©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Radiol. Dec 28, 2020; 12(12): 302-315
Published online Dec 28, 2020. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v12.i12.302
Published online Dec 28, 2020. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v12.i12.302
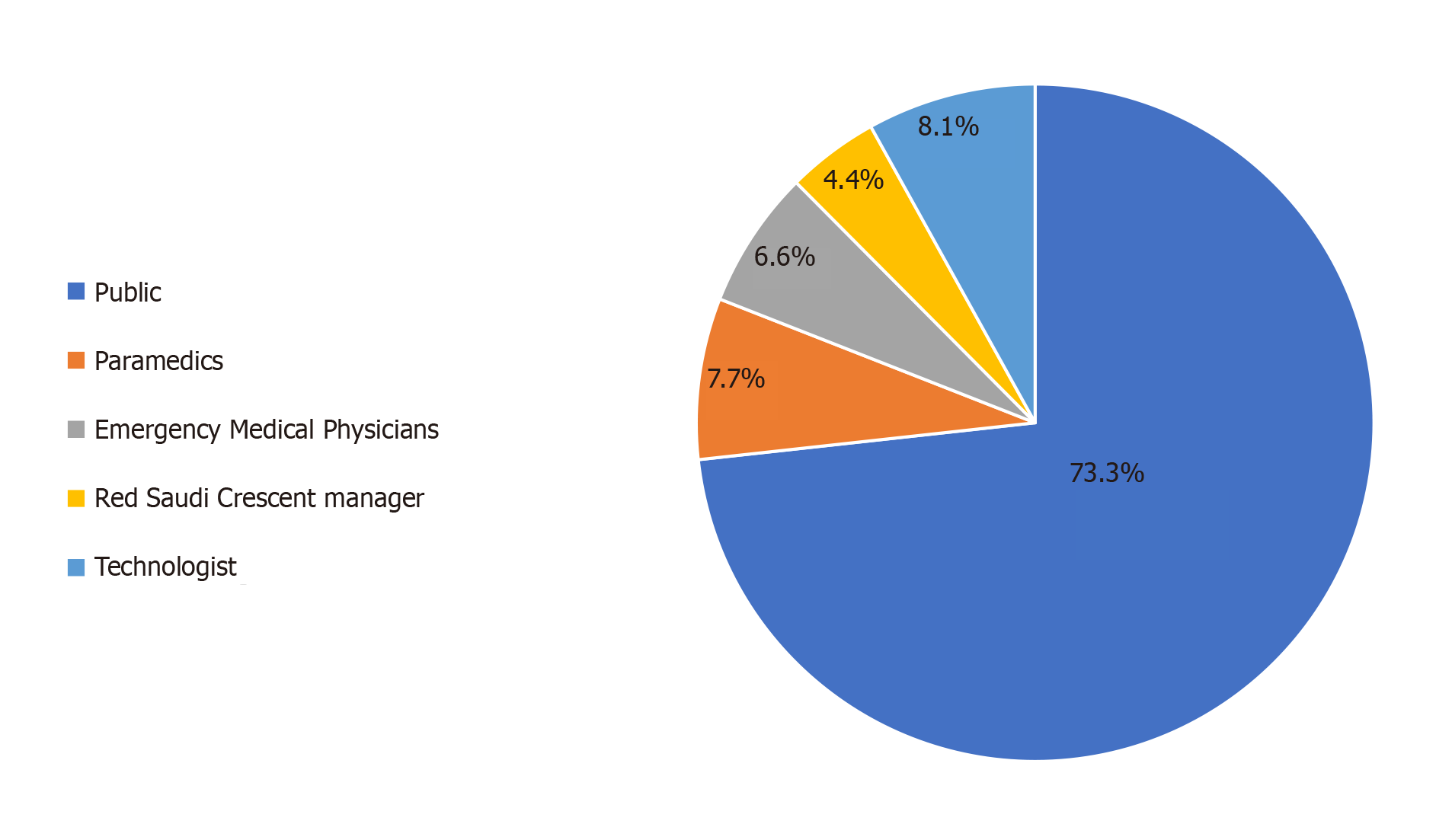
Figure 1 Distribution of study sample.
Figure 2 Knowledge on ultrasound.
