©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Cardiol. Oct 26, 2025; 17(10): 111462
Published online Oct 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i10.111462
Published online Oct 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i10.111462
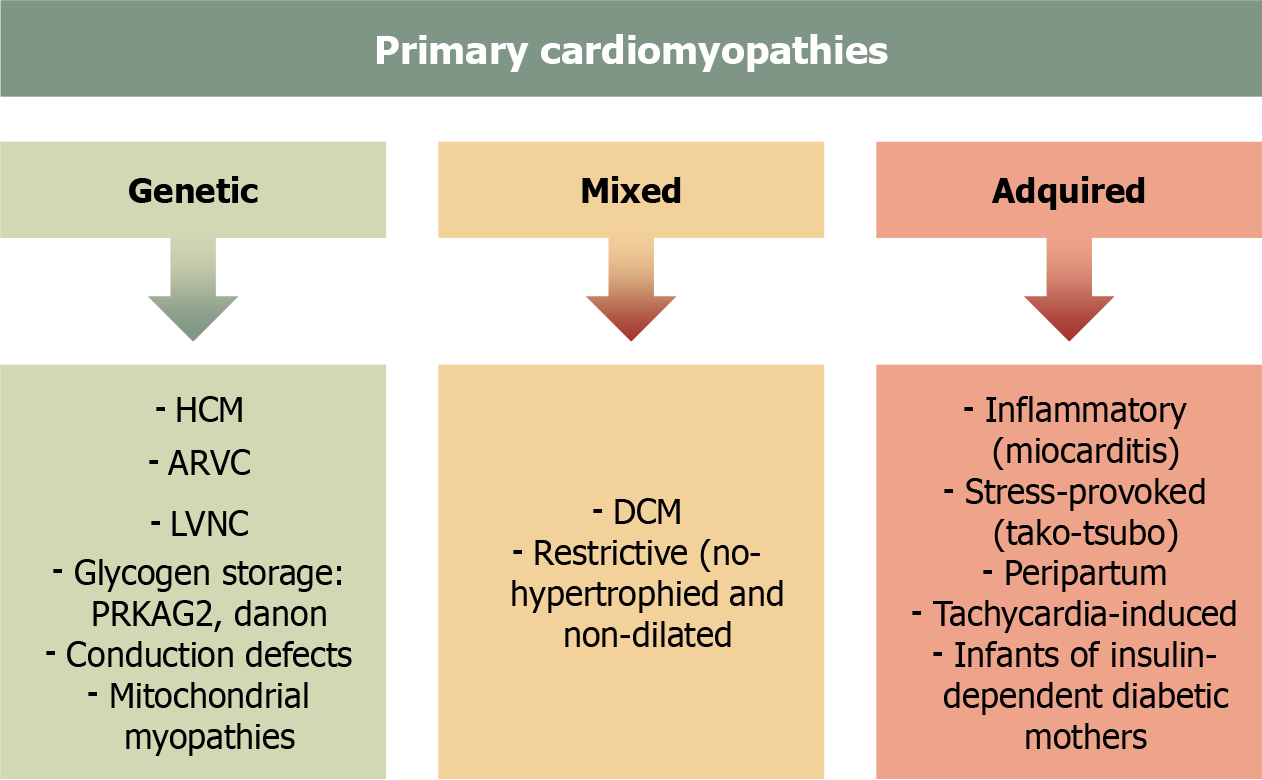
Figure 1 Classification of primary cardiomyopathy.
HCM: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; DCM: Dilated cardiomyopathy; LVNC: Left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy.
