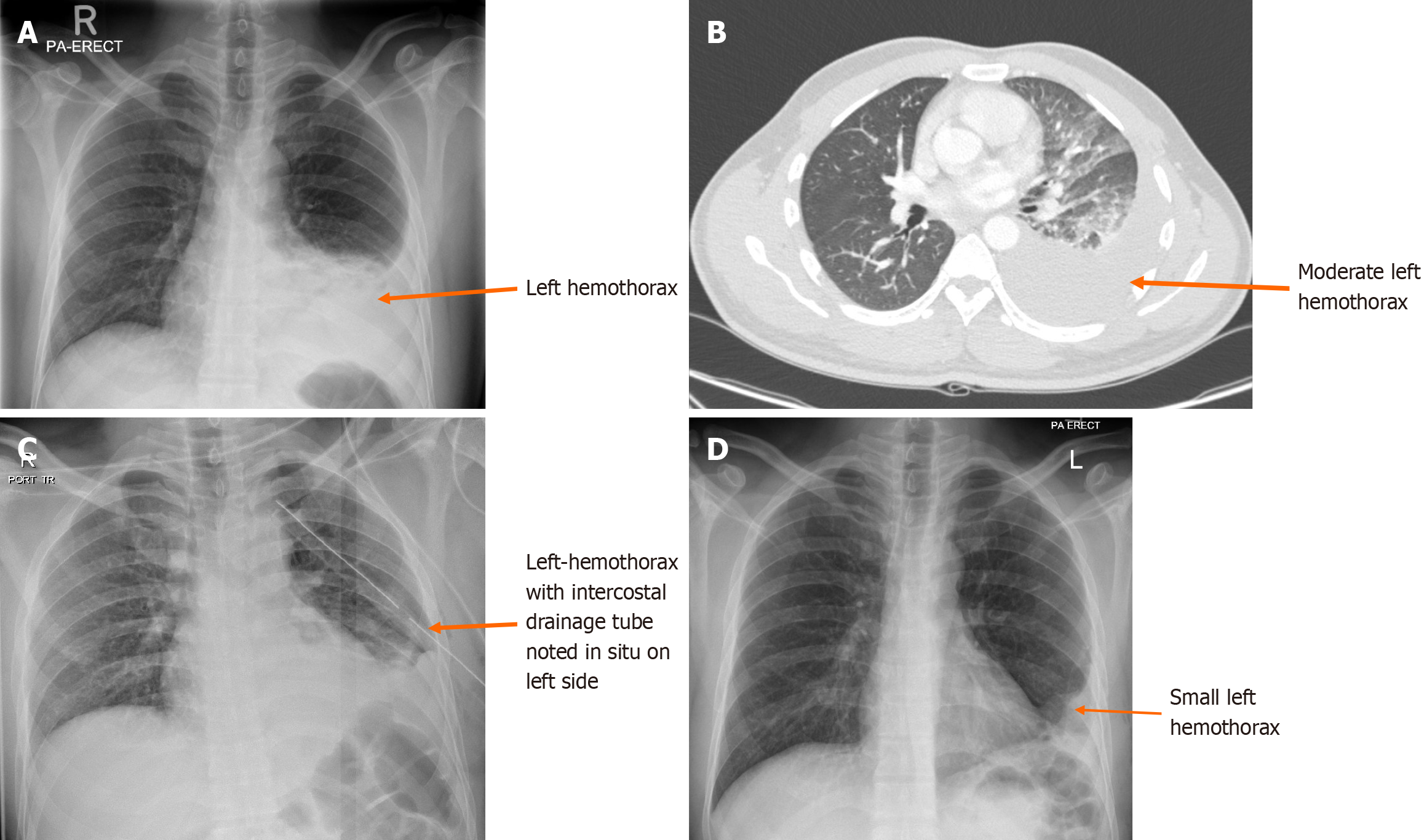
Figure 3 Chest X-ray and computed tomography of hemothorax.
A: Initial chest X-ray in trauma room showing left hemothorax; B: Computed tomography (CT) scan showing mild to moderate left-sided pleural effusion with underlying consolidation and contusion in the lingula and left lower lobe; C: Left chest tube insertion post CT scan; D: After a 1-week X-Ray chest showing left chest tube was removed, however a small left hemothorax with the pleural thickening remains detected. Lungs are clear.
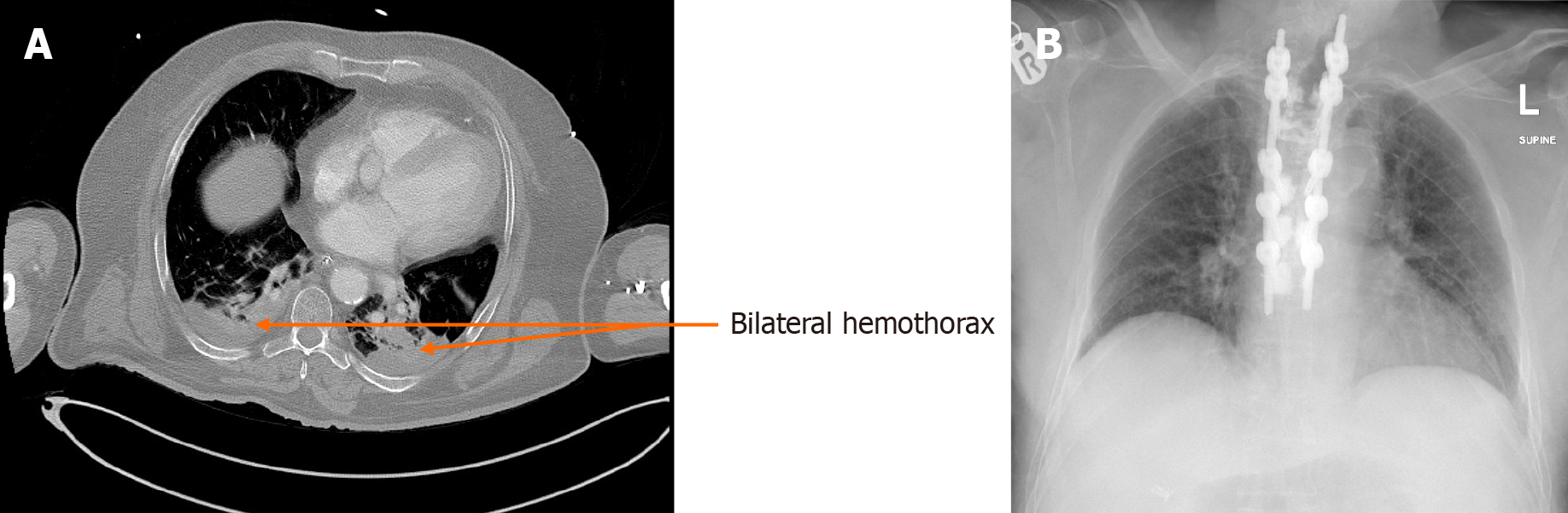
Figure 4 Images of bilateral hemothorax and its clearance.
A: Initial computed tomography scan on admission showing bilateral hemothorax with segmental compression atelectasis; B: Follow up after 1 month-chest X-Ray costophrenic angles are clear (without chest tube insertion). It shows also thoracic spine fixation.
- Citation: Ahmed K, Al-Hassani A, El-Menyar A, Nabir S, Ahmed MN, Almadani A, Mahmood I, Mekkodathil A, Peralta R, Rizoli S, Al-Thani H. Time to resolution of radiologically detected hemothorax in trauma patients: A retrospective observational study. World J Radiol 2025; 17(4): 105960
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v17/i4/105960.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v17.i4.105960