©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Biol Chem. May 26, 2014; 5(2): 169-179
Published online May 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.169
Published online May 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.169
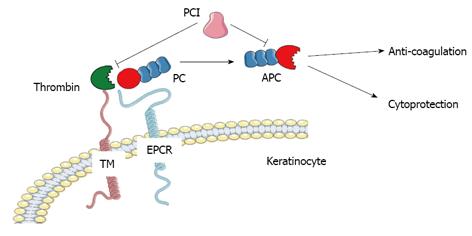
Figure 1 Schematic representation of protein C/activated protein C activation and cellular effects.
APC: Activated protein C; EPCR: Endothelial protein C receptor; PC: Protein C; PCI: Protein C inhibitor; TM: Thrombomodulin. Figure was produced using Servier Medical Art - http://www.servier.com.
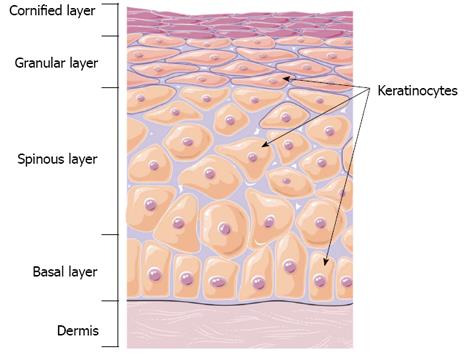
Figure 2 Schematic representation of the structure of skin showing the epidermal layers.
Figure was produced using Servier Medical Art - http://www.servier.com.
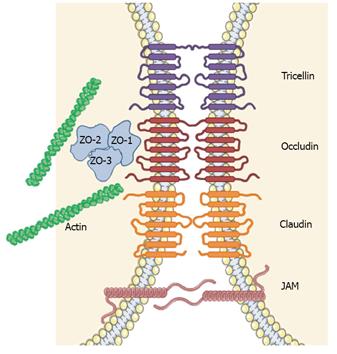
Figure 3 Schematic representation of epidermal tight junction complex.
JAM: Junctional adhesion molecule; ZO: Zona occludin. Figure was produced using Servier Medical Art - http://www.servier.com.
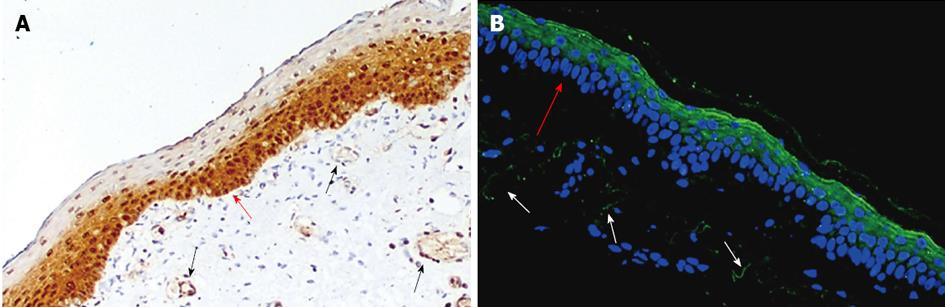
Figure 4 Immunostaining of protein C/activated protein C in human neonatal and adult skin epidermis.
A: Neonatal; B: Adult. PC/APC indicated by brown and green staining in the epidermis (red arrow) and dermal blood vessels (arrow). APC: Activated protein C; PC: Protein C.
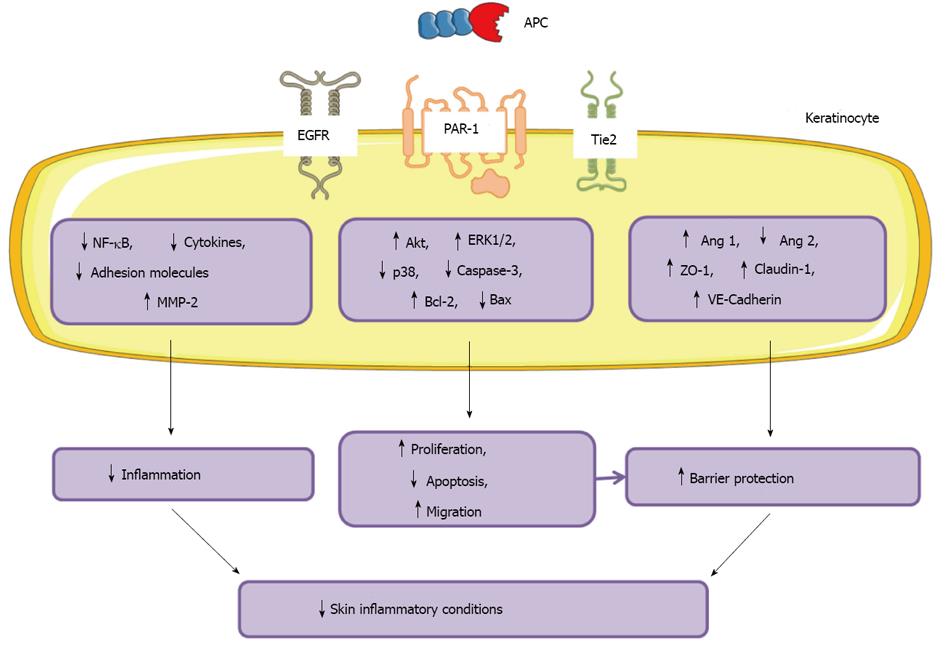
Figure 5 Schematic representation of protein C/activated protein C effects on skin epidermal keratinocyte function.
APC: Activated protein C; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; PAR-1: Protease-activated receptor 1. Figure was produced using Servier Medical Art - http://www.servier.com.
- Citation: McKelvey K, Jackson CJ, Xue M. Activated protein C: A regulator of human skin epidermal keratinocyte function. World J Biol Chem 2014; 5(2): 169-179
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v5/i2/169.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.169