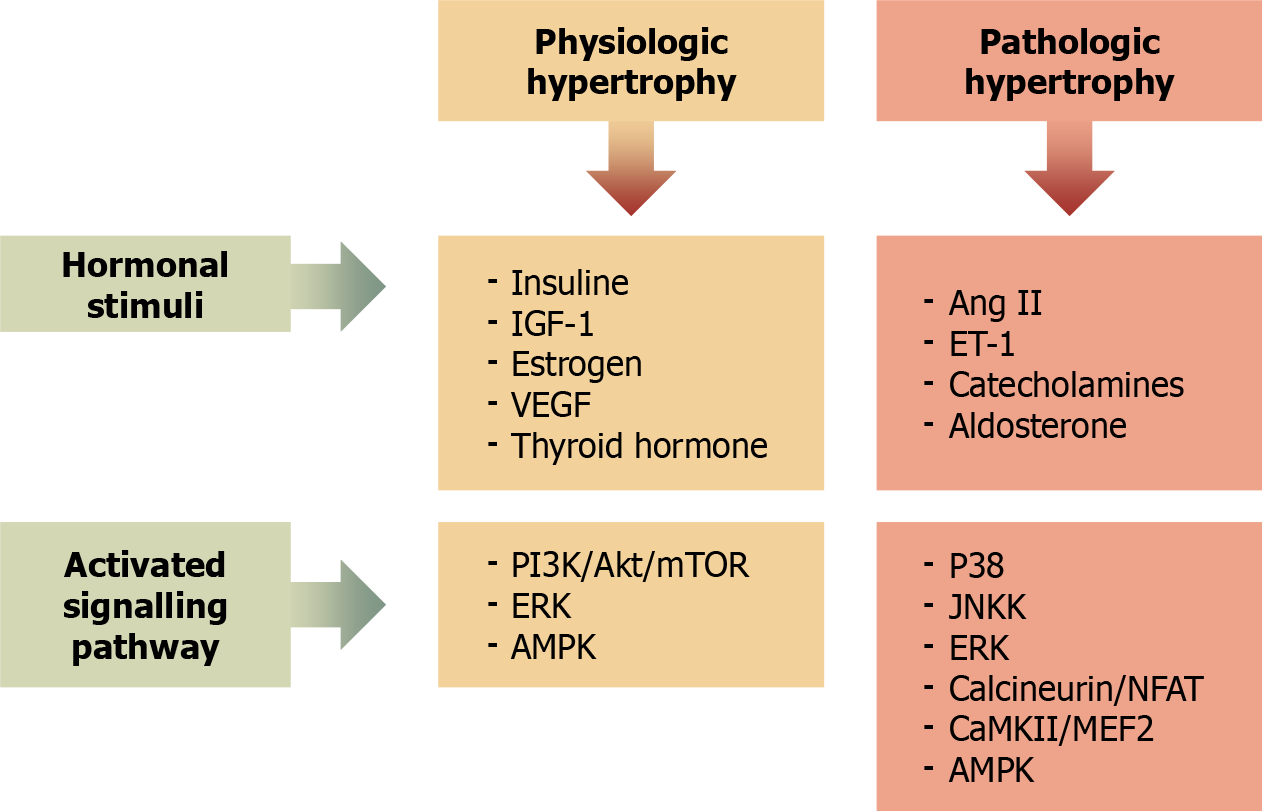
Figure 2 Pathophysiological mechanisms.
IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor 1; Ang II: Angiotensin II; ET-1: Endothelin; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; CaMKII: Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; MEF2: Myocyte enhancer factor 2; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase.
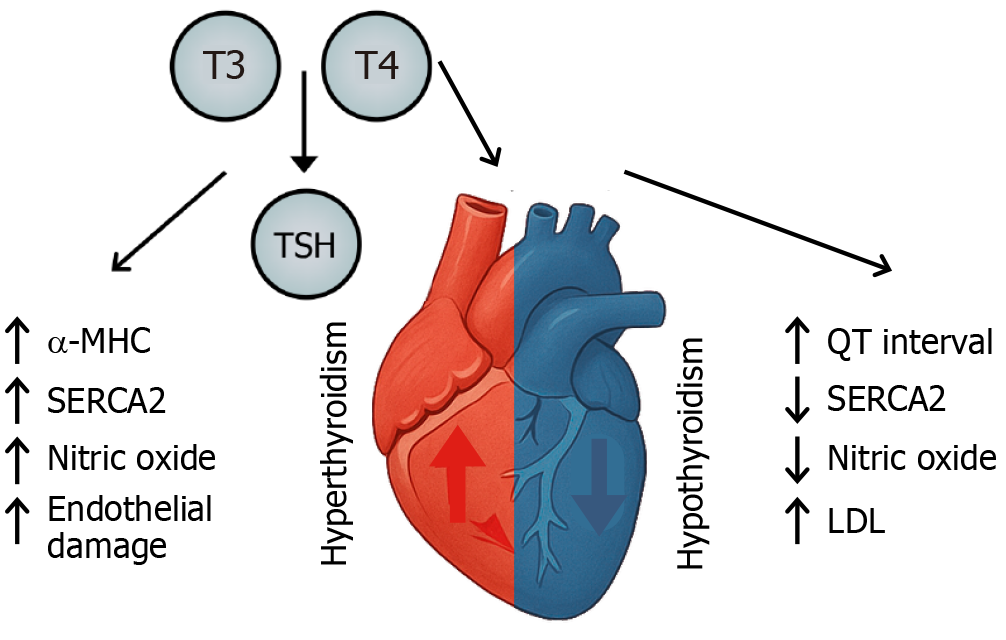
Figure 3 Pathophysiology of cardiomyopathy in hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism.
