©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Nov 27, 2025; 17(11): 110864
Published online Nov 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i11.110864
Published online Nov 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i11.110864
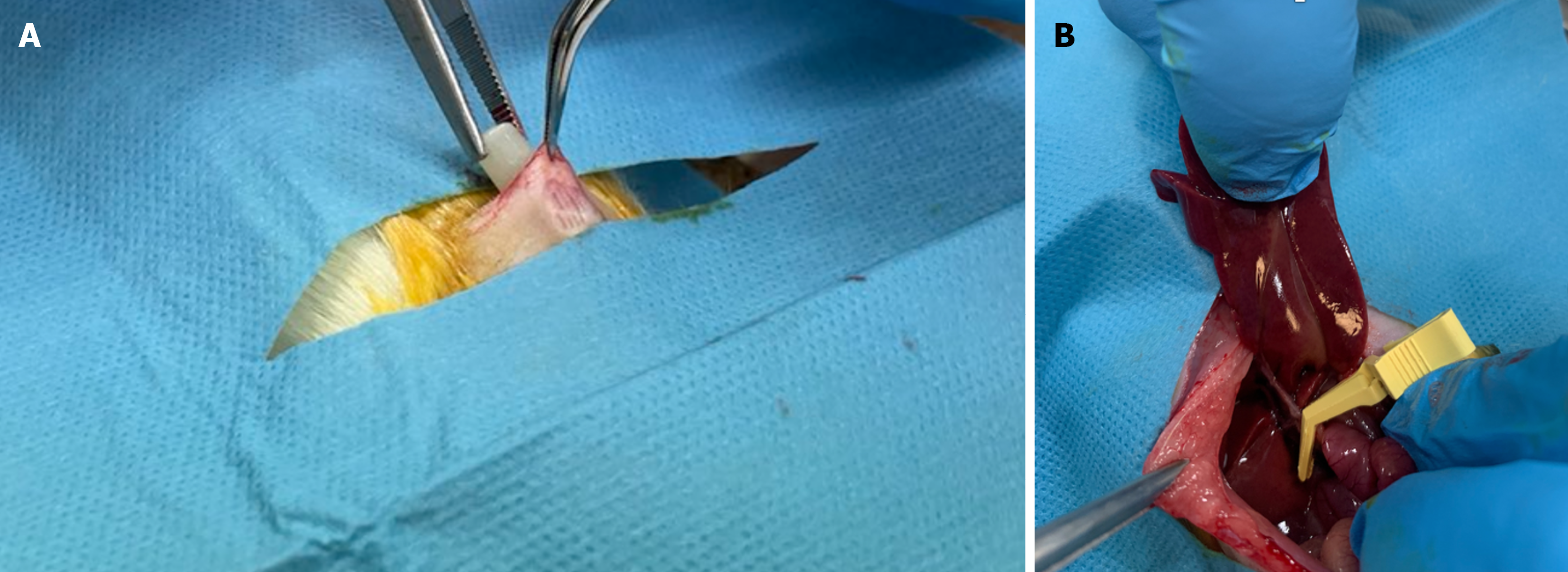
Figure 1 Subcutaneous osmotic minipump implantation.
A: Subcutaneous osmotic minipump implantation in rats pre-treated with treprostinil; B: An occlusion of hepatoduodenal ligament using atraumatic bulldog clamp.
