©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Dec 27, 2025; 17(12): 110644
Published online Dec 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i12.110644
Published online Dec 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i12.110644
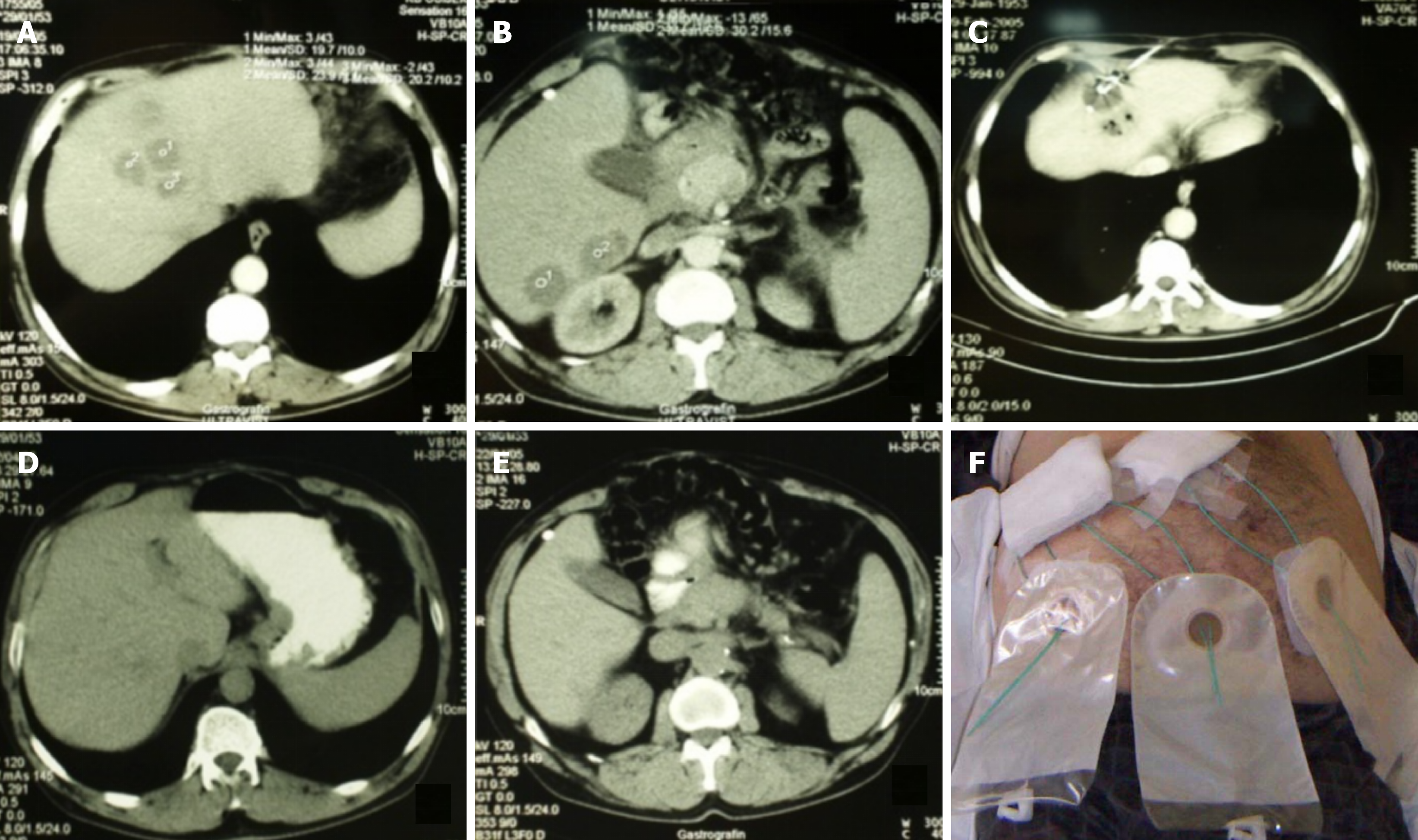
Figure 1 Percutaneous treatment of multiple liver abscesses (a total of 10) using needle aspiration for those < 30 mm and catheter drainage for those > 30 mm.
A and B: Abscess collections prior to the intervention; C: Catheter placed in one of the abscess collections; D and E: The same liver region six weeks after the intervention; F: Same patient as in panels A-E, with six catheters visible shortly after the procedure.