T3: Triiodothyronine; T4: Thyroxine; a-MHC: Alpha-myosin heavy chain; SERCA2: Sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2; LDL: Low-density lipoprotein; TSH: Thyroid-stimulating hormone.
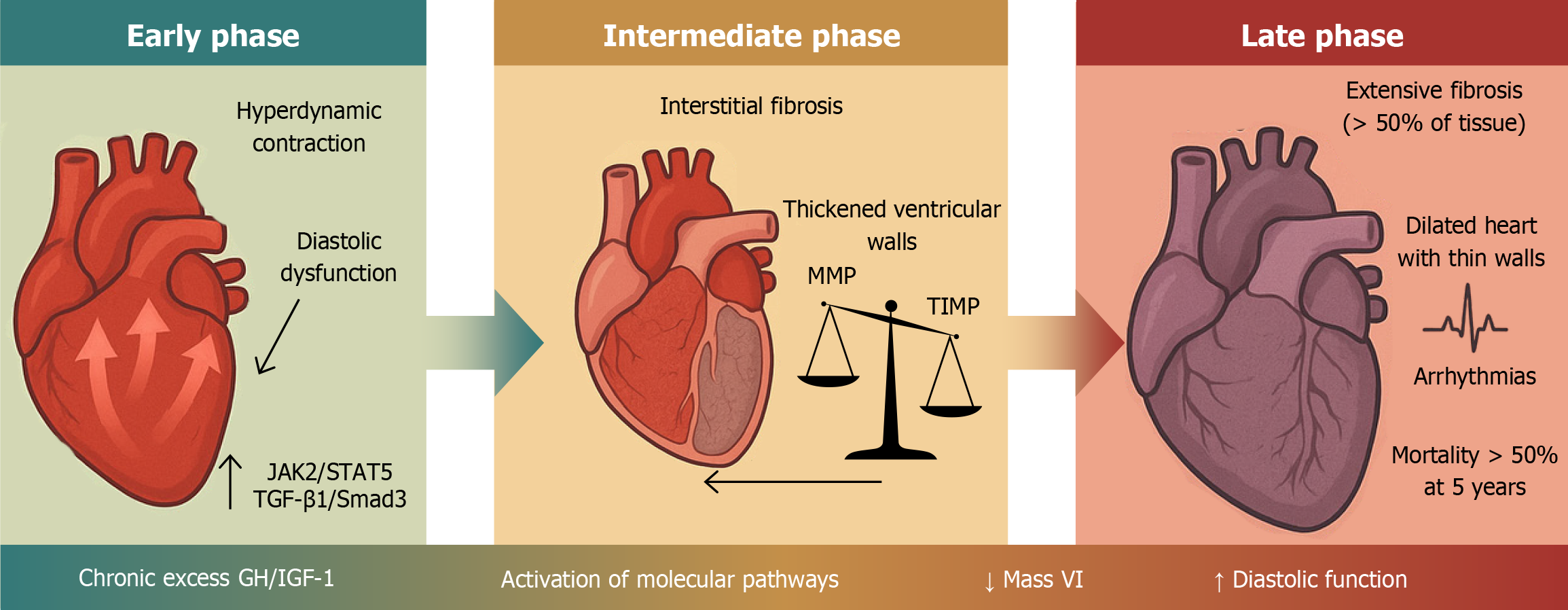
Figure 4 Phases of acromegalic heart disease.