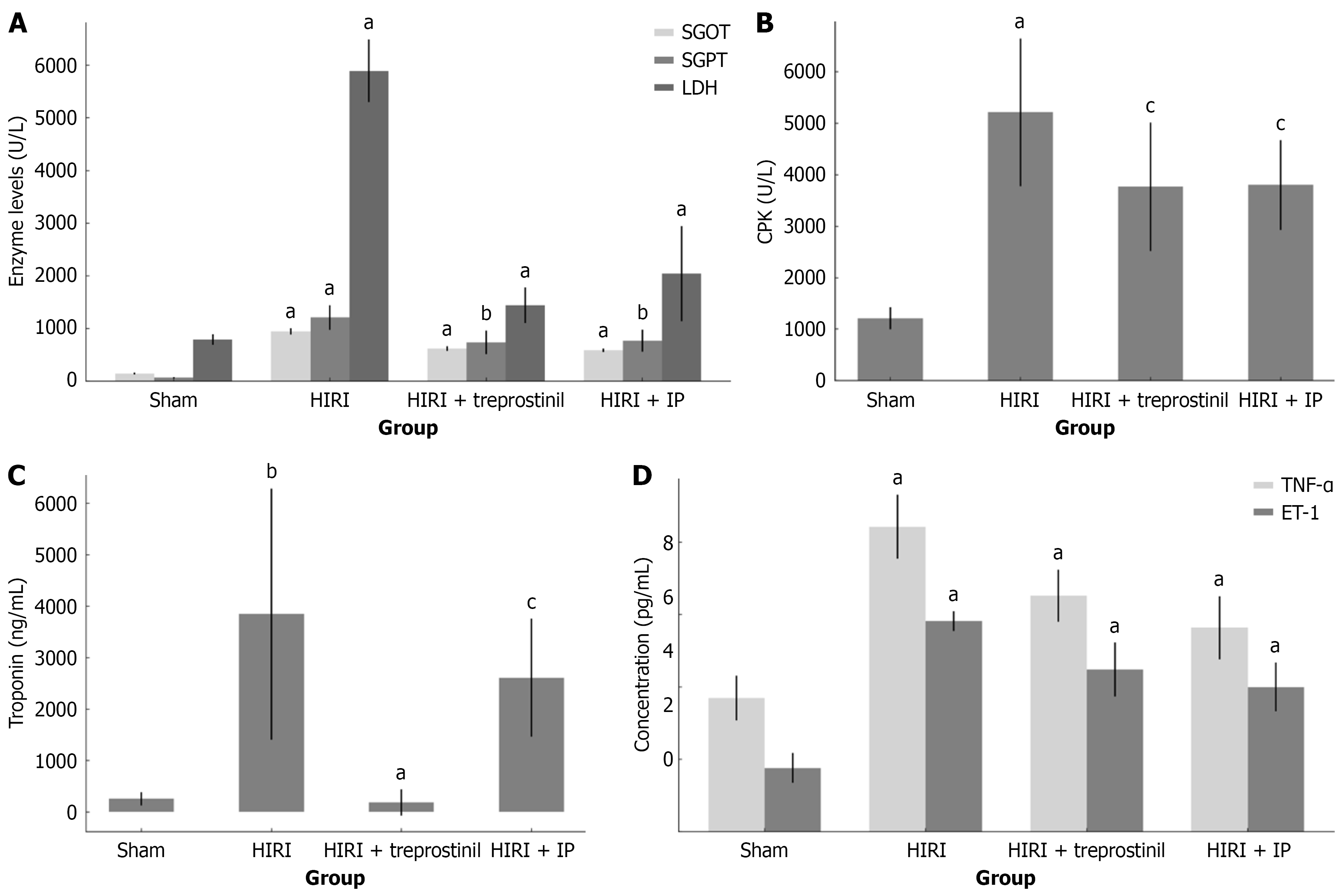
Figure 2 Effect of treprostinil and ischemic preconditioning in rats subjected to hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury.
A: Effect of treprostinil and ischemic preconditioning (IP) on serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT), serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase (SGPT), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels in rats subjected to hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury (HIRI). Serum SGOT, SGPT, and LDH levels in the HIRI group were significantly different from sham group. In treprostinil and IP groups, serum SGOT, SGPT, and LDH levels were significantly decreased compared to HIRI; B: Effect of treprostinil and IP on serum creatine phosphokinase (CPK) values in rats subjected to HIRI. Serum CPK levels in the HIRI group were significantly different from the sham group, confirming the presence of myocardial injury. In treprostinil and IP groups, serum CPK levels were reduced compared to the HIRI group, but no significant difference was observed; C: Effect of treprostinil and IP on serum troponin I values in rats subjected to HIRI. Serum troponin I levels in the HIRI group were significantly different from the sham group, confirming the presence of cardiac damage. The treprostinil group significantly reduced serum troponin I levels. Rats pre-tretated with IP also had lower serum troponin I levels, but no statistically significant difference was observed; D: Effect of treprostinil and IP on serum tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and endothelin-1 (ET-1) values in rats subjected to HIRI. Serum TNF-α and ET-1 levels in the HIRI group were significantly elevated compared with the sham group, confirming the upregulated inflammatory response. In the treprostinil and IP group, serum TNF-α and ET-1 levels were significantly reduced compared to the HIRI group. Black lines on the top of the bars represent SD. HIRI: Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury; IP: Ischemic preconditioning; SGOT: Serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase; SGPT: Serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase; LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase; CPK: Creatine phosphokinase; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; ET-1: Endothelin-1. aP < 0.001, bP < 0.05, and cP > 0.05.
