©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Radiol. Oct 28, 2024; 16(10): 621-628
Published online Oct 28, 2024. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v16.i10.621
Published online Oct 28, 2024. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v16.i10.621
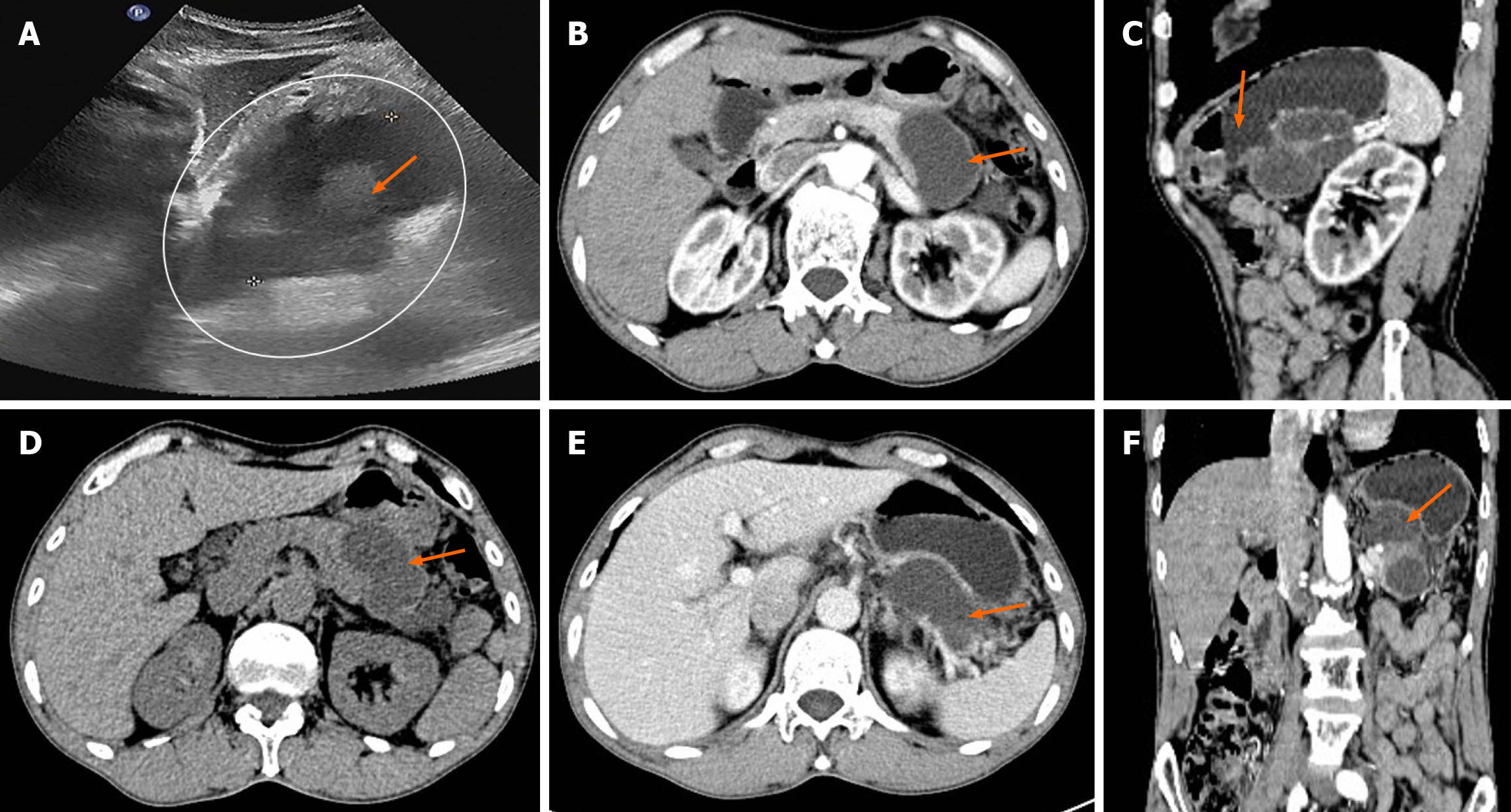
Figure 1 Preoperative ultrasound and computed tomography imaging results.