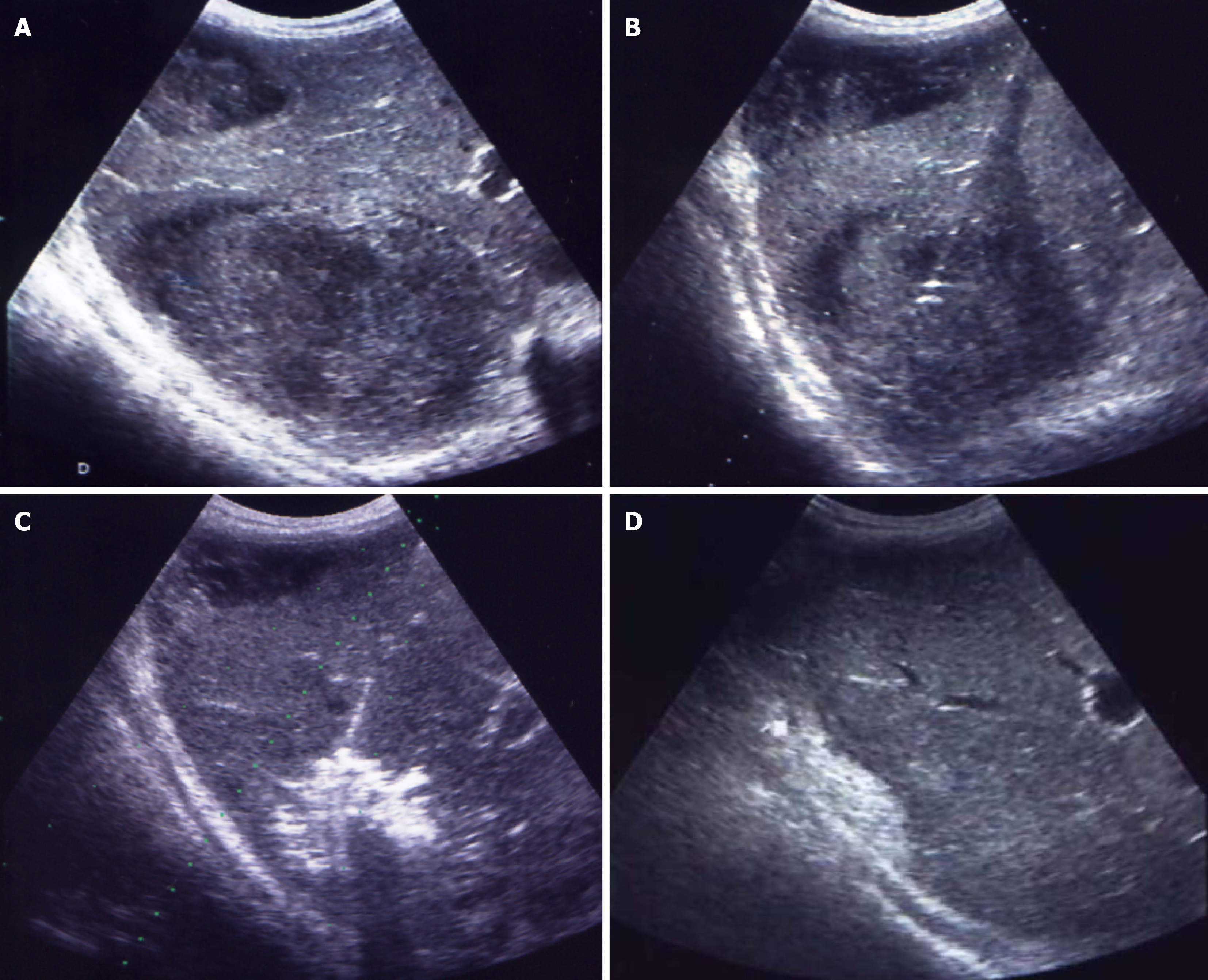
Figure 2 Percutaneous drainage of a double abscess collection in the right liver lobe, formed two weeks after appendectomy.
A: Two abscess collections in the right liver lobe; B: Transhepatic access to the abscess collection using the trocar technique; C: Vigorous irrigation of the abscess cavity with a 50/50 mixture of iodine and saline through a catheter; D: Scar formation in liver tissue three weeks post-intervention.
- Citation: Zerem E, Jovanovic P, Kunosic S, Kurtcehajic A, Zerem D, Zerem O. Optimal timing of pyogenic liver abscess evacuation: The role of early ultrasound-guided intervention. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(12): 110644
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i12/110644.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i12.110644