©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Radiol. Jan 28, 2025; 17(1): 102579
Published online Jan 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i1.102579
Published online Jan 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i1.102579
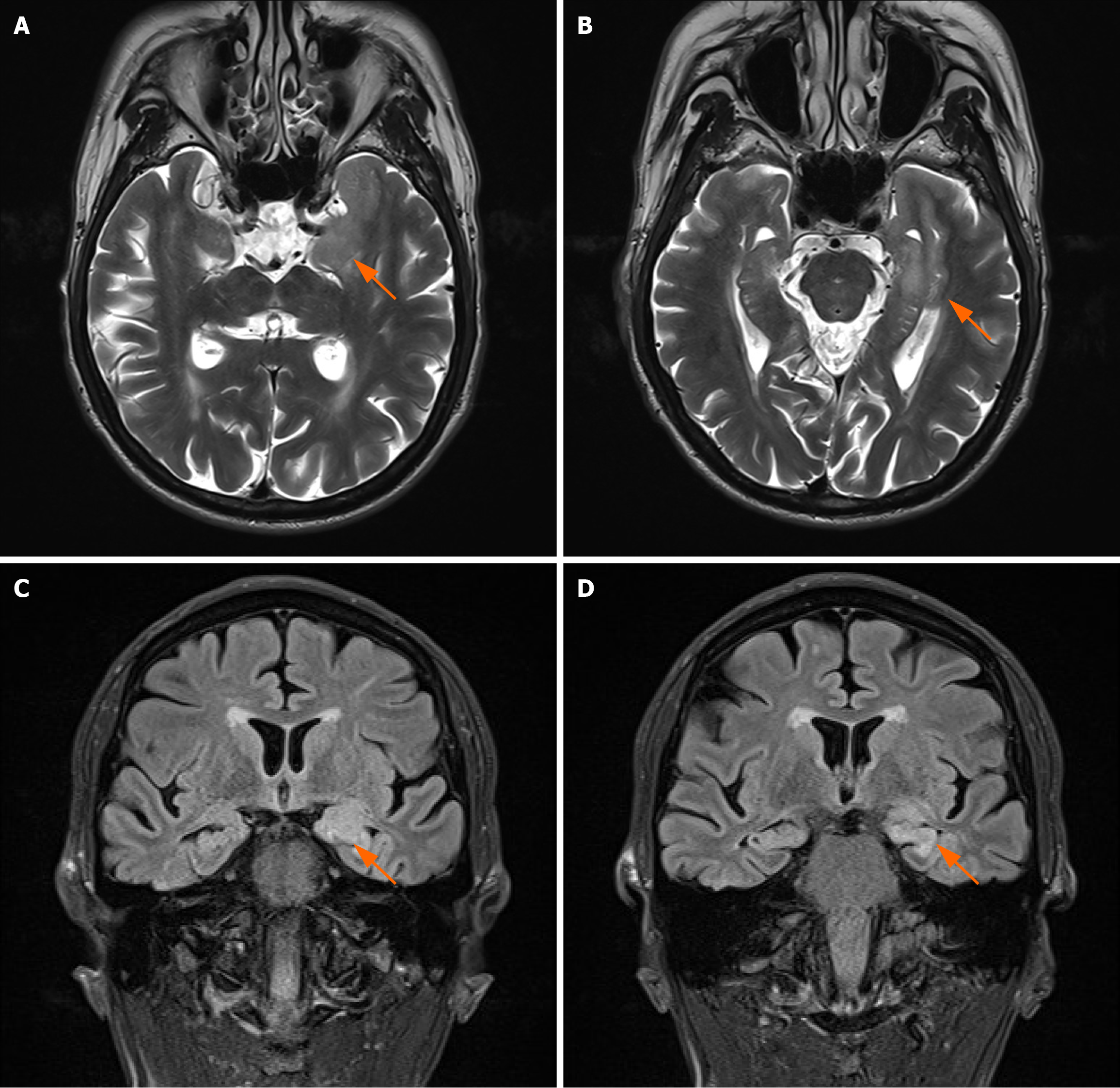
Figure 1 Magnetic resonance imaging scan of the patient’s brain.
A and B: T2-weighted imaging axial image; C and D: T2 fluid attenuated inversion recovery coronal image. It can be seen that the T2 fluid attenuated inversion recovery signal in both hippocampi is increased, with a more significant increase on the left side, indicating that hippocampal sclerosis may be present.