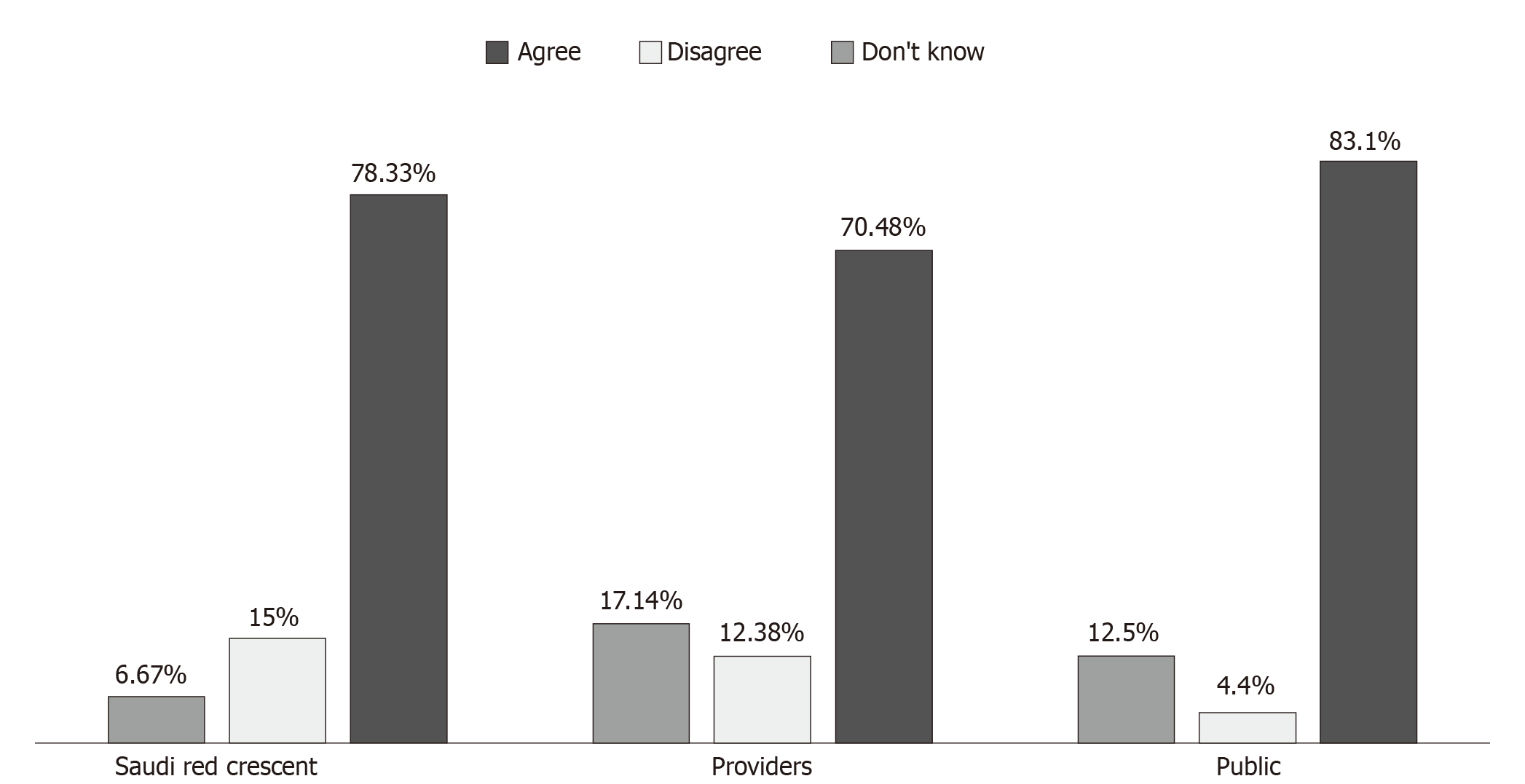
Figure 3 Opinion on the inclusion of an ultrasound device in an ambulance.
