©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Radiol. Mar 28, 2021; 13(3): 64-74
Published online Mar 28, 2021. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v13.i3.64
Published online Mar 28, 2021. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v13.i3.64
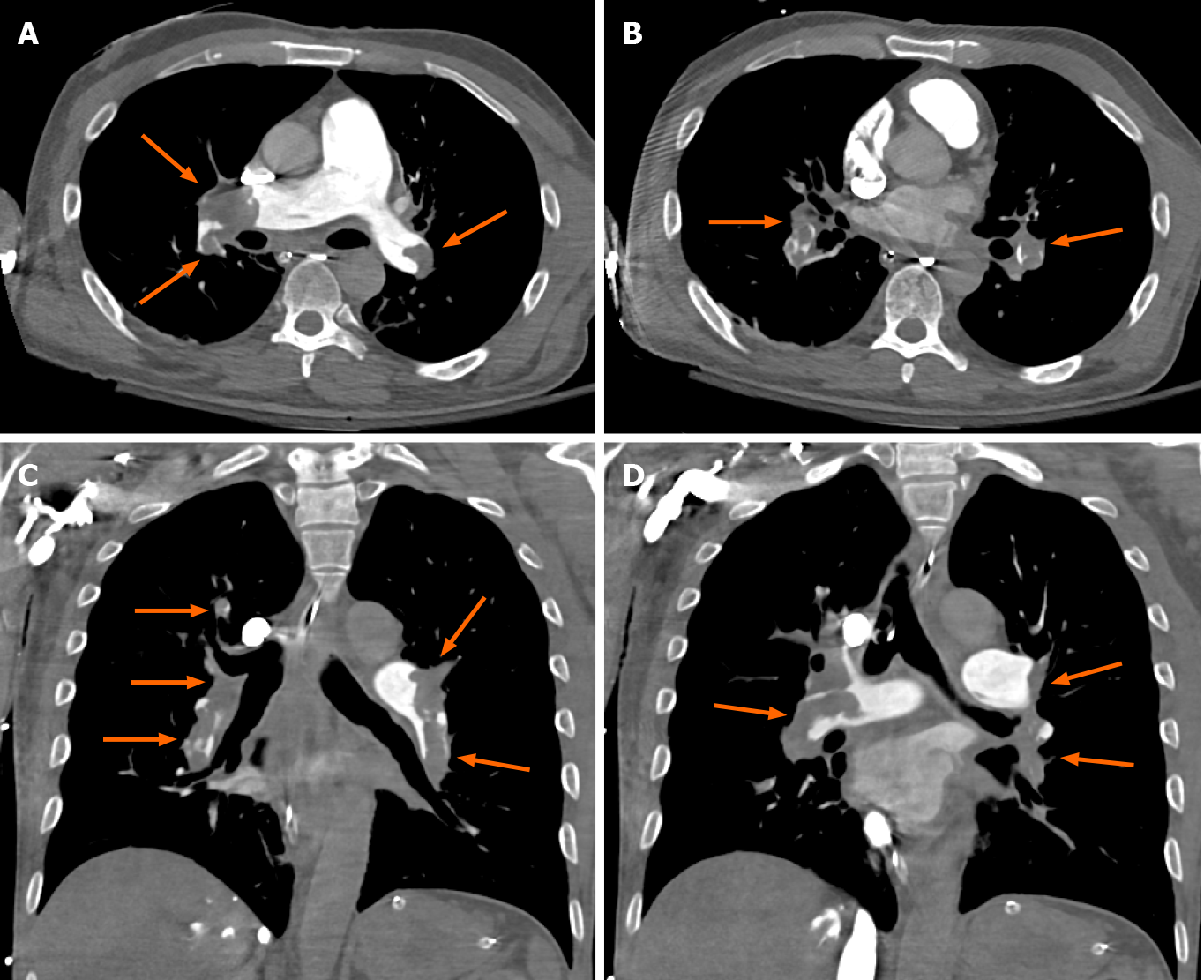
Figure 1 Computed tomography angiography images.
A and B: Chest axial views; C and D: Chest coronal views. Computed tomography angiography chest axial and coronal views soft tissue window shows large hypodense filling defects in distal right and left main pulmonary arteries and all segmental pulmonary branches in both lungs (orange arrows) in a 58-year male patient with shortness of breath. Findings are compatible with bilateral extensive pulmonary embolisms.