GH: Growth hormone; IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor 1; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor beta 1; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinases; TIMP: Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases.
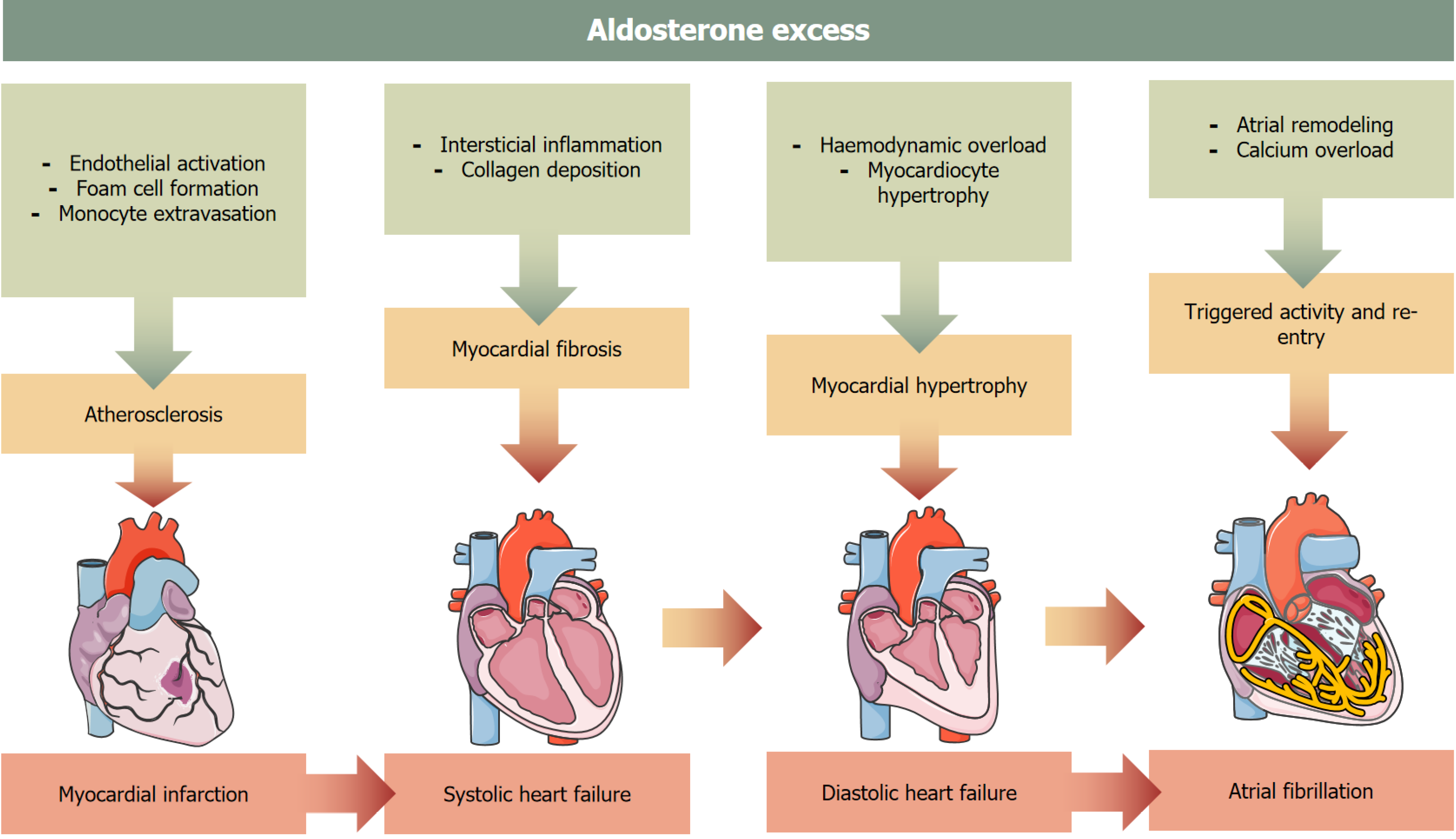
Figure 5 Pathological mechanisms of cardiomyopathy in primary hyperaldosteronism Created based on reference[49].