A: Ultrasound imaging showed that the cystic lesion of the body and tail of the pancreas (within the ellipse) was irregular and heterogeneous hypoechoic (shown by the arrow); B: On the non-enhanced axial image, the low-density cystic mass (indicated by the arrow) in the tail of the pancreas protruding outside the outline; C: On the axial image in the arterial phase of contrast enhanced scan, the cystic mass (indicated by the arrow) does not communicate with the main pancreatic duct and the cyst wall is not exactly enhanced; D: On the axial image of the portal vein phase of contrast enhanced scan, the cystic mass (arrow) compresses the posterior wall of the gastric body and is not clearly separated from the blood vessels of the spleen; E: On the sagittal images of the arterial phase of contrast enhanced scan, the cystic mass surrounds the splenic vessels and narrows its lumen (as indicated by the arrow); F: The shape of the cystic mass on the coronal image of the arterial phase is irregular (indicated by the arrow).
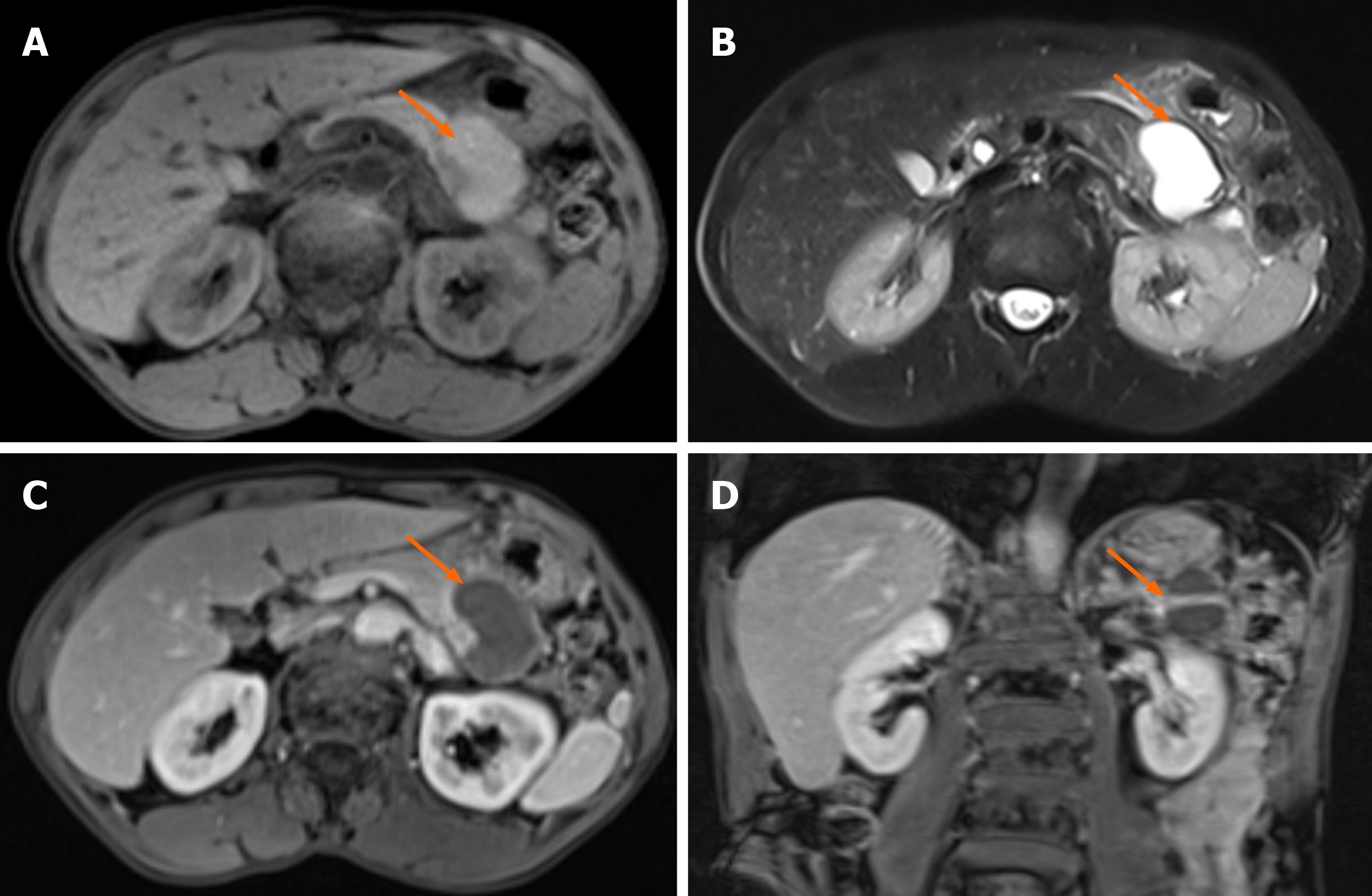
Figure 2 Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging results.
