©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Aug 27, 2015; 7(8): 170-173
Published online Aug 27, 2015. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v7.i8.170
Published online Aug 27, 2015. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v7.i8.170
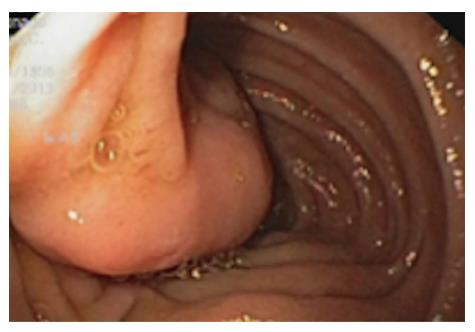
Figure 1 Endoscopic image of the tumor.
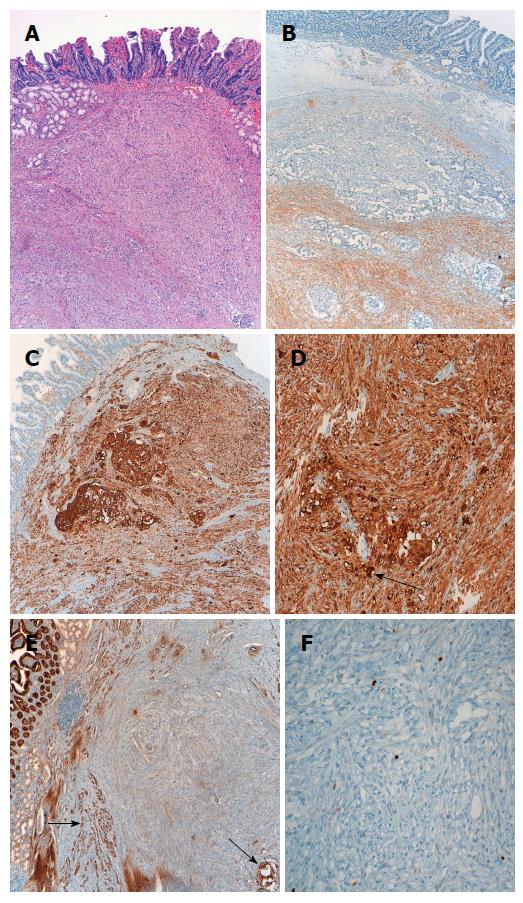
Figure 2 Histologic characteristics of the gangliocytic paraganglioma.
A: Submucosal location of the tumor (× 40); B: Immunohistochemistry showing S-100 positivity of the spindle cell component (× 40); C: Immunohistochemistry showing positive staining for neuron-specific enolase in three cellular components (× 40); D: Epithelioid cells showing cytokeratin expression. Black arrow indicates ganglion-like cells (× 40); E, F: Nuclear staining with Ki-67 showing a proliferative index of < 2% (but ranged from 5% to up to 20% in other fields). Black arrows indicate epithelioid (paraganglioma-like) cells (E: × 40; F: × 100).
- Citation: Hernández AG, Lanuza EDA, Matias AC, Huertas RP, Rodriguez KMG, Perez PG, Mompean FO. Large gangliocytic paraganglioma of the duodenum: A rare entity. World J Gastrointest Surg 2015; 7(8): 170-173
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v7/i8/170.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v7.i8.170