©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Cardiol. Apr 26, 2025; 17(4): 105021
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i4.105021
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i4.105021
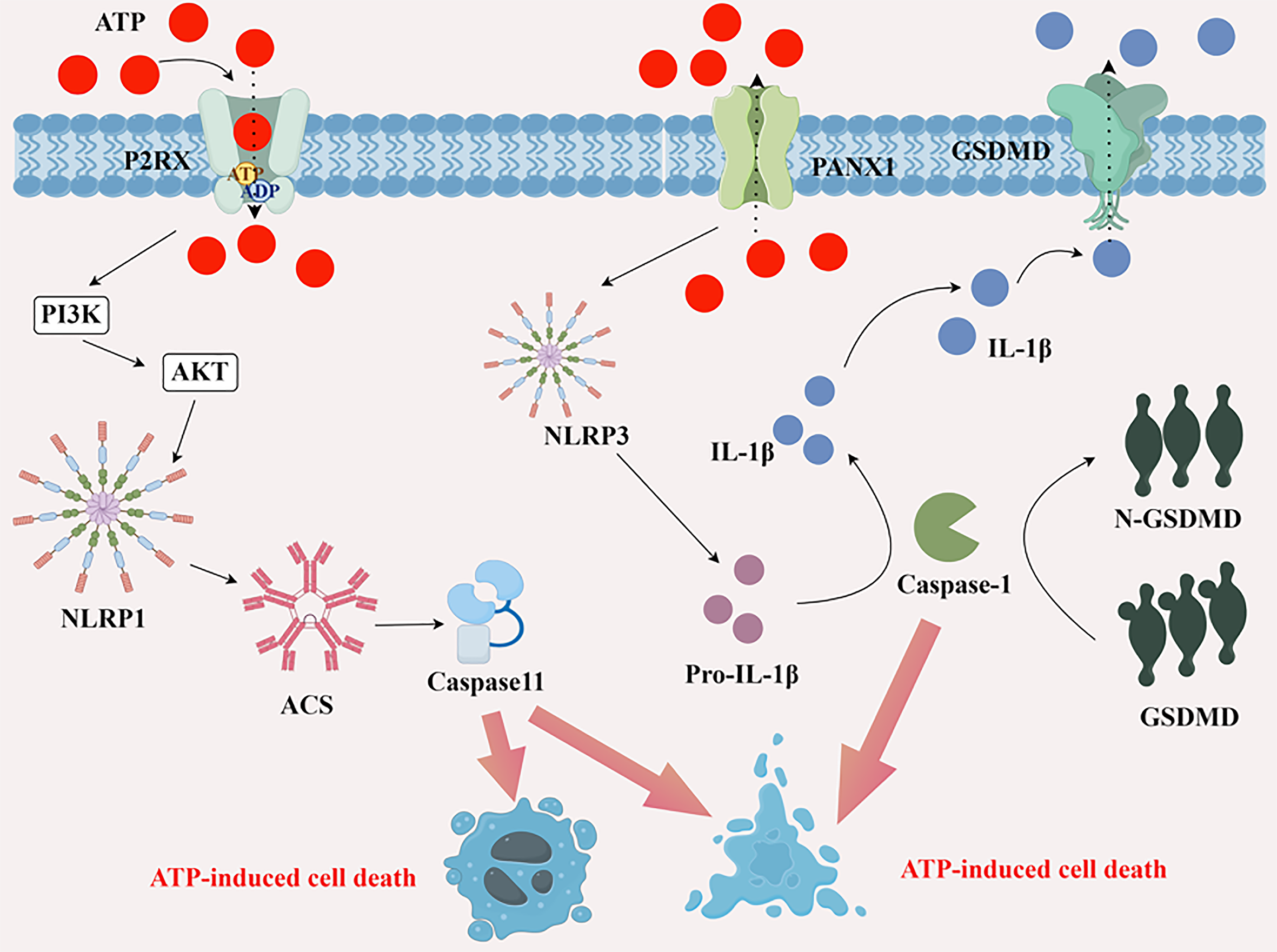
Figure 1 P2 receptor activation pathway.
ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; ADP: Adenosine diphosphate; P2RX: Purinoceptor receptor P2X; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; NLRP1: NLR family pyrin domain-containing protein 1; IL-1β: Interleukin-1 beta; Pro-IL-1β: Pro-forms of Interleukin-1 beta; PANX1: Pannexin 1; N-GSDMD: N-Gasdermin D; GSDMD: Gasdermin D. Drawn by Figdraw.
