©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Biol Chem. Jun 5, 2025; 16(2): 107042
Published online Jun 5, 2025. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v16.i2.107042
Published online Jun 5, 2025. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v16.i2.107042
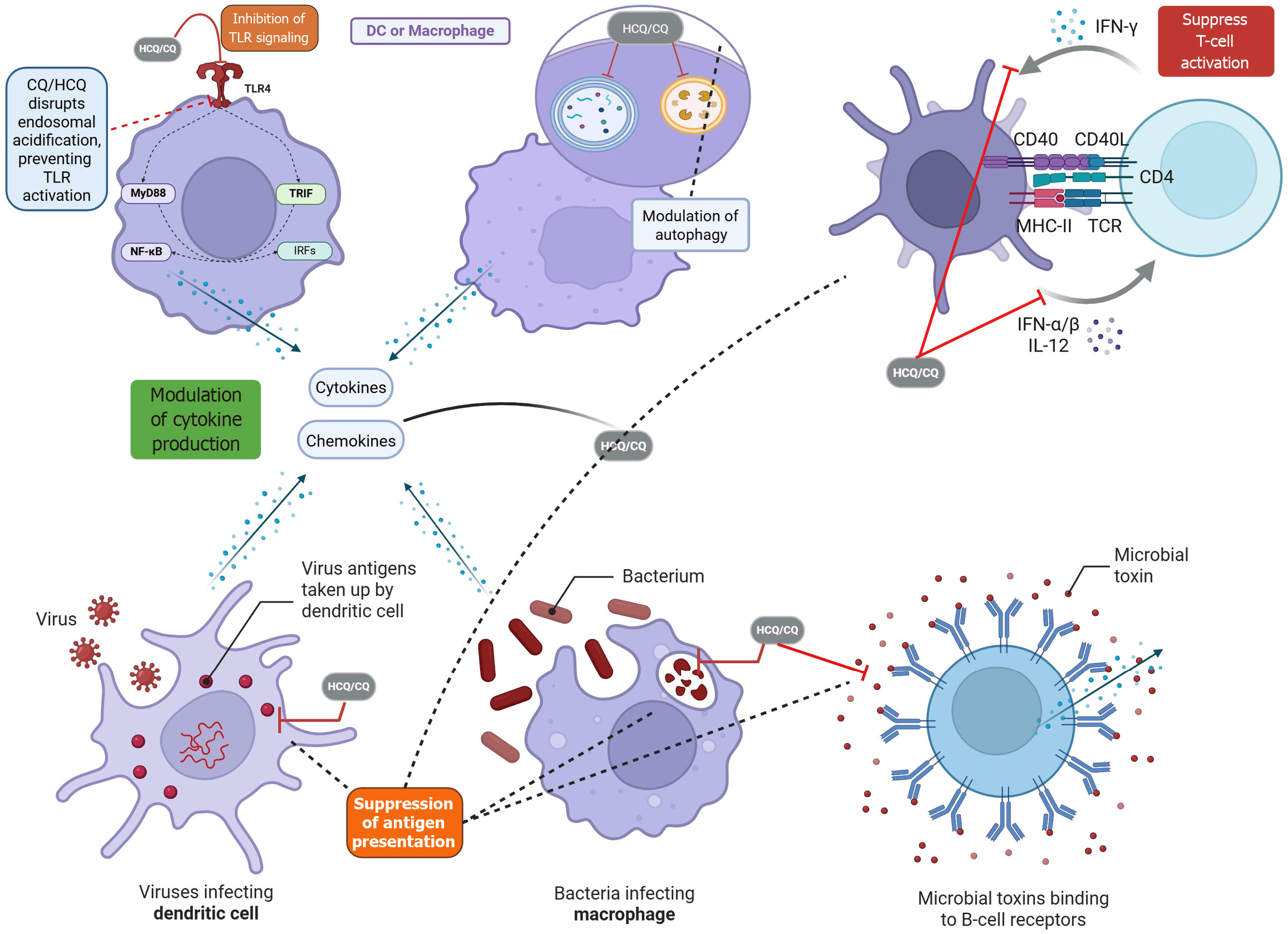
Figure 1 Immunomodulatory effects of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine on key immune cells.
This figure illustrates the impact of chloroquine (CQ) and hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) on various immune cell types, including dendritic cells (DCs), macrophages, T cells, and B cells. CQ and HCQ modulate DCs by disruption of Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling (TLR4, TLR9) and inhibition of antigen presentation via lysosomal interference, reducing pro-inflammatory cytokine production (tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-12). In Macrophages, they suppress TLR signaling and phagocytosis, and promote of M2 anti-inflammatory polarization, and modulation of cytokine release. In T cells, they inhibit autoreactive T cell activation via impaired antigen presentation, suppression of Th1/Th17 subsets, and potential enhancement of regulatory T cells (Tregs), and in B cells, the act via reduction in autoantibody production by interfering with B cell activation and plasma cell differentiation.