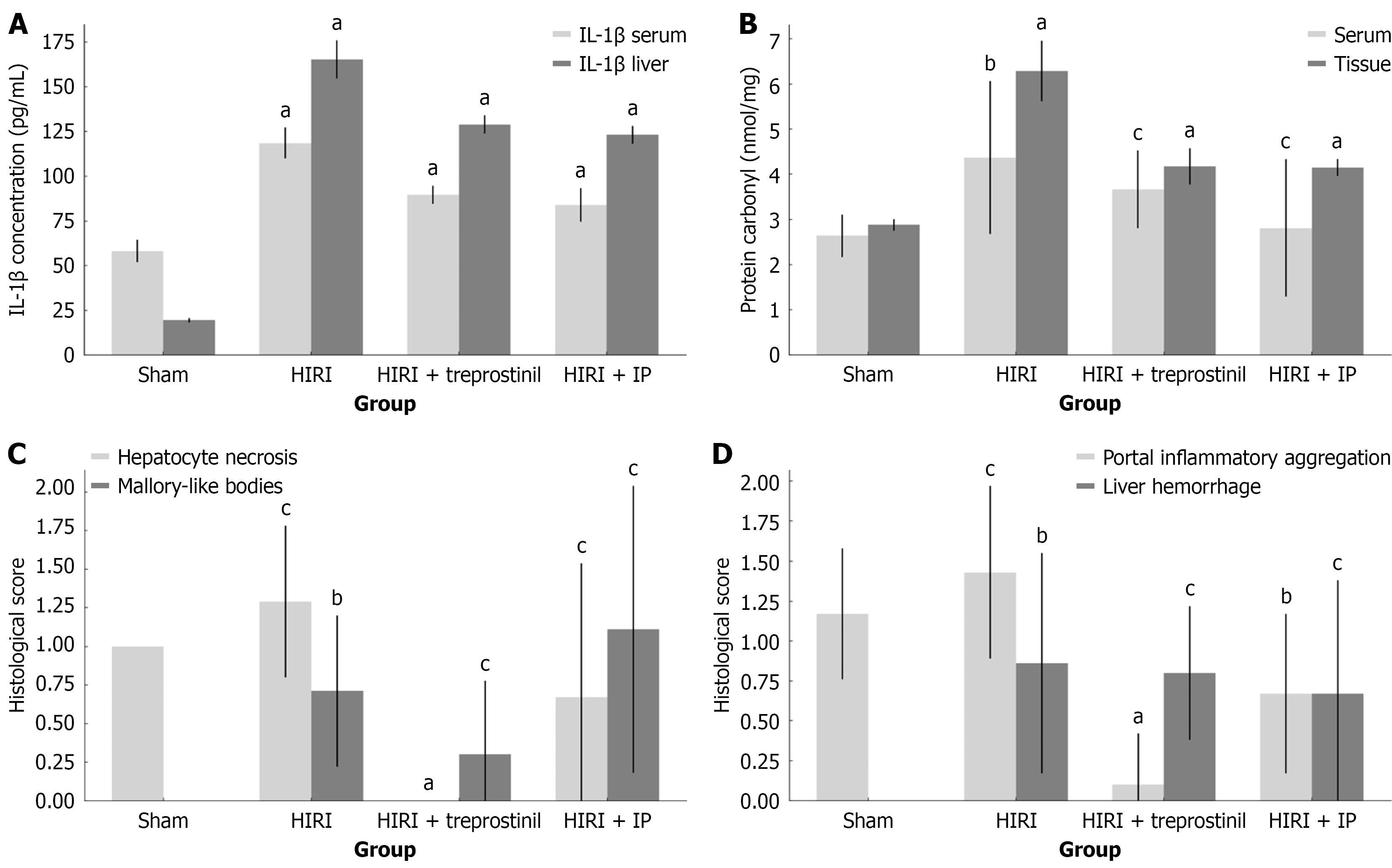
Figure 3 Effect of treprostinil and ischemic preconditioning in rats subjected to hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury.