A: The cystic lesions (arrow) showed high signal intensity in the cyst and low signal intensity in the cyst wall on the T1-weighted axial images; B: The cystic lesions (arrow) showed obvious high signal intensity and the cystic wall showed low signal intensity on the T2-weighted axial images; C: Contrast-enhanced axial images showed enhancement of the cyst wall (arrow); D: The shape of the cyst (arrow) was irregular and the cyst wall was enhanced on the contrast-enhanced coronal images.
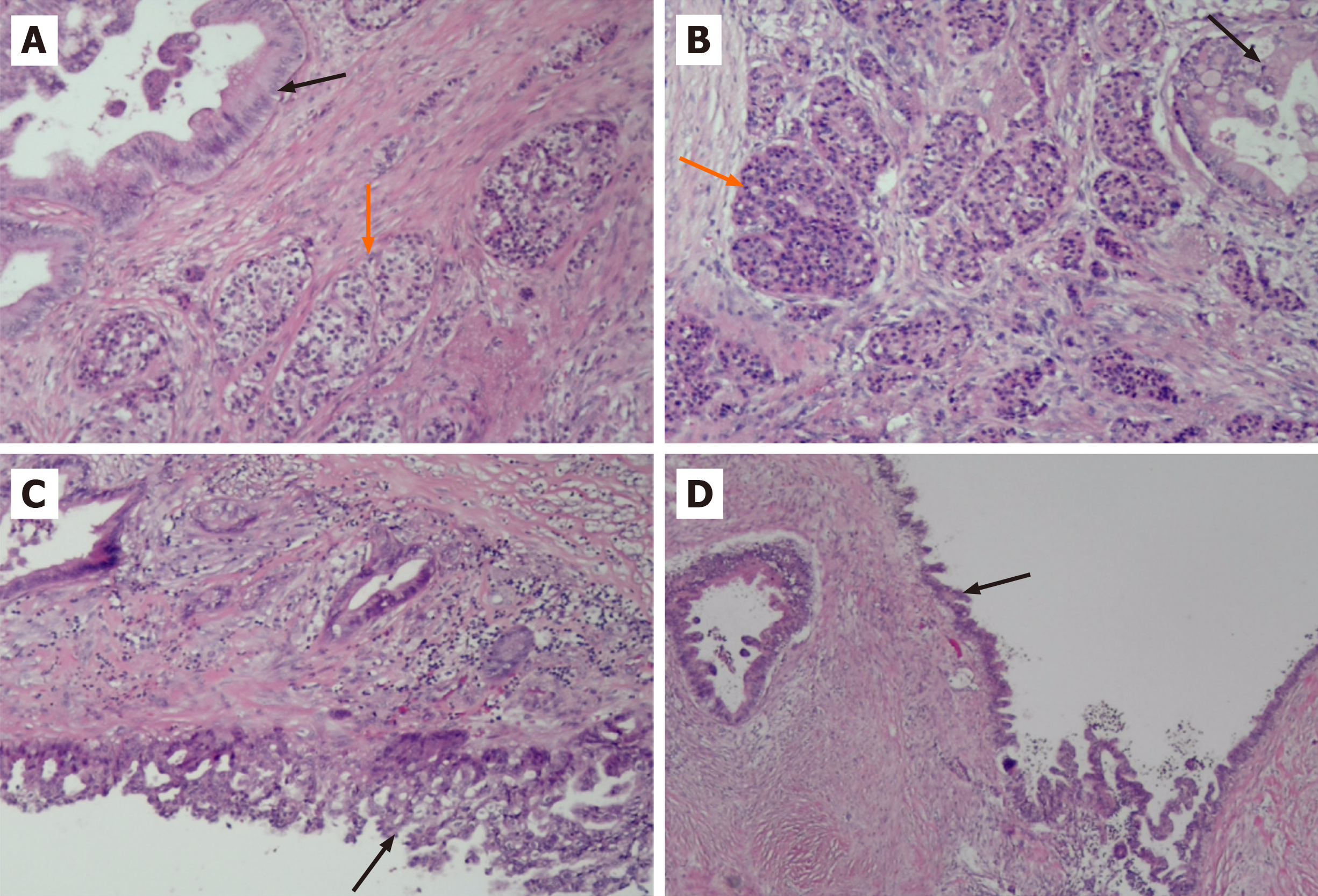
Figure 3 Ductal adenocarcinoma with neuroendocrine tumor.
