©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Biol Chem. Dec 5, 2025; 16(4): 111258
Published online Dec 5, 2025. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v16.i4.111258
Published online Dec 5, 2025. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v16.i4.111258
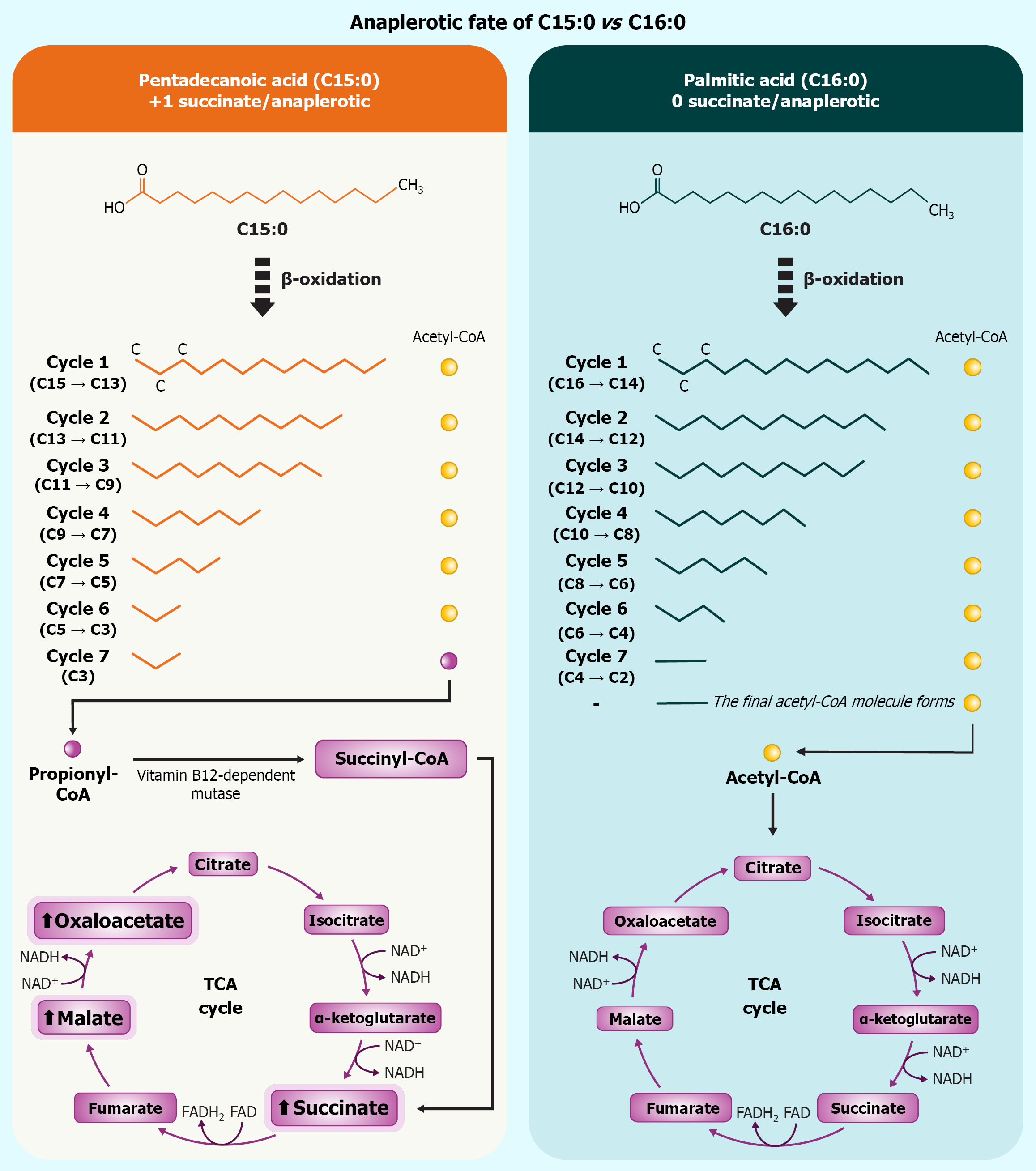
Figure 1 Odd-chain β-oxidation of pentadecanoic acid culminates in propionyl-CoA, which is carboxylated to succinyl-CoA and con
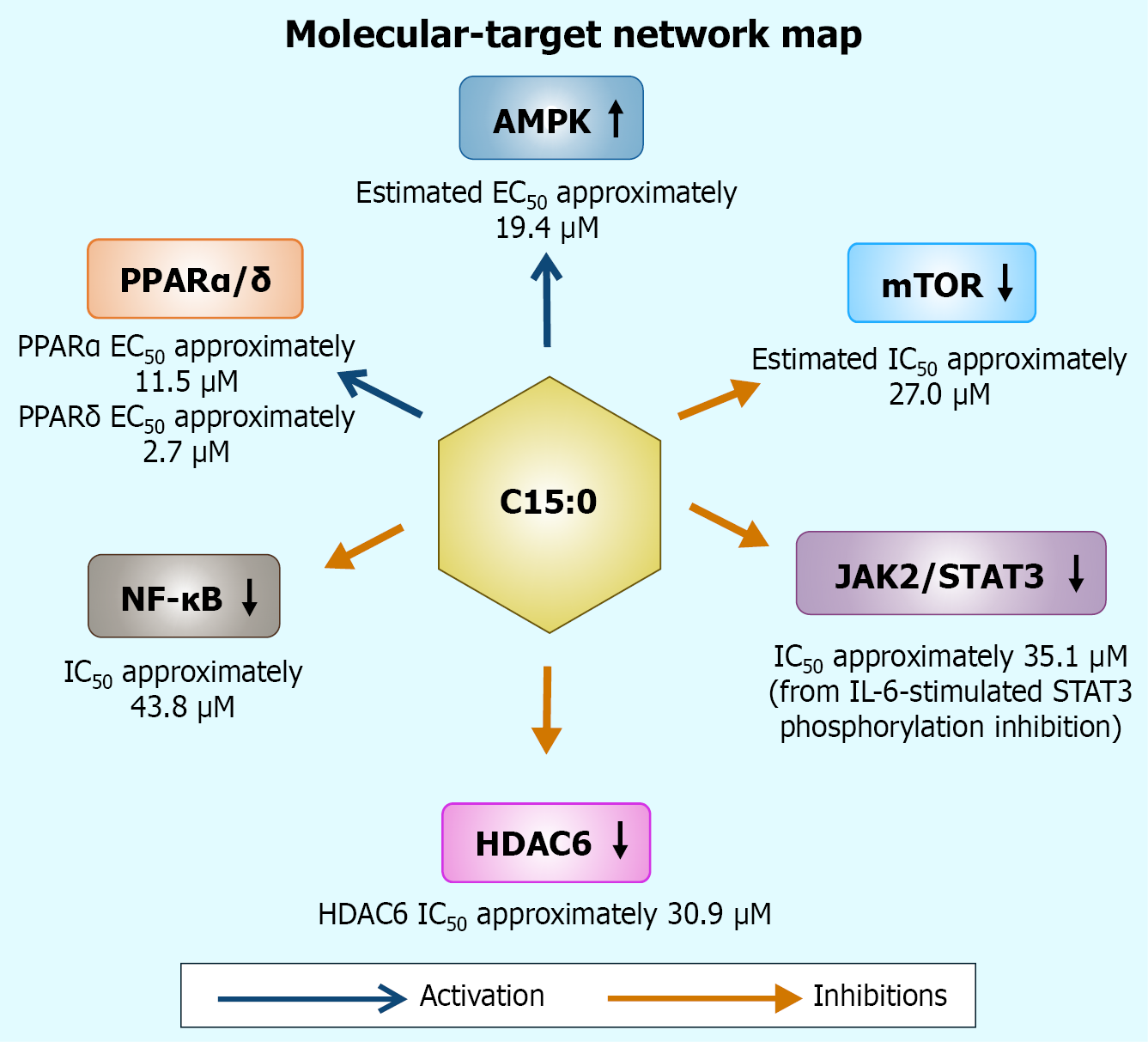
Figure 2 Integrated signaling network engaged by pentadecanoic acid.
Colored arrows denote directionality (open triangle: Activation; blunt: Inhibition). Numeric annotations indicate representative potencies or efficacies extracted from in-cell assays. AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; C15:0: Pentadecanoic acid; EC50: Half-maximal activation; JAK: Janus kinase; HDAC6: Histone deacetylase 6; mTOR: Mechanistic target of rapamycin; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; PPARα/δ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α/δ; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.