A: Effect of treprostinil and ischemic preconditioning (IP) on serum and liver tissue interleukin-1β (IL-1β) concentrations in rats subjected to hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury (HIRI). Serum and tissue IL-1β levels in the HIRI group were significantly increased compared to the sham group, confirming the induction of the inflammatory response. In the treprostinil and IP group, serum and liver tissue IL-1β concentrations were significantly reduced compared to the HIRI group; B: Effect of treprostinil and IP on serum and liver tissue protein carbonyl concentrations in rats subjected to HIRI. Serum and tissue protein carbonyl levels in the HIRI group were significantly increased compared to the sham group, confirming the induction of oxidative stress and inflammatory response. Treprostinil and IP reduced serum protein carbonyl concentration, but the difference was not statistically significant. In contrast, treprostinil and IP significantly reduced liver tissue protein carbonyl levels compared to the HIRI group; C: Effect of treprostinil and IP on hepatocyte necrosis and Mallory-like bodies formation in rats subjected to HIRI. Hepatocyte necrosis was present in the HIRI group, but no statistically significant was revealed when compared to the sham group, in contrast with Mallory-like bodies formation. Treprostinil significantly reduced the extent of cell necrosis compared to the HIRI group. Cell necrosis was also lower in the IP group, but there was no significant difference compared to the HIRI group. The presence of Mallory-like bodies was reduced in treprostinil group compared to the HIRI group, although with no statistically significant difference. However, the Mallory-like bodies formation was higher in the IP group than in the HIRI group; D: Effect of treprostinil and IP on portal inflammatory cell infiltrations and liver hemorrhage occurrence in rats subjected to HIRI. Portal inflammatory cell infiltration was present in the HIRI group compared to sham group, but no statistically significant difference was revealed, in contrast with liver hemorrhage. Both