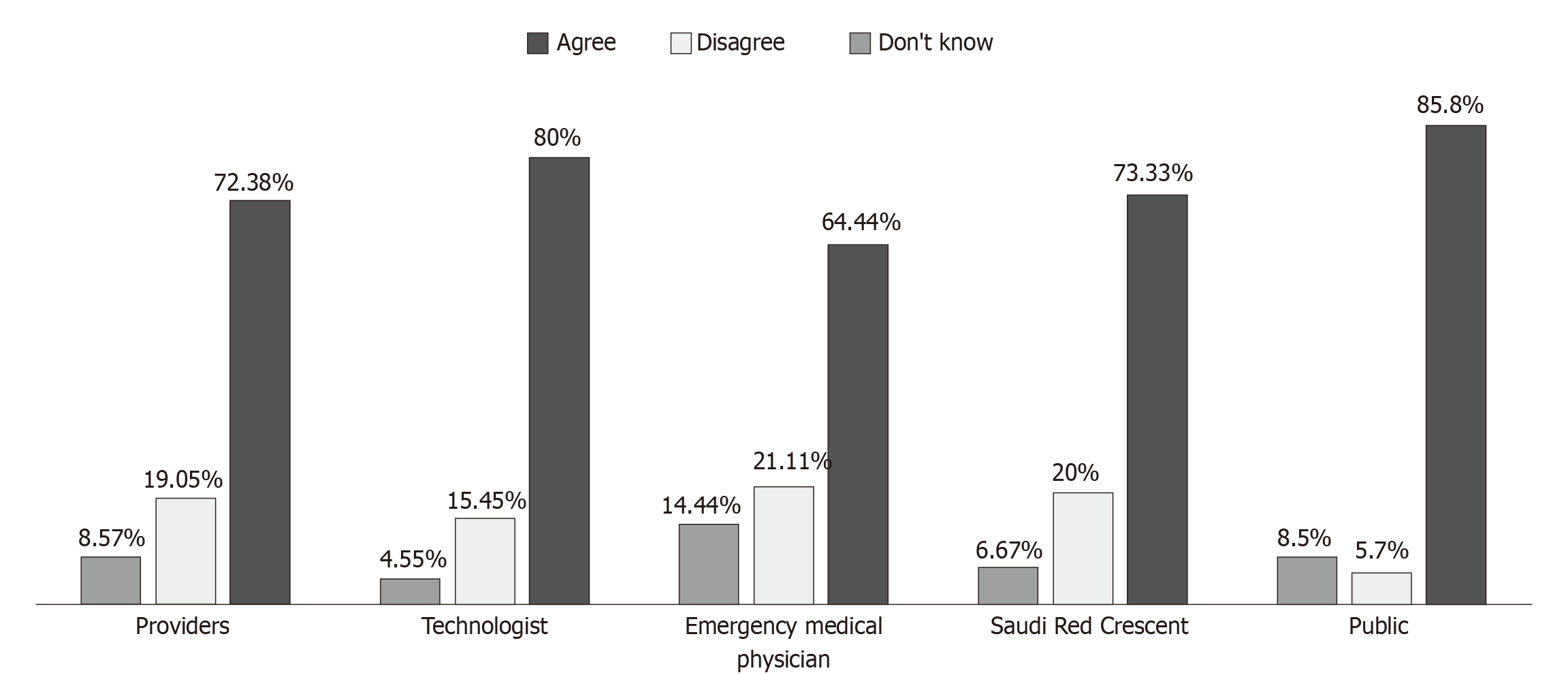
Figure 4 Diagram of the importance of providing ultrasound courses for paramedics and the presence of a sonographer in the ambulance.
A: The importance of providing ultrasound courses