Image adapted from Servier Medical Art (https://smart.servier.com/), licensed under CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by/4.0/).
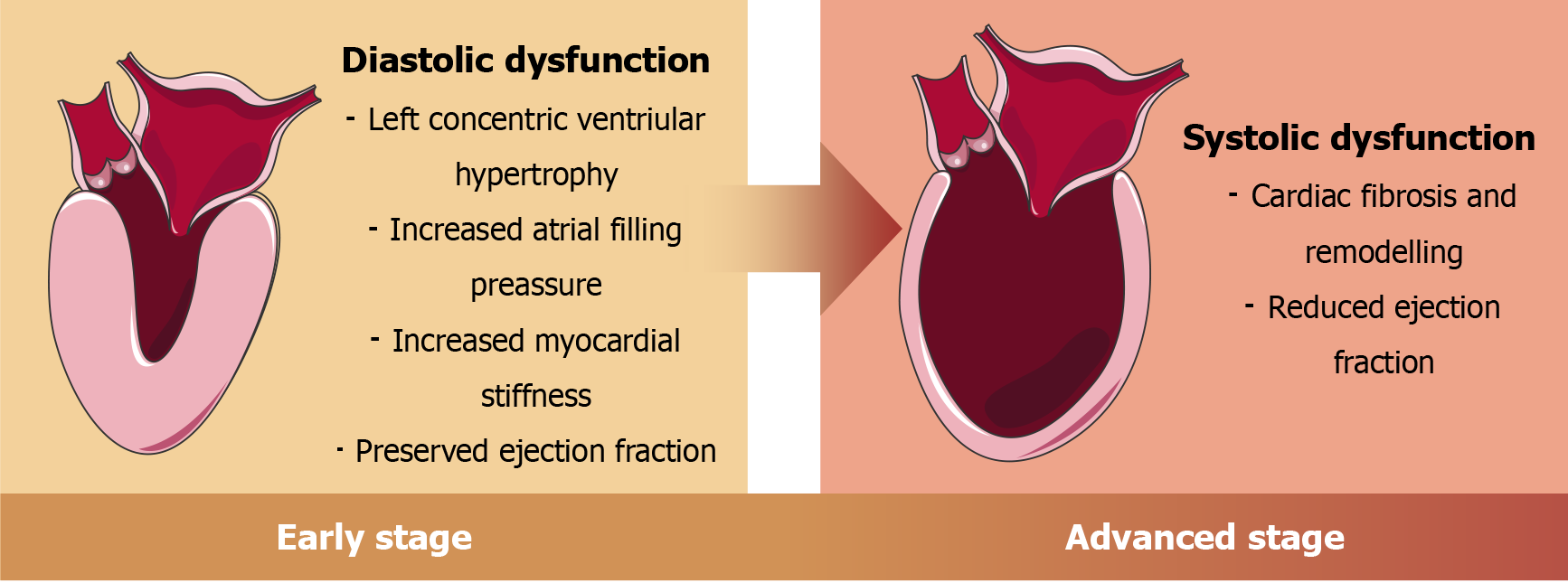
Figure 6 Phases of structural and functional changes in diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Image adapted from Servier Medical Art (https://smart.servier.com/), licensed under CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by/4.0/).