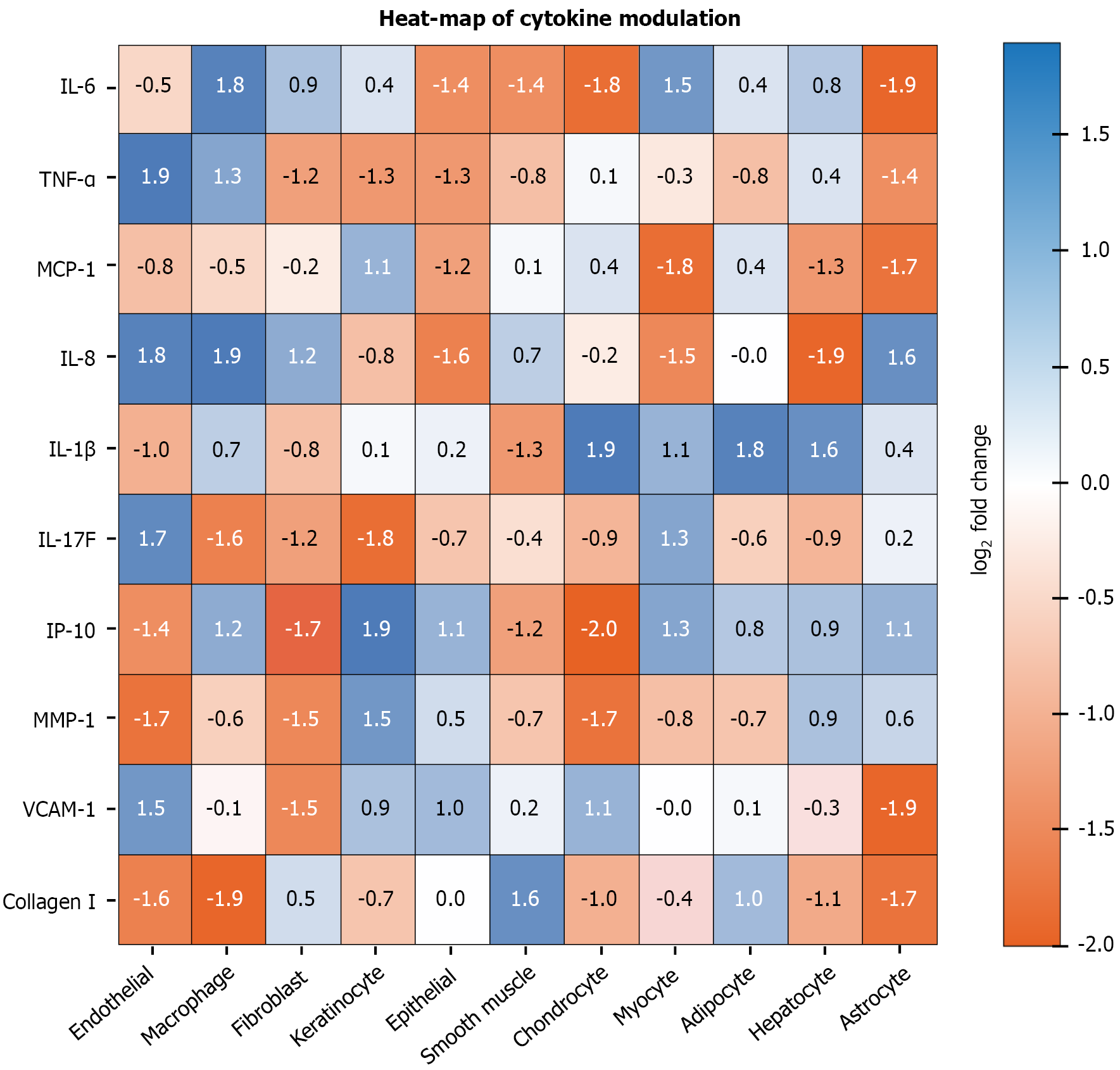
Figure 3 Log2 fold-change heat-map illustrates broad down-regulation (blue) of pro-inflammatory biomarkers by 17 μmol/L pentadecanoic acid across diverse human primary-cell systems.
Asterisks indicate P < 0.05 within BioMAP® panel. IL: Interleukin; IP-10: Inducible protein of 10 kilodaltons; MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; MMP-1: Matrix metalloproteinase-1; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; VCAM-1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1.