for paramedics; B: The importance of the presence of a sonographer in the ambulance.
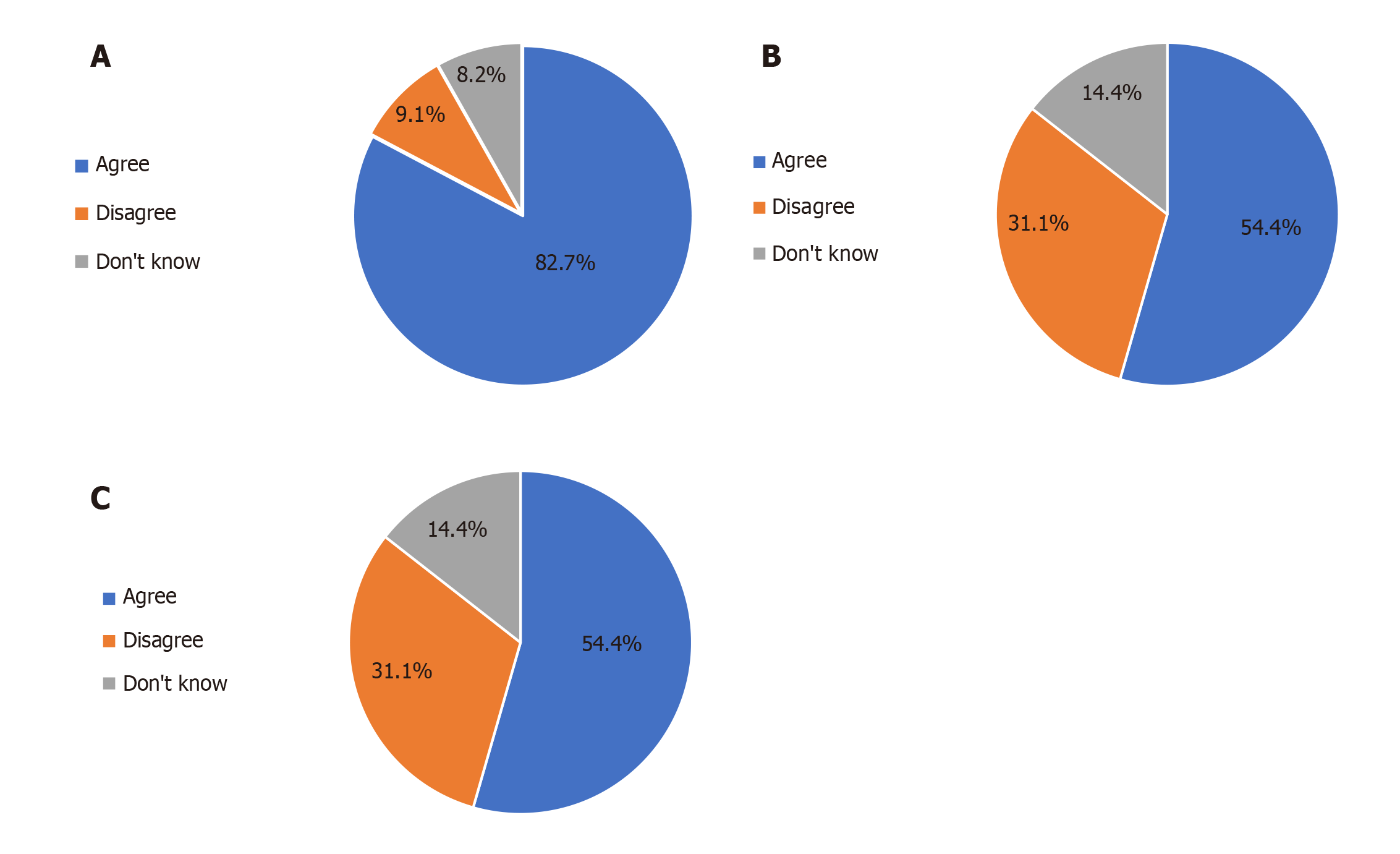
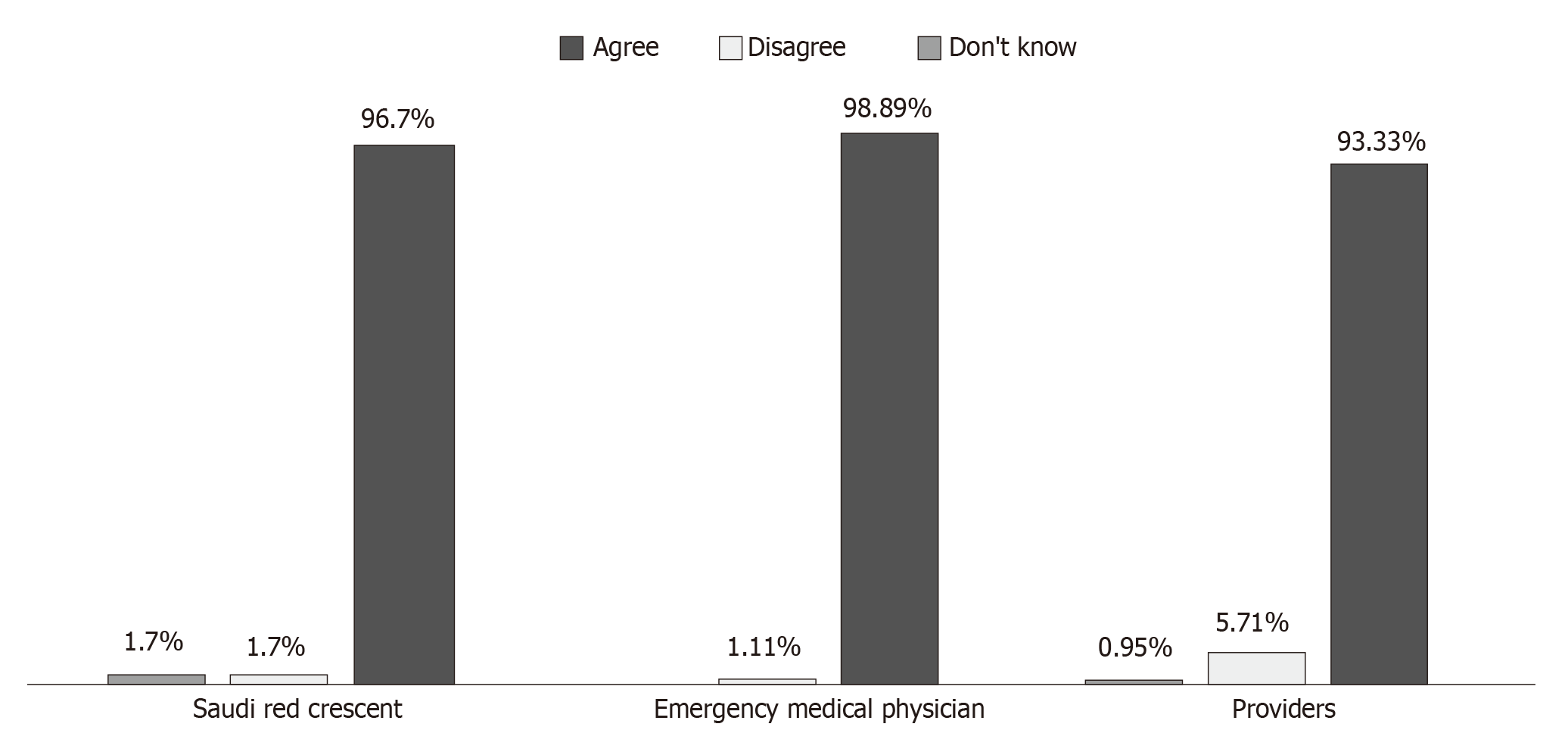
Figure 5 Diagram of sonographers and physicians opinions.