treatments significantly reduced the degree of inflammatory cell aggregation, but no statistically significant difference was observed for the occurrence of hemorrhagic lesions when compared to the HIRI group. Black lines on the top of the bars represent SD. HIRI: Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury; IP: Ischemic preconditioning; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β. aP < 0.001, bP < 0.05, and cP > 0.05.
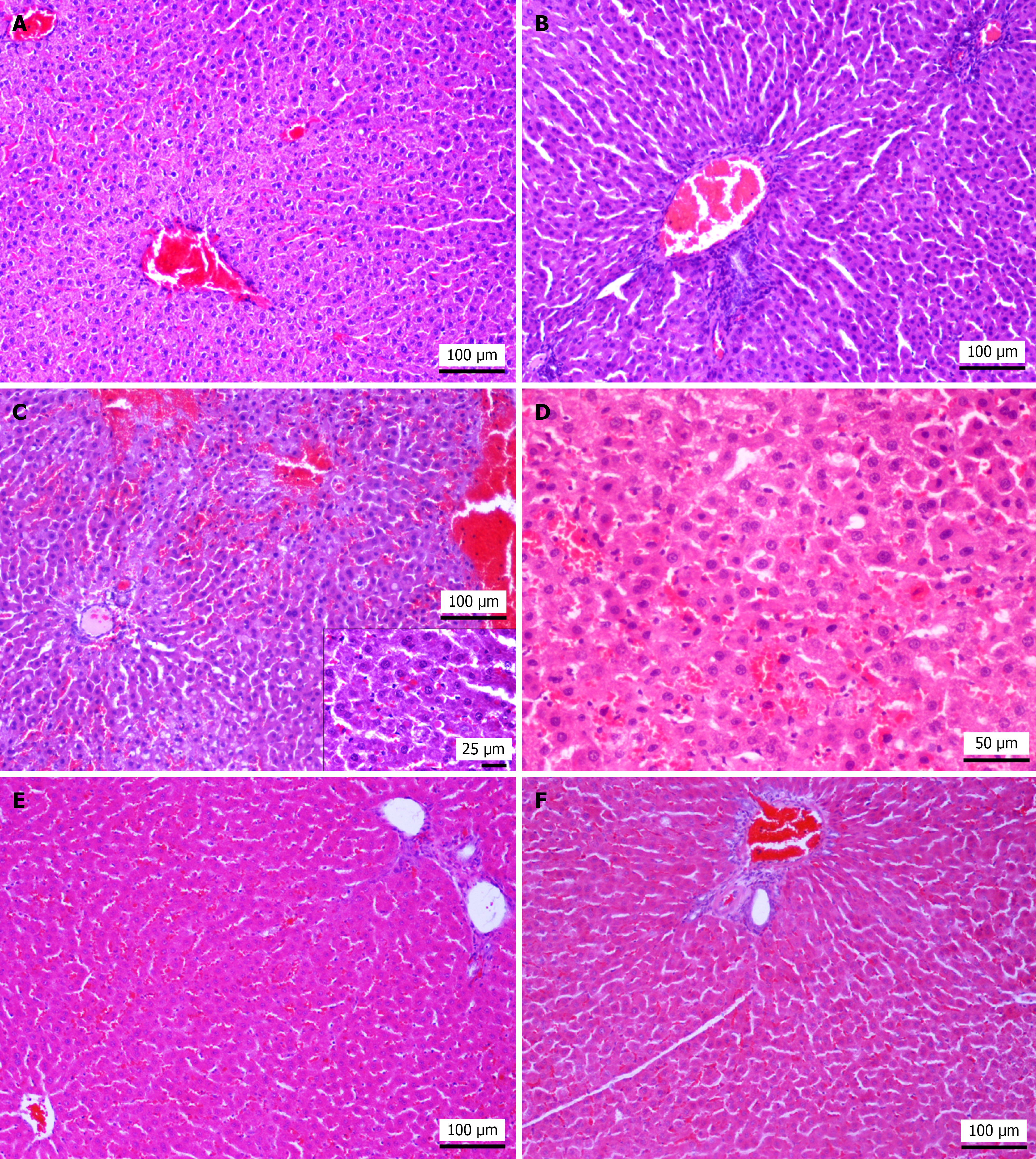
Figure 4 Histopathological findings of liver samples in sham group, hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury group, treprostinil-treated group, and ischemic preconditioning group.
A: Sham group; histological section from a rat of the sham group shows normal architecture. Hematoxylin and eosin (HE), original magnification 100 ×; B: Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury (HIRI) group; rat subjected to HIRI presents sinusoidal dilatation and portal spaces with inflammatory cell infiltration (mostly neutrophilic). HE, original magnification 100 ×; C: HIRI group; hepatic hemorrhages and sinusoidal hyperemia accompanied by hepatocyte necrosis, primarily characterized by pyknotic nuclei. Intracytoplasmic eosinophilic bodies are present in numerous hepatocytes while in lower center, there is vacuolar degeneration. Inset shows Mallory-like hyaline bodies. HE, original magnification 100 ×, inset 400 ×; D: HIRI group, hyperhemia and microhemorrhages and multiple necrotic hepatocytes characterized by homogenous eosinophilic cytoplasm and pyknotic or absent nucleus, are detectable. HE, original magnification 200 ×; E: Treprostinil treated group; treatment with treprostinil shows less disturbed/normal lobular architecture, mild sinusoidal hyperhemia and sparse inflammatory cells in portal spaces (upper right) and central vein dilatation (lower left), C × 100; F: Ischemic preconditioning group; rats pre-treated with IP preserve hepatic lobular architecture. However sparse hepatocyte necrosis and mild periportal neutrophilic infiltration are observed. HE, original magnification 100 ×.