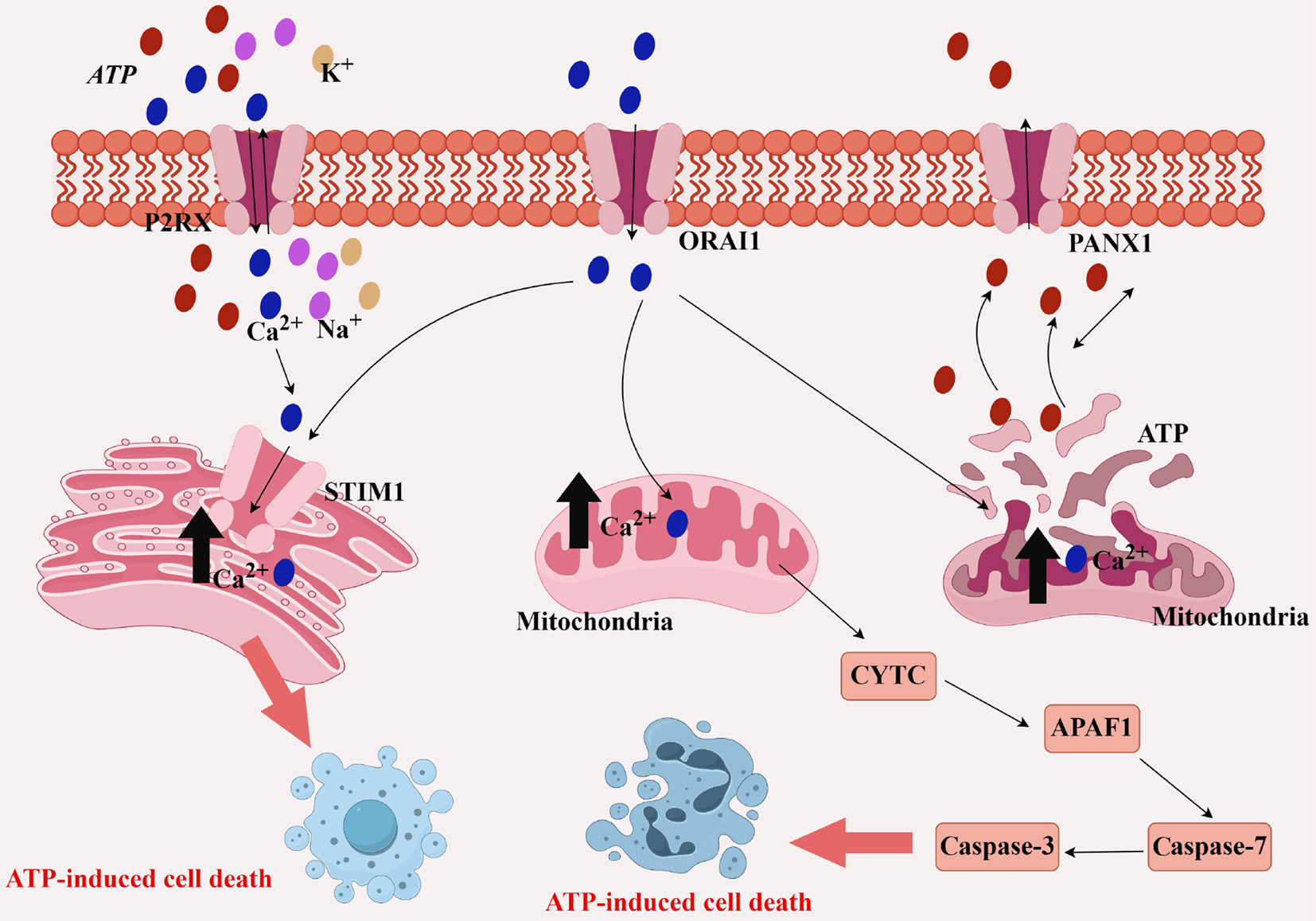
Figure 2 Ca2+ pathway induces cell death pathways.
ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; P2RX: Purinoceptor receptor P2X; ORAI1: Calcium release-activated calcium channel protein 1; PANX1: Pannexin 1; STIM1: Stromal interaction molecule 1; CYTC: Cytochrome C; APAF1: Apoptotic protease-activating factor 1. Drawn by Figdraw.