A: Sonographers opinions on paramedic ultrasound training; B: Physicians opinions on the presence of ultrasound devices in ambulances; and C: The dependence of emergency physicians on the report by trained paramedics or sonographers.
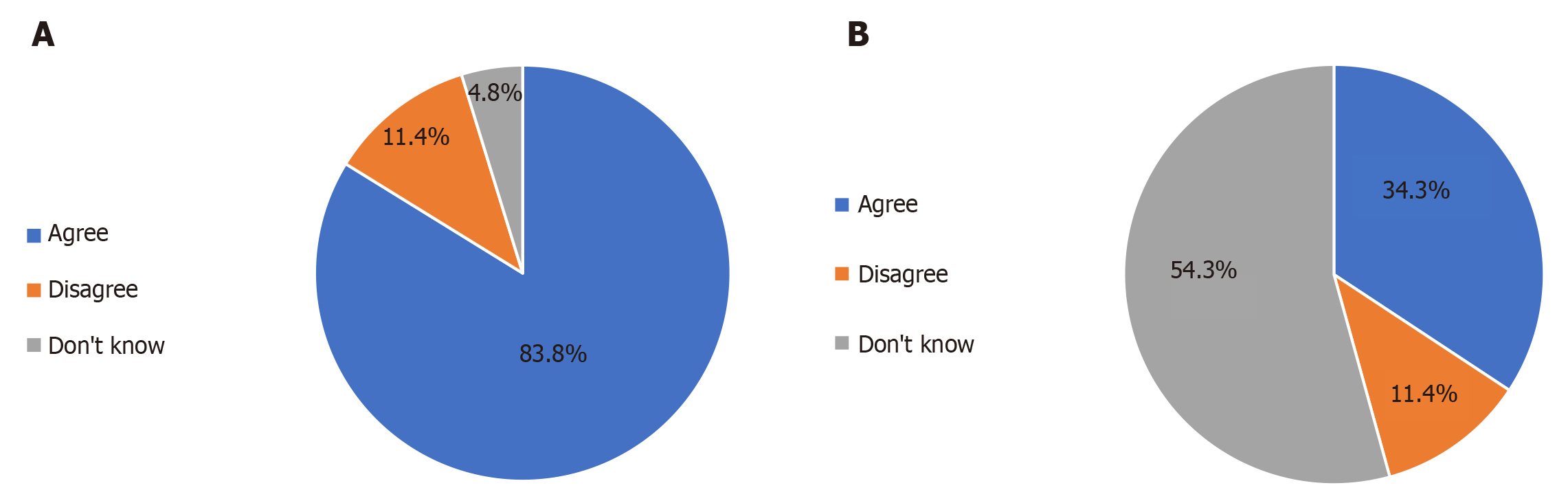
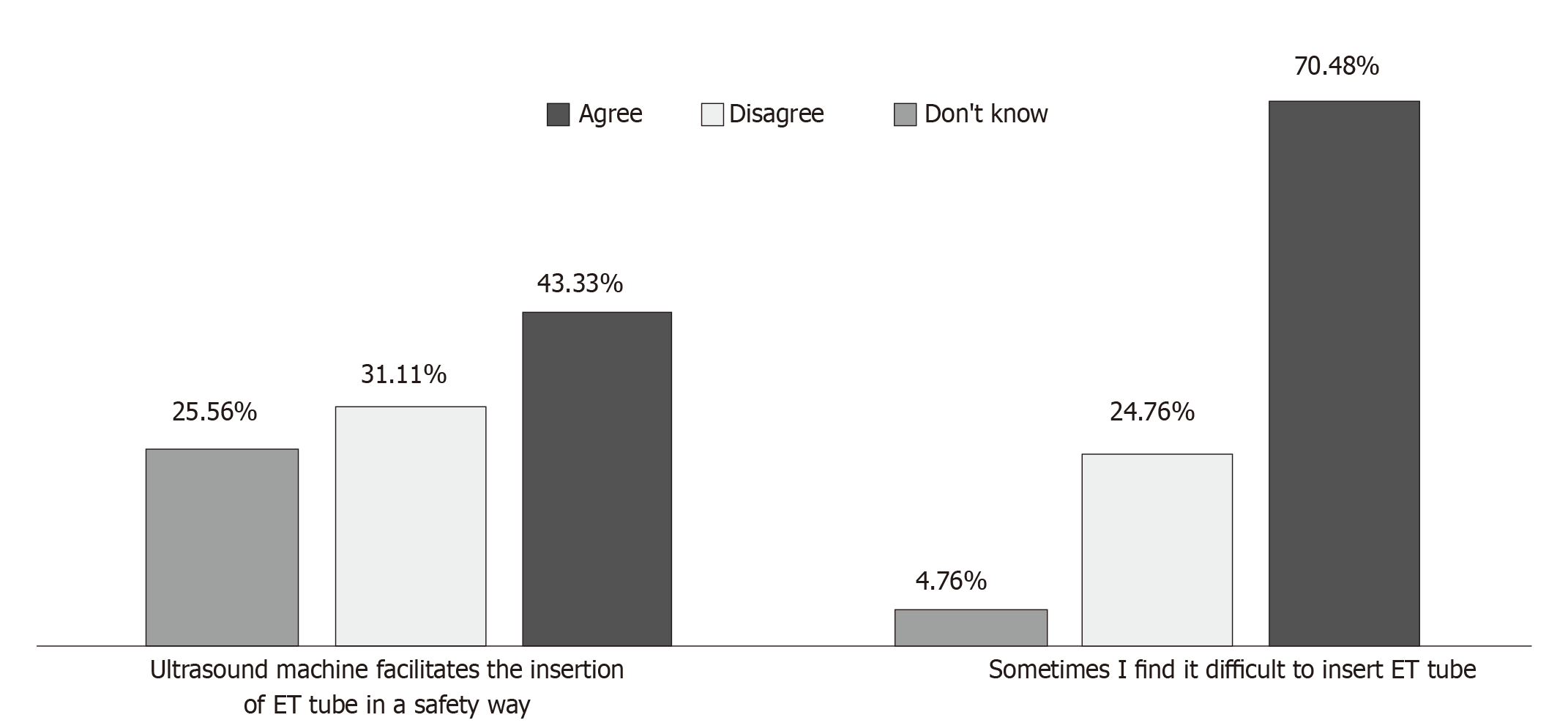