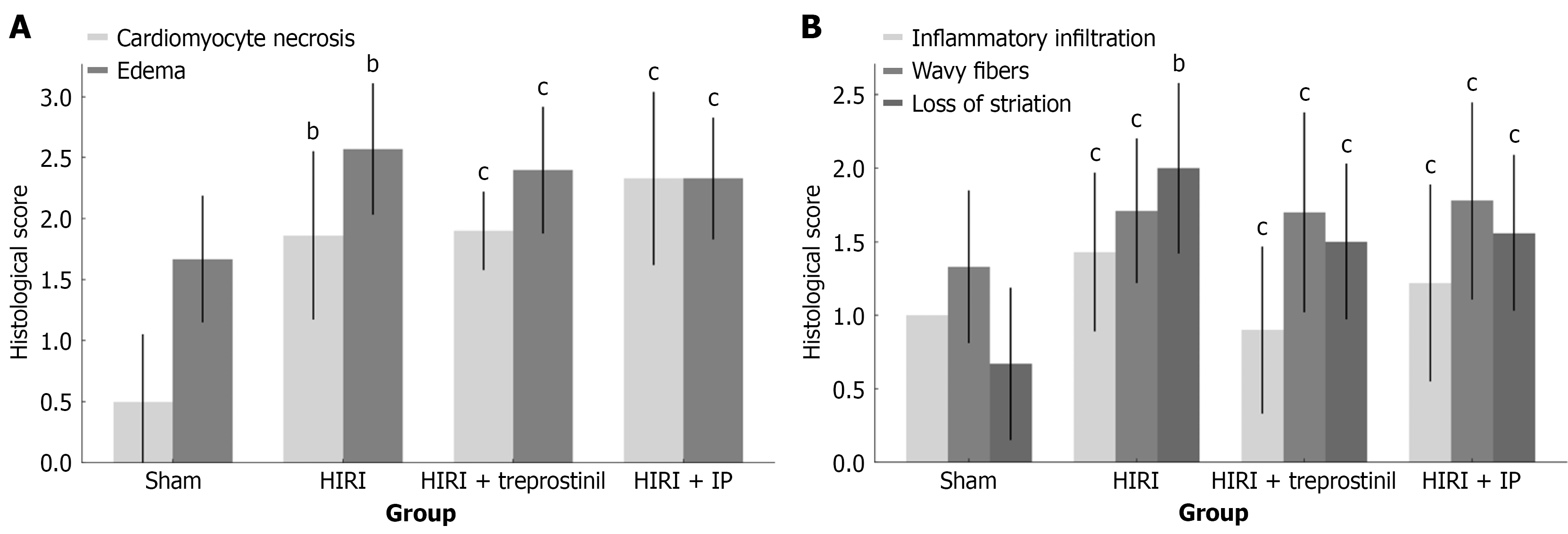
Figure 5 Effect of treprostinil and ischemic preconditioning in rats subjected to hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury.
A: Effect of treprostinil and ischemia-reperfusion (IP) on cardiomyocyte necrosis and edema in rats subjected to hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury (HIRI). The degree of cardiomyocyte necrosis and edema was significantly increased in the HIRI group compared to the sham group. Nonetheless, no statistically significant difference was found between either of the treatment groups and the HIRI group; B: Effect of treprostinil and ischemia-reperfusion on myocardium inflammatory cell infiltrations, presence of wavy fibers and loss of striation in rats subjected to HIRI. The degree of myocardial inflammatory cell infiltrations, presence of wavy fibers and loss of striation was increased in the HIRI group compared to the sham group, but a statistically significant difference was only detected for the loss of striation. There was no statistically significant difference between either treatment group and the HIRI group. Black lines on the top of the bars represent SD. HIRI: Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury; IP: Ischemic preconditioning. bP < 0.05, and cP > 0.05.
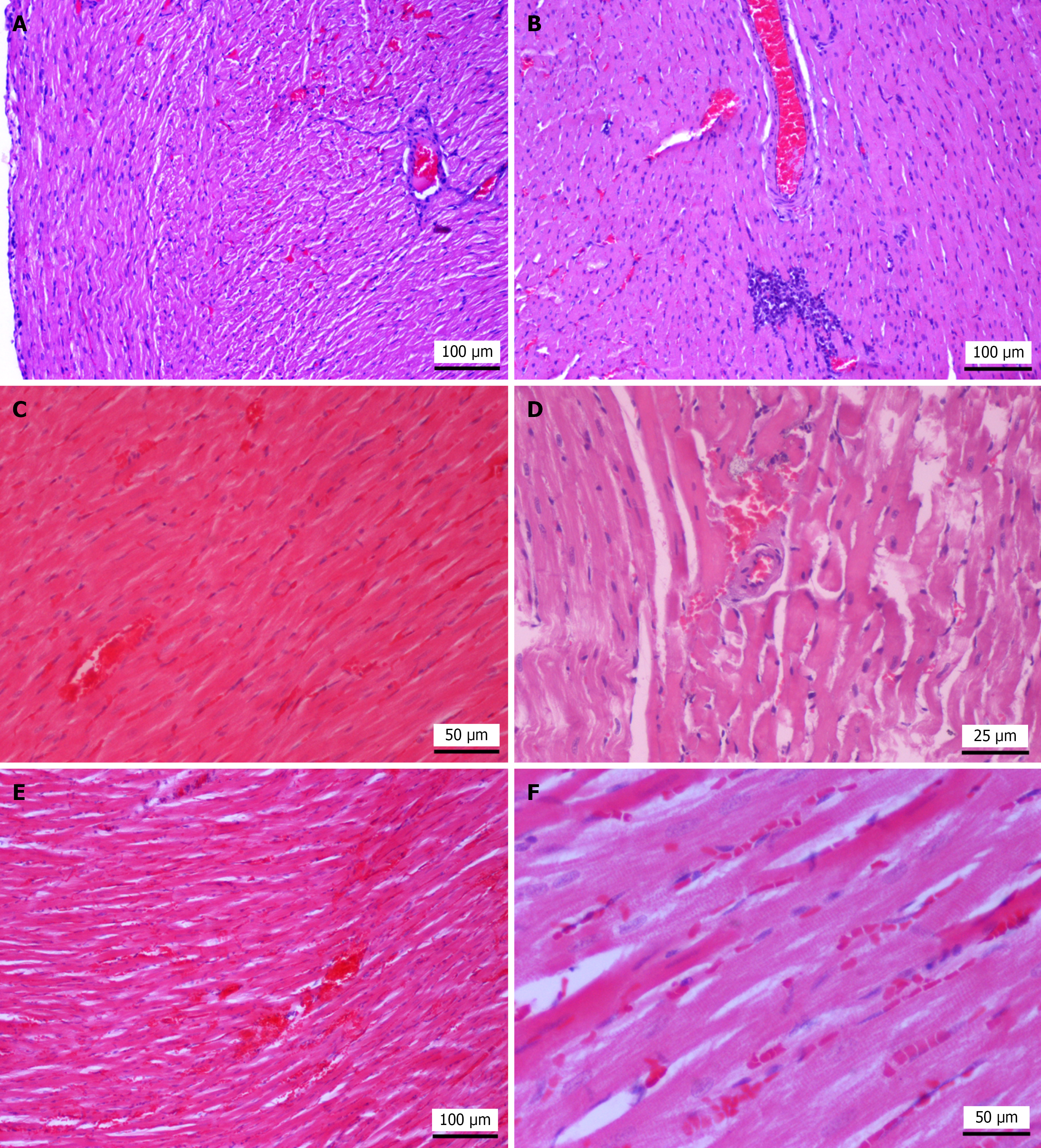
Figure 6 Representative histopathological images of heart tissue in sham group, hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury group, treprostinil treated group, and ischemic preconditioning group.