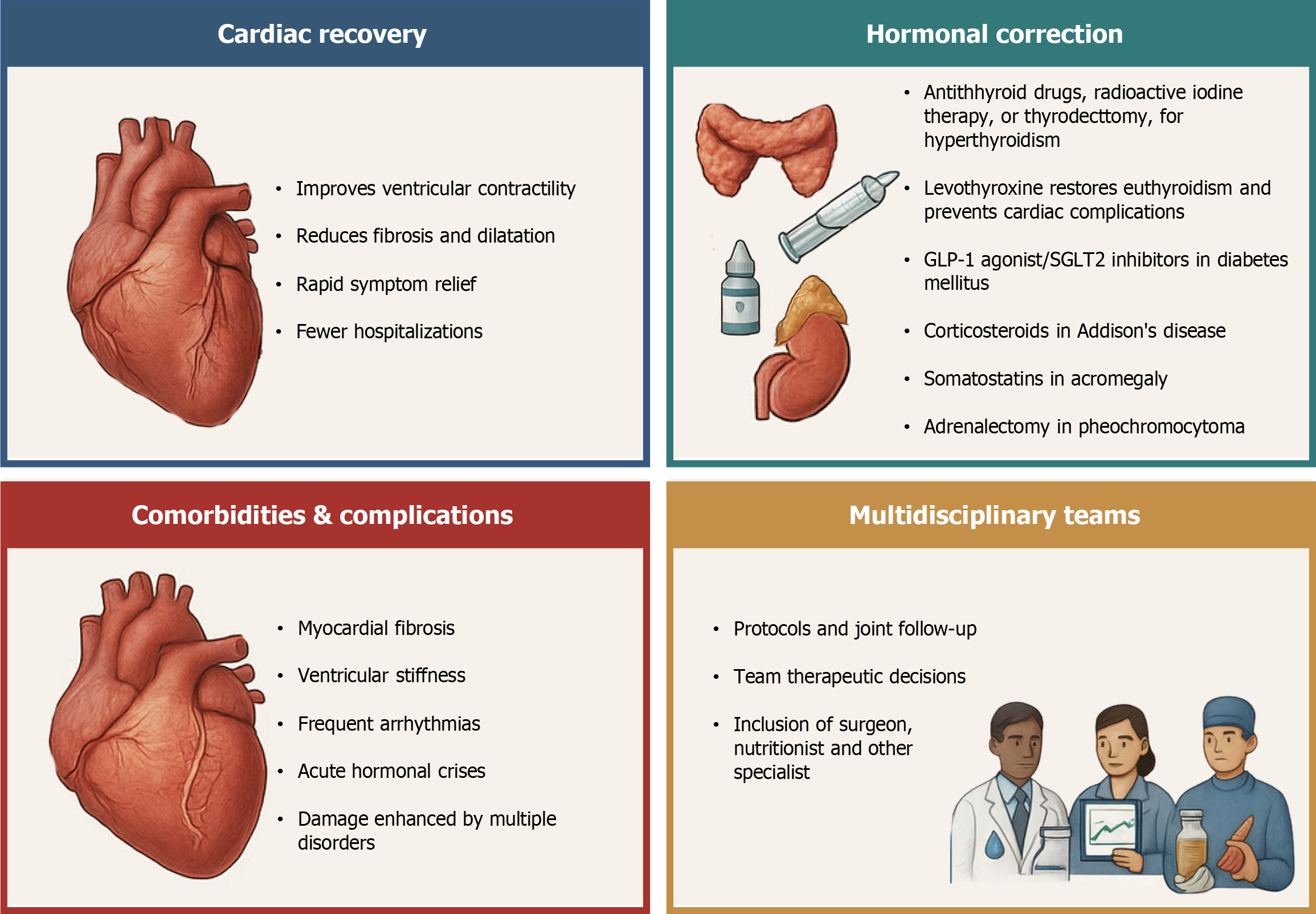
Figure 7 Therapeutic strategies in cardiomyopathy of endocrine origin.
GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1; SGLT2: Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2.