Figure 6 Endotracheal tube insertion.
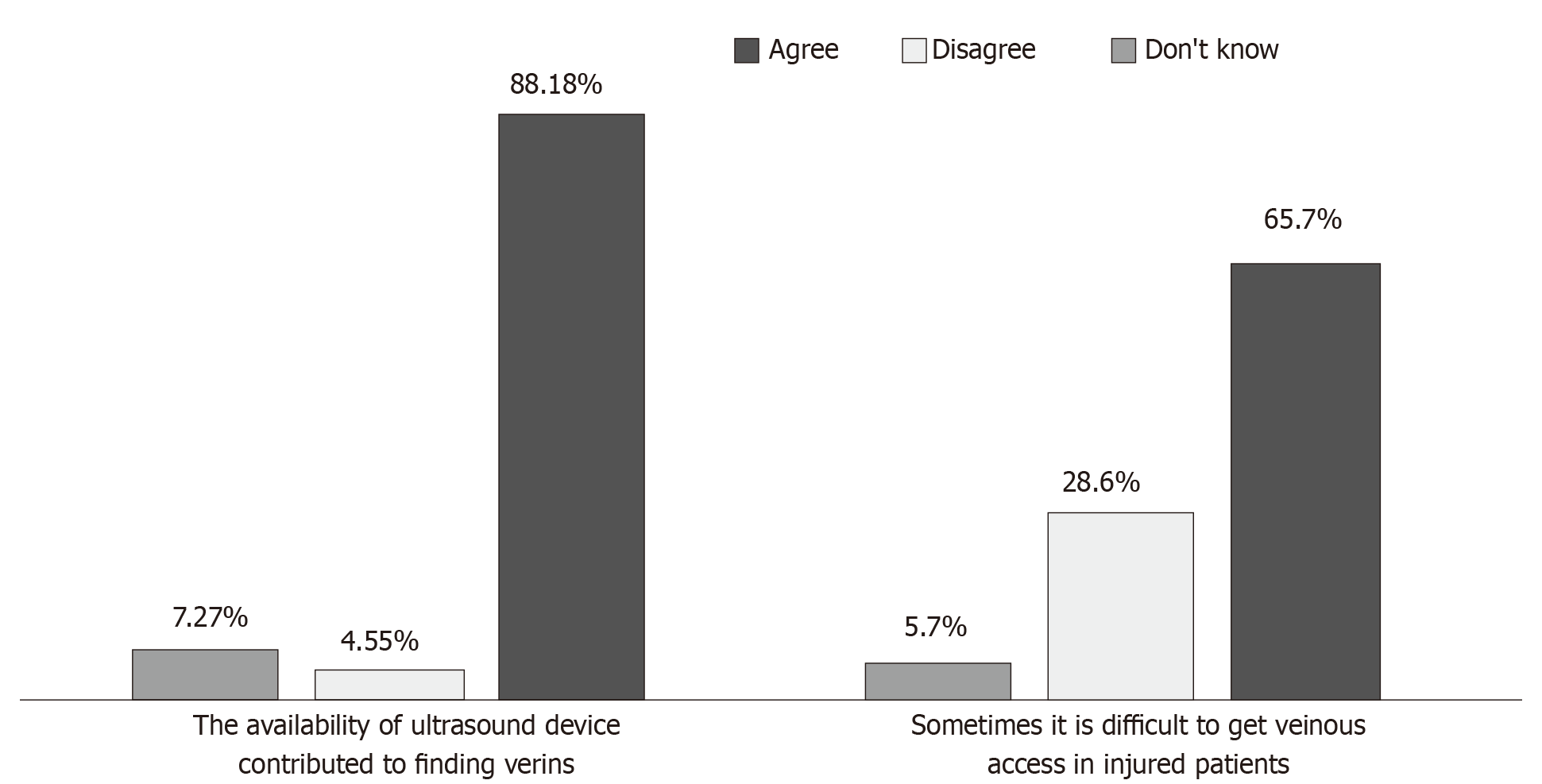
Figure 7 Venous access.
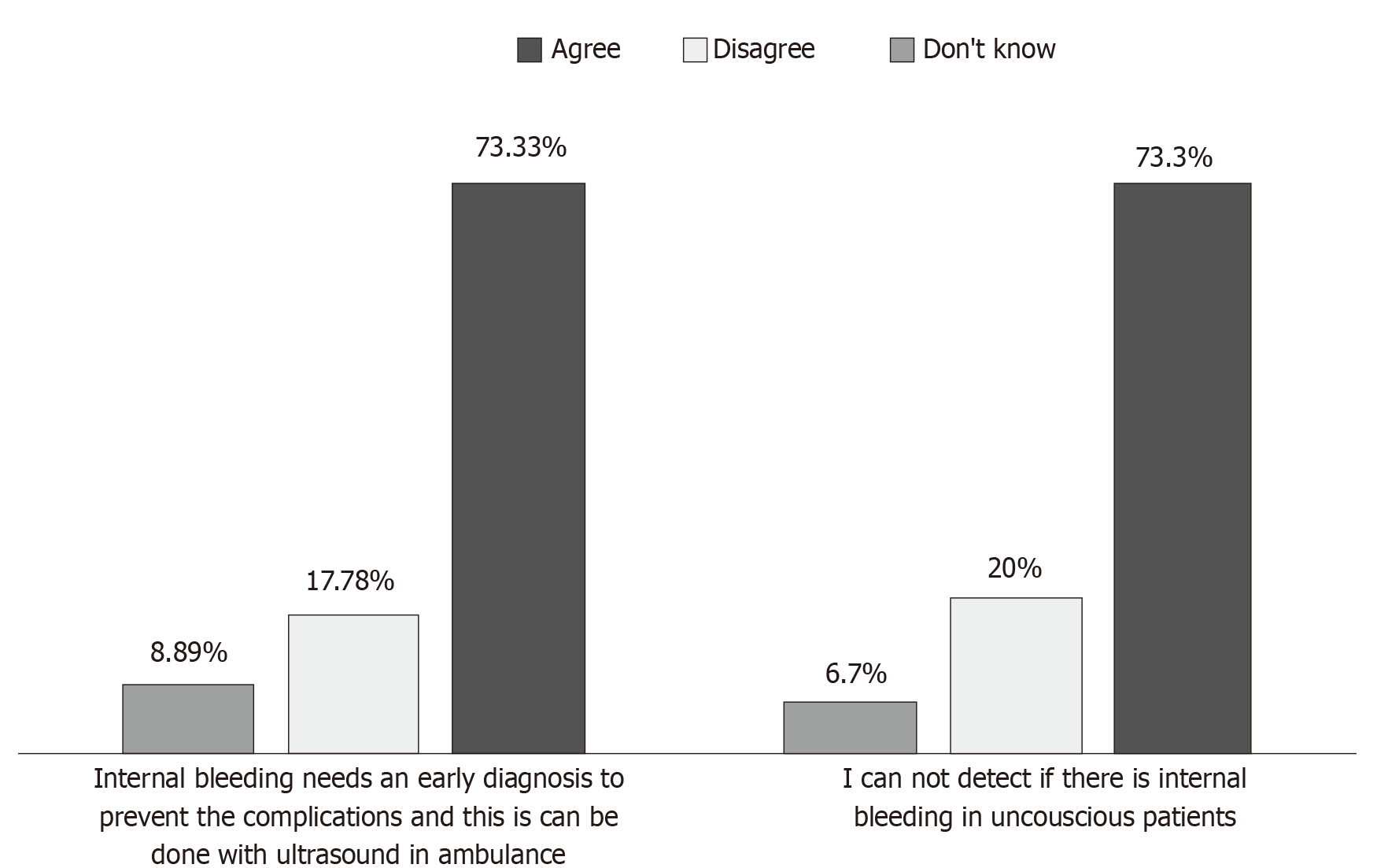
Figure 8 Internal bleeding.