A: Sham group; the myocardium in a rat from the sham group shows well-preserved cardiomyocytes. Mild interstitial edema, sinusoidal hyperhemia and presence of wavy fibers located subepicardially are also observed. Hematoxylin and eosin (HE), original magnification, 100 ×; B: Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury group (HIRI); rat subjected to HIRI shows loss of striation with homogenously eosinophilic sarcoplasm, a large mononuclear cell aggregate and pyknotic nuclei (necrosis). HE, original magnification, 100 ×; C: Treprostinil-treated group; treprostinil-treated rat shows mild edema and cardiomyocyte necrosis. HE, original magnification, 200 ×; D: Ischemic preconditioning (IP) group; rats subjected to hepatic IP show mild interstitial edema, segmental loss of striation and eosinophilic sarcoplasm. HE, original magnification, 400 ×; E: IP group, rats subjected to hepatic IP show hyperhemia, hemorrhage and edema. HE, original magnification, 100 ×; F: IP group; rats subjected to hepatic IP show eosinophilic sarcoplasm, pyknotic nuclei necrosis and presence of sparse mononuclear cells. HE, original magnification, 200 ×.
- Citation: Mouratidou C, Pavlidis ET, Katsanos G, Kotoulas SC, Papaioannou M, Tsoulfas G, Apostolopoulou E, Brellou GD, Galanis IN, Pavlidis TE. Protective effects of treprostinil and ischemic preconditioning on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury and biomarkers in experimental studies in rats. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(11): 110864
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i11/110864.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i11.110864