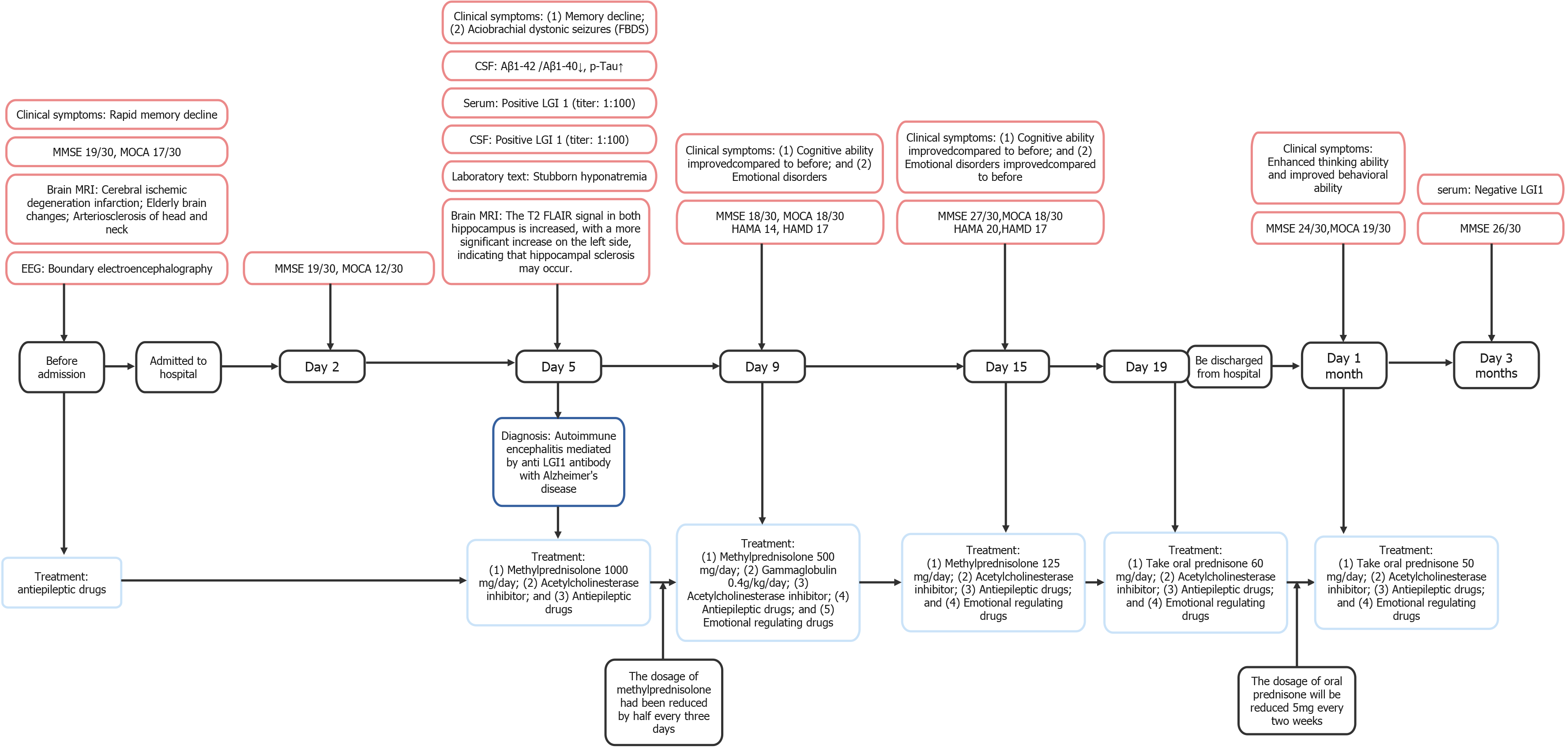
Figure 2 The timeline of relevant results and interventions during the diagnosis and treatment of this patient.
MMSE: Mini mental state examination; MOCA: Montreal cognitive assessment; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; EEG: Electroencephalogram; CSF: Cerebrospinal fluid; Aβ: Amyloid β-protein; FBDS: Faciobrachial dystonic seizure; Tau: Micro tubule-associated protein; LGI1: Leucine-rich glioma inactivated 1; FLAIR: Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery; HAMA: Hamilton anxiety scale; HAMD: Hamilton depression scale.
- Citation: Chen XH, Xia W, Ma JB, Chen J, Hu J, Shi X, Yu JJ, Gong J, Liu L, Sun YA, Liu ZG. Rare mixed dementia: A case report. World J Radiol 2025; 17(1): 102579
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v17/i1/102579.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v17.i1.102579