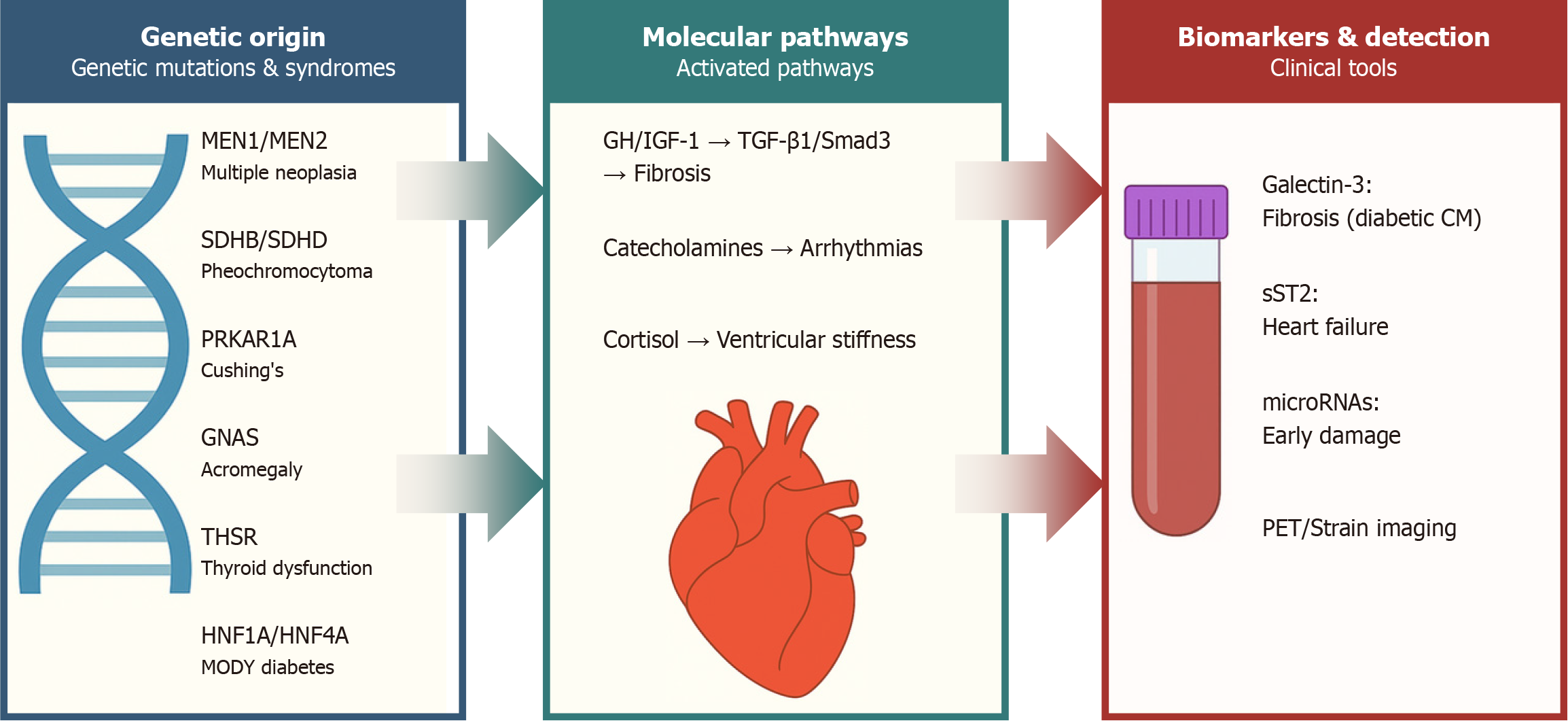
Figure 8 Endocrinopathies and genes involved in cardiomyopathies.
MEN1: Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1; MEN2: Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2; SDHB: Succinate dehydrogenase complex subunit B; SDHD: Succinate dehydrogenase complex subunit D; PRKAR1A: Protein kinase cAMP-dependent type I regulatory subunit alpha; GNAS: GNAS complex locus; THSR: Thyroid hormone receptor; HNF1A: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha; HNF4A: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha; MODY: Maturity-onset diabetes of the young; GH: Growth hormone; IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor 1; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor beta 1; sST2: Soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2; microRNAs: Micro ribonucleic acids; PET: Positron emission tomography; CM: Cardiomyopathy.
- Citation: Fuentes-Mendoza JM, Concepción-Zavaleta MJ, Morón-Siguas JC, Muñoz-Moreno JM, Pérez-Reyes AI, Martinez-Galaviz R, Aguilar-Castañeda RD, González-Godoy O, Concepción-Urteaga LA, Paz-Ibarra J. Cardiomyopathies of endocrine origin: A state-of-the-art review. World J Cardiol 2025; 17(10): 111462
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v17/i10/111462.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v17.i10.111462