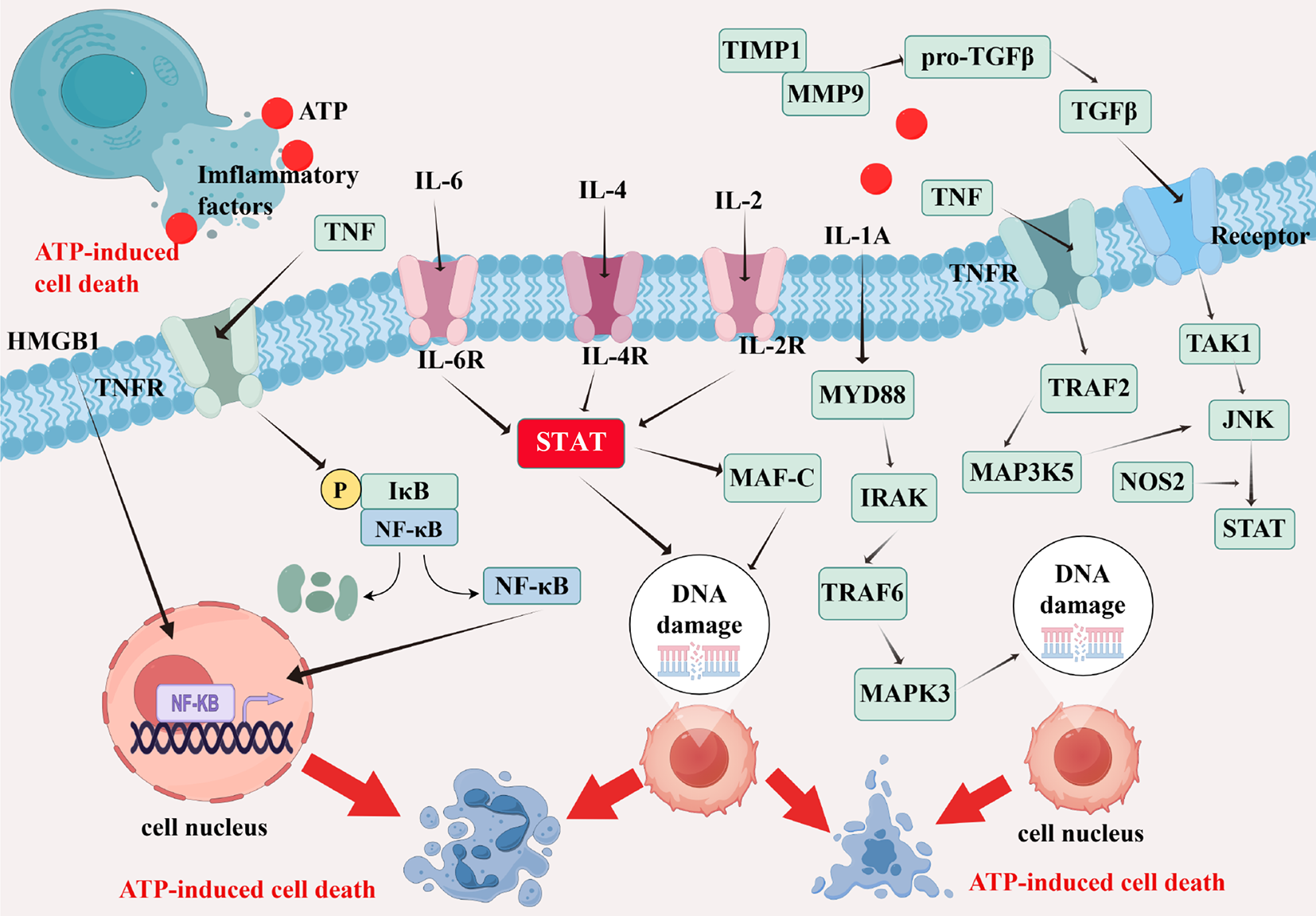
Figure 3 Adenosine triphosphate triggers the release of immune-inflammatory factors from cells, activating immune pathways.
ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; HMGB1: High mobility group box-1 protein; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor ; TNFR: Tumor necrosis factor receptor; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; IκB: I kappa B; DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-6R: Interleukin-6 receptor; IL-4: Interleukin-4; IL-4R: Interleukin-4 receptor; IL-2: Interleukin-2; IL-2R: Interleukin-2 receptor; IL-1A: Interleukin-1a; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; MAF-C: Musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene; MYD88: The canonical adaptor for inflammatory signaling pathways downstream of members of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) and interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor families; IRAK: IL-1R-associated kinase; TRAF6: TNF receptor associated factor 6; MAPK3: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3; TRAF2: TNF receptor associated factor 2; MAP3K5: Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 5; TIMP1: The tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1; MMP9: Matrix metallopeptidase 9; pro-TGFβ: Pro-transforming growth factor-beta; TAK1: Transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1; JNK: C-Jun N-terminal kinase; NOS2: Nitric oxide synthase. Drawn by Figdraw.
