©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Feb 27, 2016; 8(2): 115-123
Published online Feb 27, 2016. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v8.i2.115
Published online Feb 27, 2016. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v8.i2.115
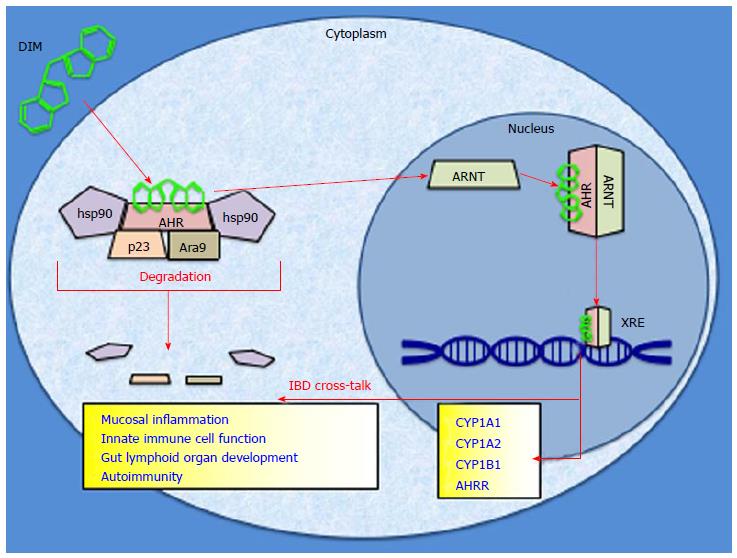
Figure 1 The aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling pathway is depicted with 3,3′-diindolylmethane as a model agonist.
Upon binding to a ligand, aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) sheds its cytosolic chaperones and translocates to the nucleus to heterodimerize with aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT). This complex binds to the xenobiotic response element (XRE) within the genome and drives transcription of cytochrome P450 detoxifying enzymes. Proposed avenues of cross-talk with inflammatory bowel disease pathology are listed. IBD : Inflammatory bowel disease.
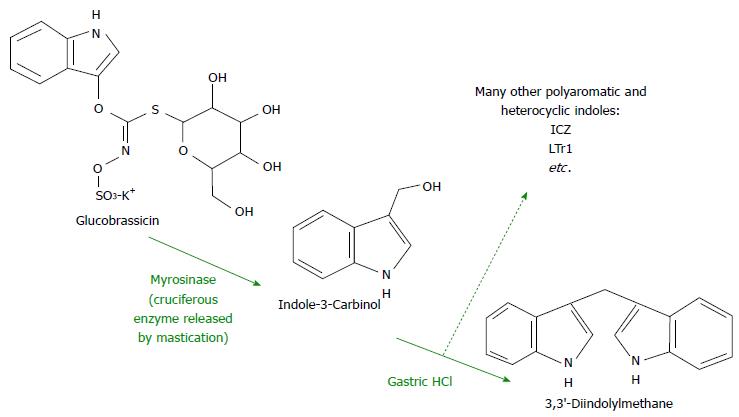
Figure 2 Presented is a simplified model for glucobrassicin digestion.
I3C is freed from glucobrassicin by the mastication-released enzyme myrosinase. Gastric HCl drives dimerization of I3C to 3,3′-diindolylmethane, as well as other indole complexes that are released to the duodenum and distal digestive tract. I3C: Indole-3-Carbinol.
- Citation: Megna BW, Carney PR, Kennedy GD. Intestinal inflammation and the diet: Is food friend or foe? World J Gastrointest Surg 2016; 8(2): 115-123
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v8/i2/115.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v8.i2.115