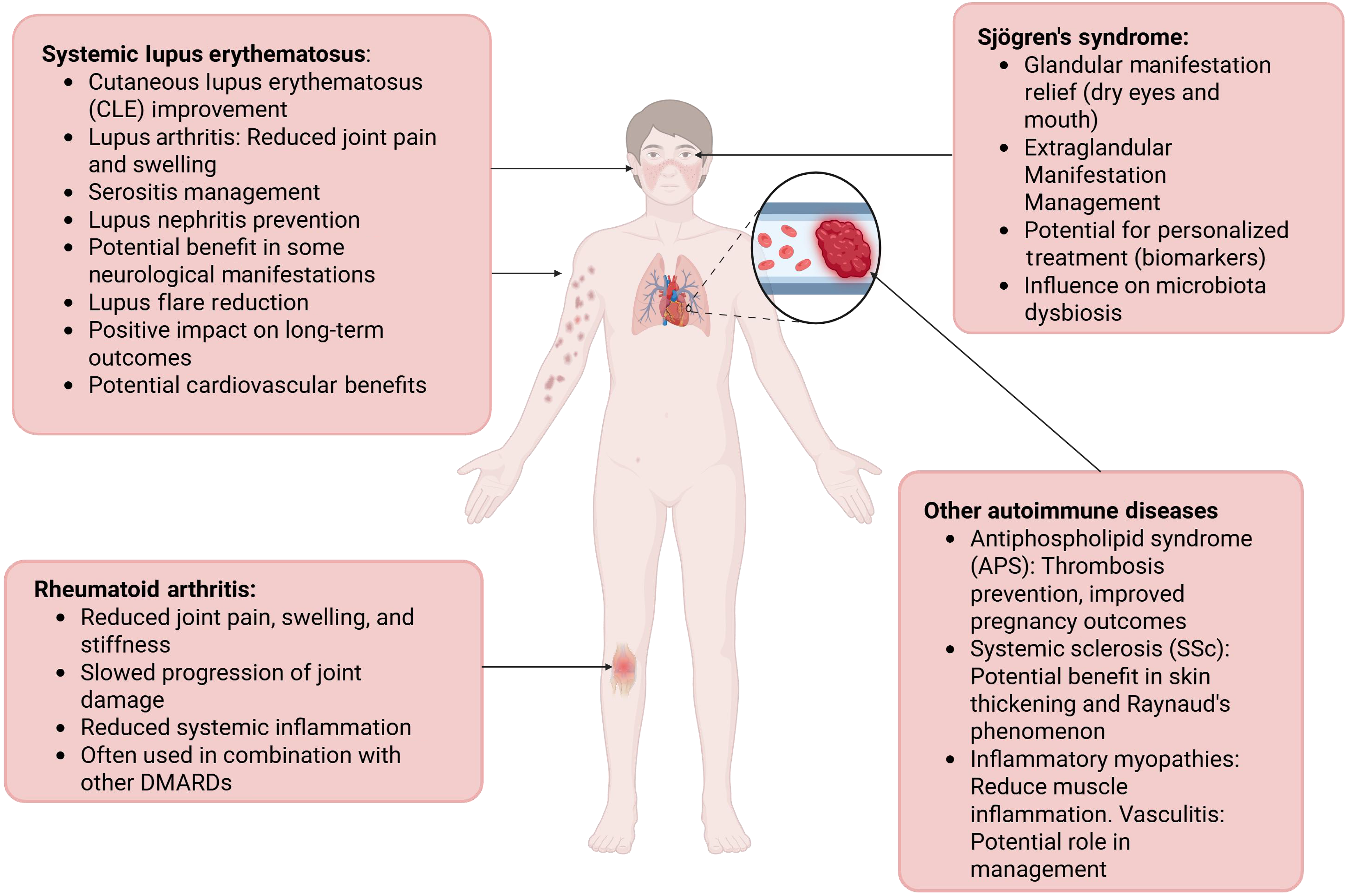
Figure 2 Clinical applications of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine for autoimmune diseases.
This figure summarizes the clinical applications of chloroquine (CQ) and hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) across various autoimmune diseases, including Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Sjögren's Syndrome (SS), antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), Systemic sclerosis, Inflammatory Myopathies (Dermatomyositis/Polymyositis), and Vasculitis. In SLE, CQ and HCQ reduce flares, cutaneous lesions, and lupus nephritis risk, in RA they are involved in pain relief, slowed joint damage, and synergy with methotrexate, in SS, they aid in the alleviation of sicca symptoms and extraglandular manifestations, and in APS, they prevent Thrombosis and improved pregnancy outcomes.
- Citation: Al-Hamadani M, Darweesh M, Mohammadi S, Al-Harrasi A. Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine: Immunomodulatory effects in autoimmune diseases. World J Biol Chem 2025; 16(2): 107042
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v16/i2/107042.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v16.i2.107042