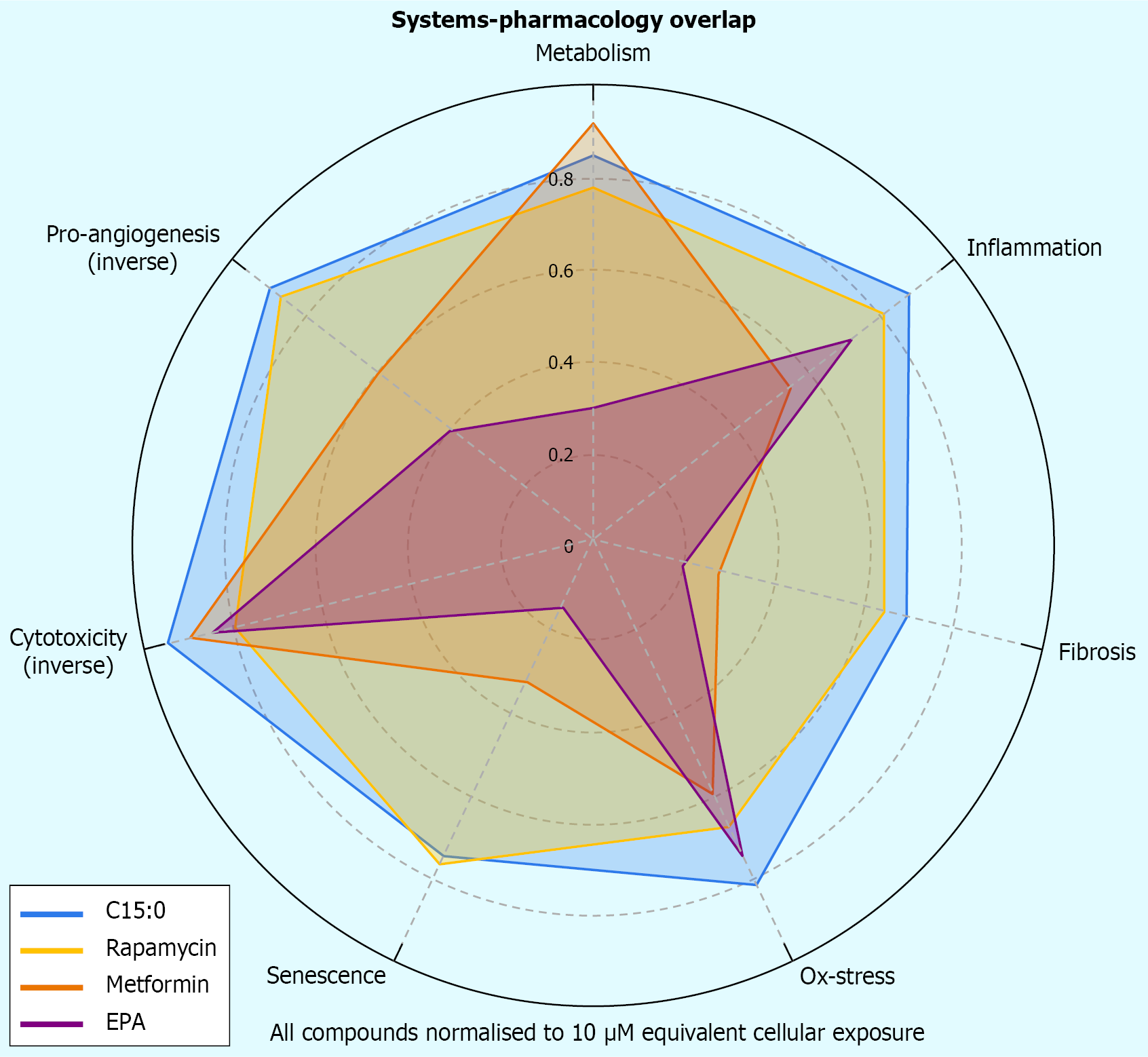
Figure 4 Radar plot compares seven pathophysiological domains of biomarker overlap.
Pentadecanoic acid (teal) achieves broad modulation rivaling rapamycin and metformin, and exceeds eicosapentaenoic acid in antifibrotic and antisenescent domains. C15:0: Pentadecanoic acid; EPA: Eicosapentaenoic acid.
- Citation: Mercola J. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of pentadecanoic acid. World J Biol Chem 2025; 16(4): 111258
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v16/i4/111258.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v16.i4.111258