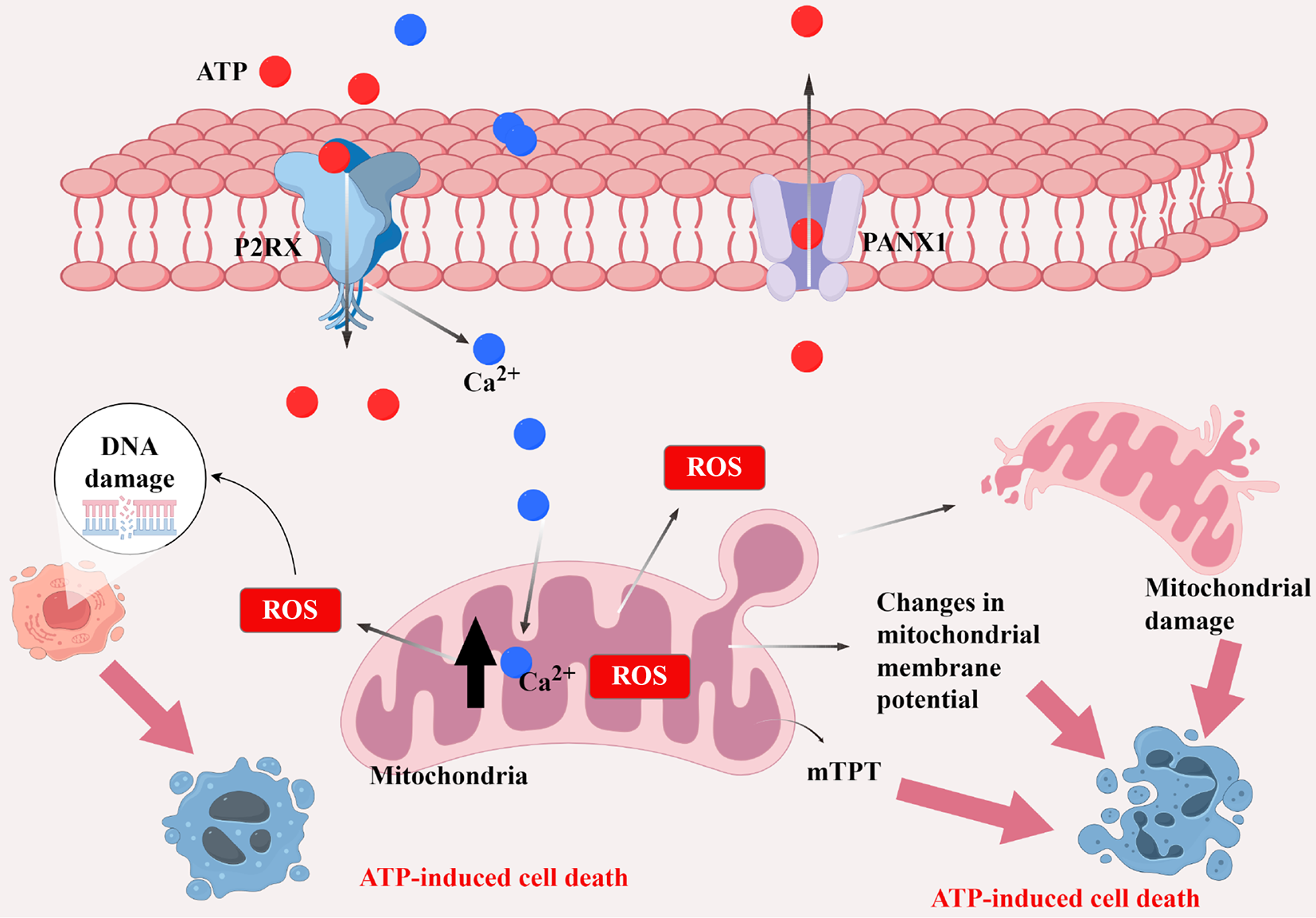
Figure 4 Adenosine triphosphate causes the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, the disruption of mitochondrial integrity, the production of reactive oxygen species and alterations in mitochondrial membrane permeability, collectively leading to cell deaths.
ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; P2RX: Purinoceptor receptor P2X; PANX1: Pannexin 1; DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; mPTP: Mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Drawn by Figdraw.
- Citation: Zhang JJ, Cheng L, Qiao Q, Xiao XL, Lin SJ, He YF, Sha RL, Sha J, Ma Y, Zhang HL, Ye XR. Adenosine triphosphate-induced cell death in heart failure: Is there a link? World J Cardiol 2025; 17(4): 105021
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v17/i4/105021.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v17.i4.105021