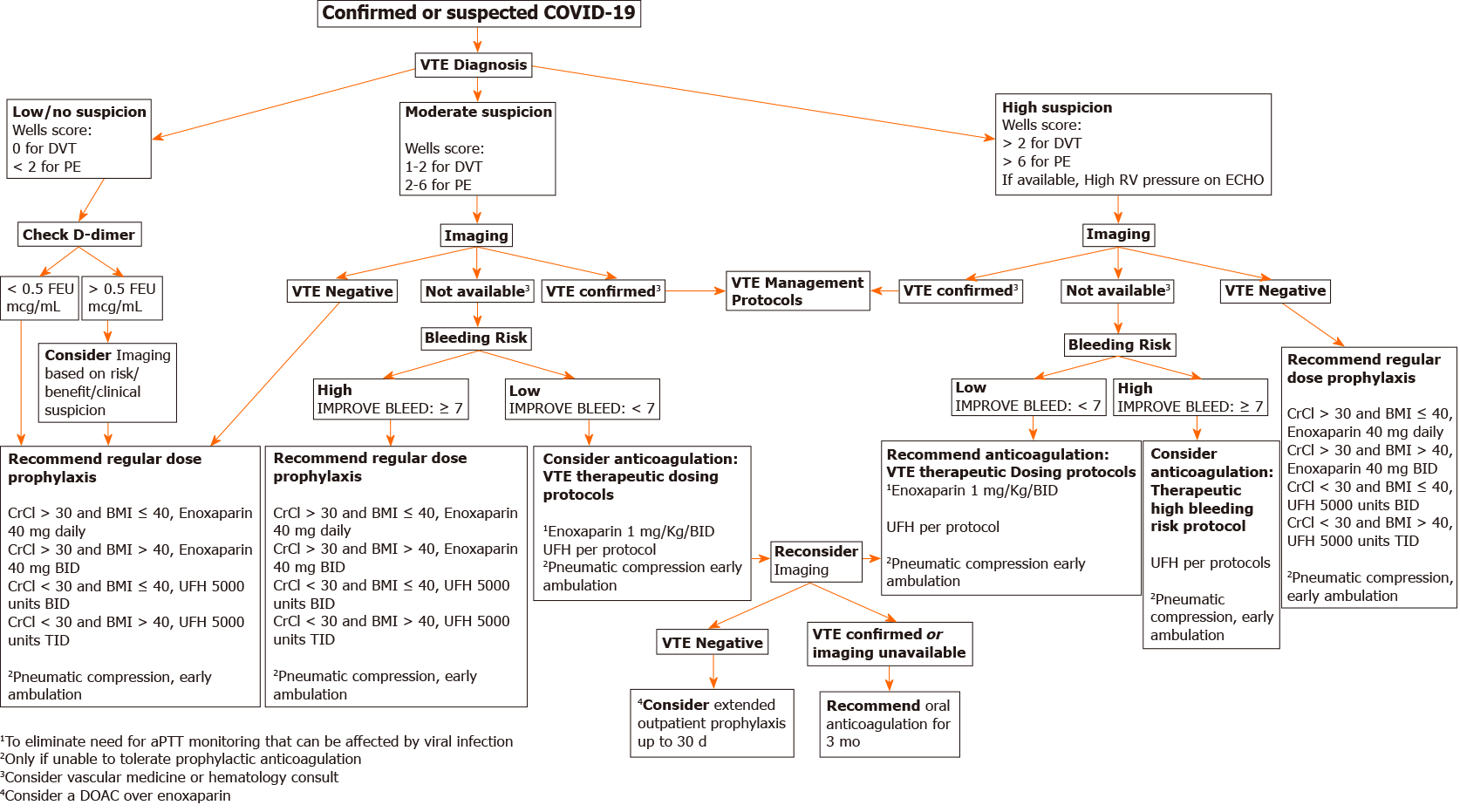
Figure 2 Diagnosis and management of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease-2019.
COVID-19: Coronavirus disease-2019; DVT: Deep vein thrombosis; PE: Pulmonary embolism; VTE: Venous thromboembolism.
- Citation: Patel L, Gandhi D, Westergard E, Ornes M, Lillyblad M, Skeik N. COVID-19 and venous thromboembolism: Known and unknown for imaging decisions. World J Radiol 2021; 13(3): 64-74
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v13/i3/64.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v13.i3.64