A and B: The black arrow indicates ductal adenocarcinoma and the orange arrow indicates neuroendocrine tumor. H&E staining, magnification, ×100; C and D: The black arrow indicates the atypical epithelial cells lined with the cyst wall. H&E staining, magnification, x100.
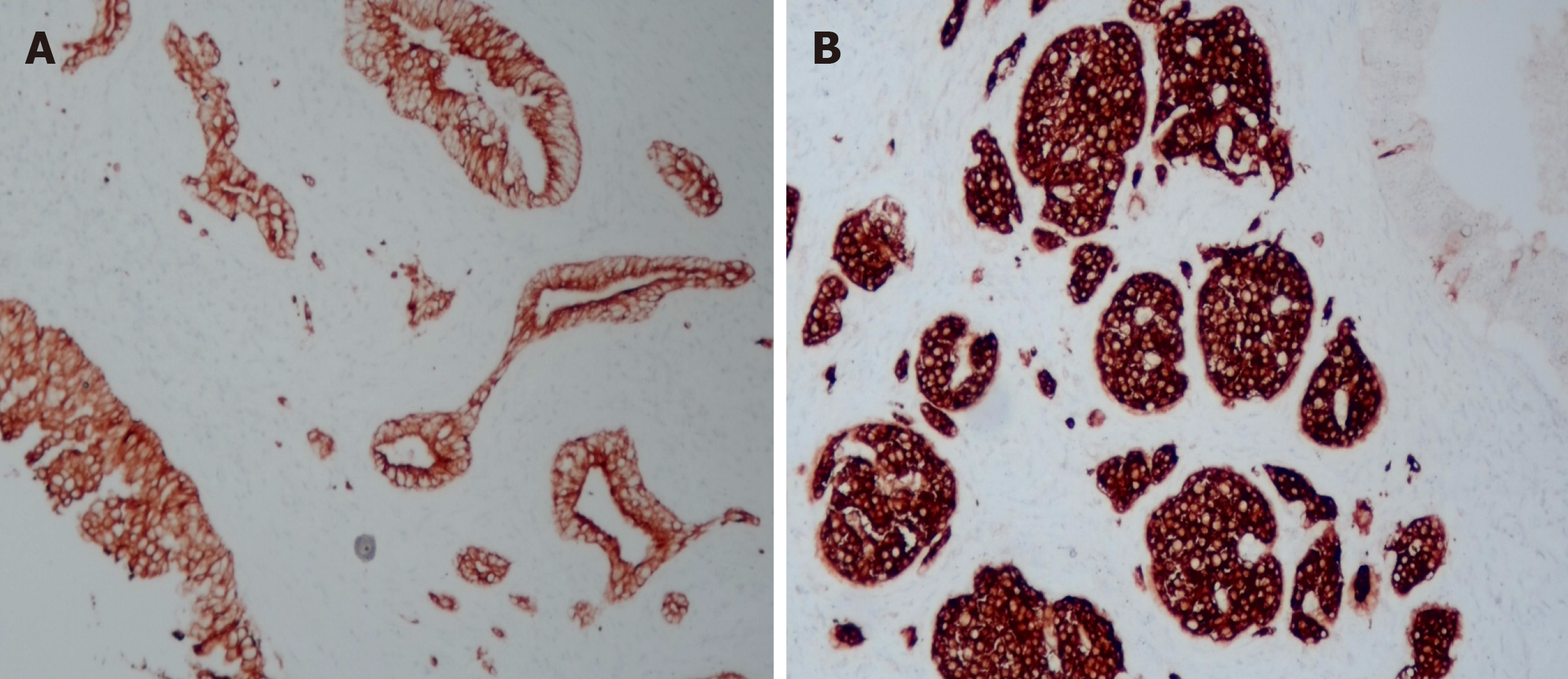
Figure 4 Immunohistochemistry results.
A: Cytokeratin 8 immunohistochemical staining was positive as a marker of glandular epithelium in ductal adenocarcinoma. Magnification, ×200; B: As a neuroendocrine tumor marker, synaptophysin was positive in immunohistochemical staining. Magnification, ×200.
- Citation: Zou DM, Shu ZY, Cao X. Cystic ductal adenocarcinoma of pancreas complicated with neuroendocrine tumor: A case report and review of literature. World J Radiol 2024; 16(10): 621-628
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v16/i10/621.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v16.i10.621