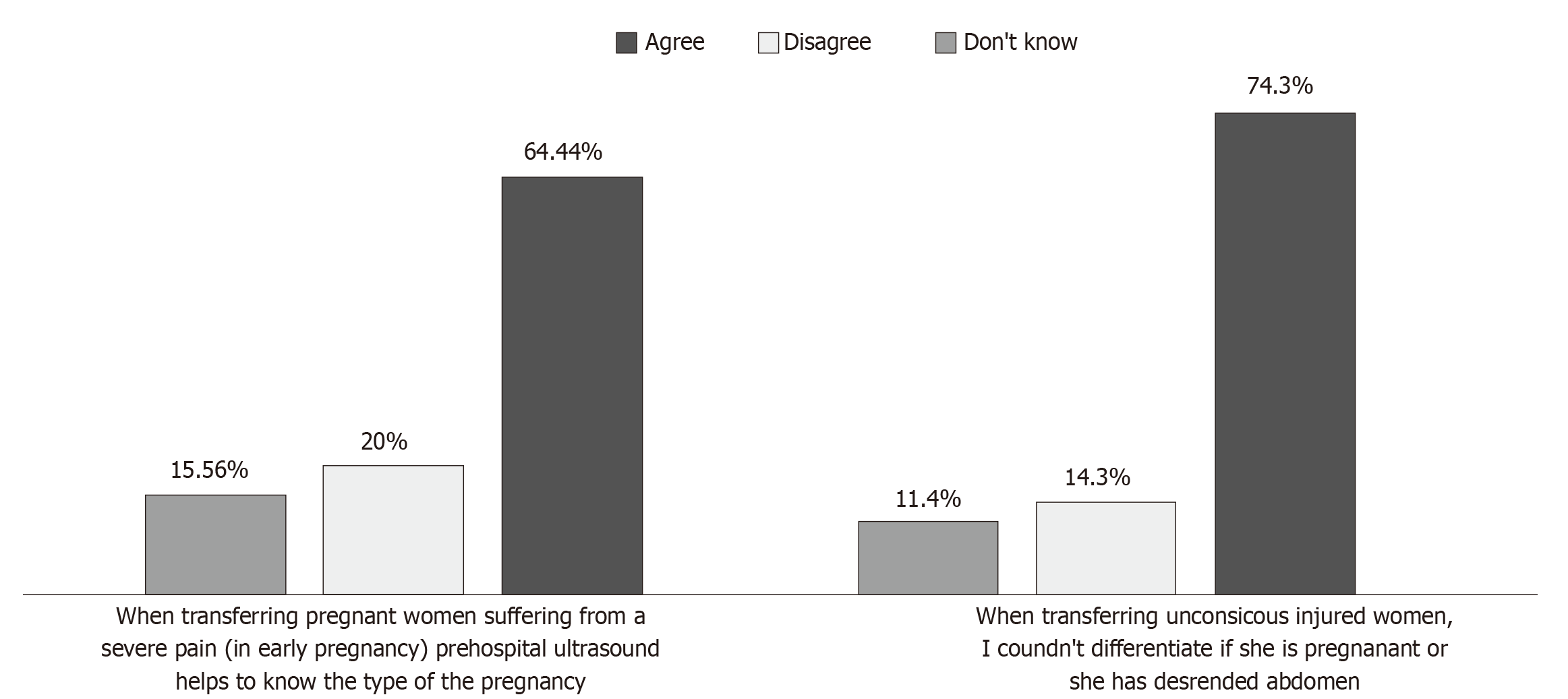
Figure 9 Pregnancy status.
Figure 10 Communication between ambulances and emergency departments.
- Citation: Abbas I, Shakhreet BZ, Alghamdi A, Wali B, Alelyani B, Alshehri T. Feasibility of using ultrasound in ambulances in Saudi Arabia. World J Radiol 2020; 12(12): 302-315
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v12/i12/302.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v12.i12.302