©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Oct 27, 2025; 17(10): 106389
Published online Oct 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i10.106389
Published online Oct 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i10.106389
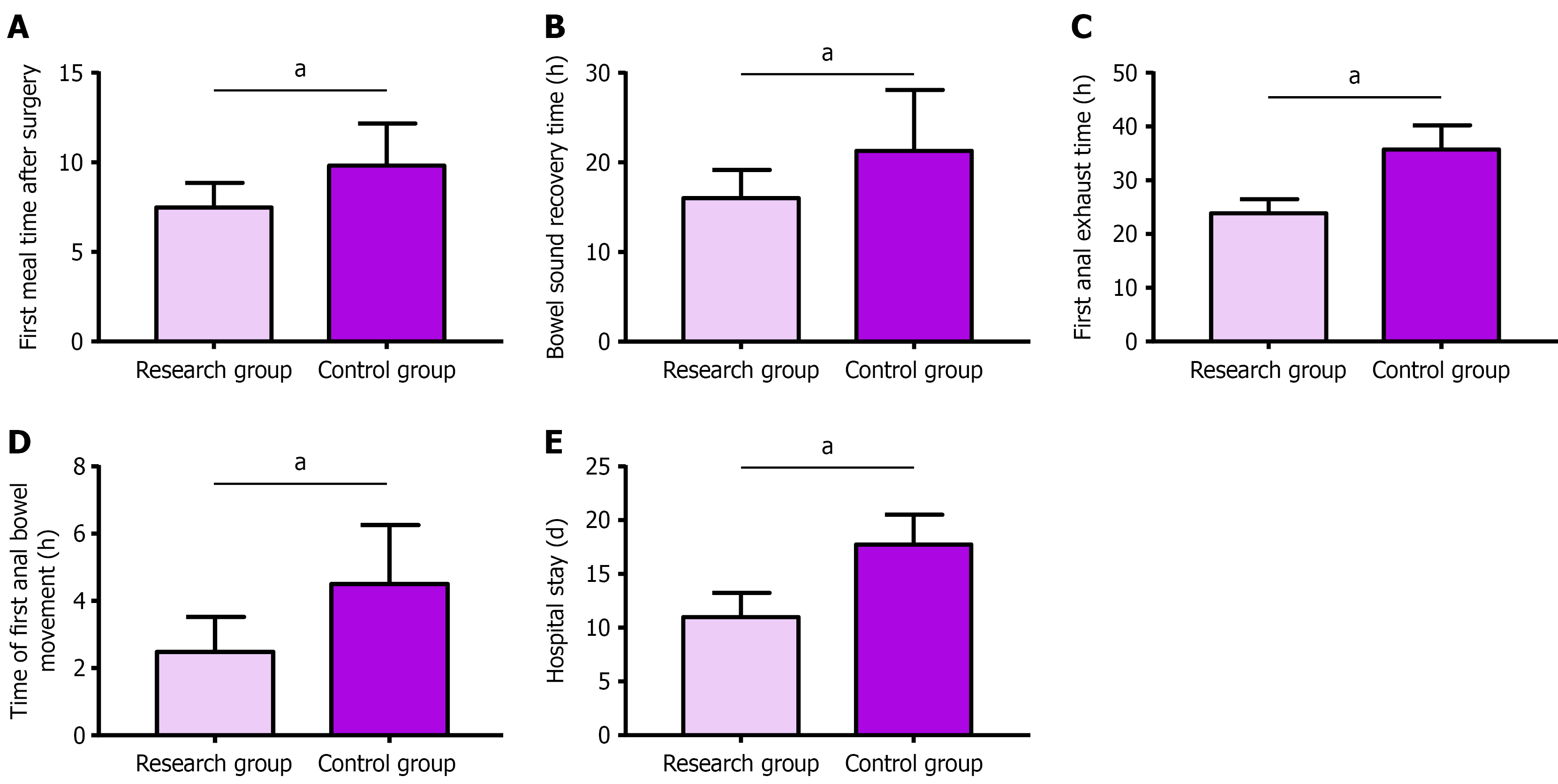
Figure 1 Comparative analysis of gastrointestinal function of two groups of patients.
A: The research group had earlier postoperative oral food intake than the control group; B: The research group had faster postoperative bowel sound recovery than the control group; C: The research group had shorter time to first postoperative anal exhaustion than the control group; D: The research group had shorter time to first postoperative bowel movement than the control group; E: The research group had shorter hospital stays than the control group. aP < 0.05.
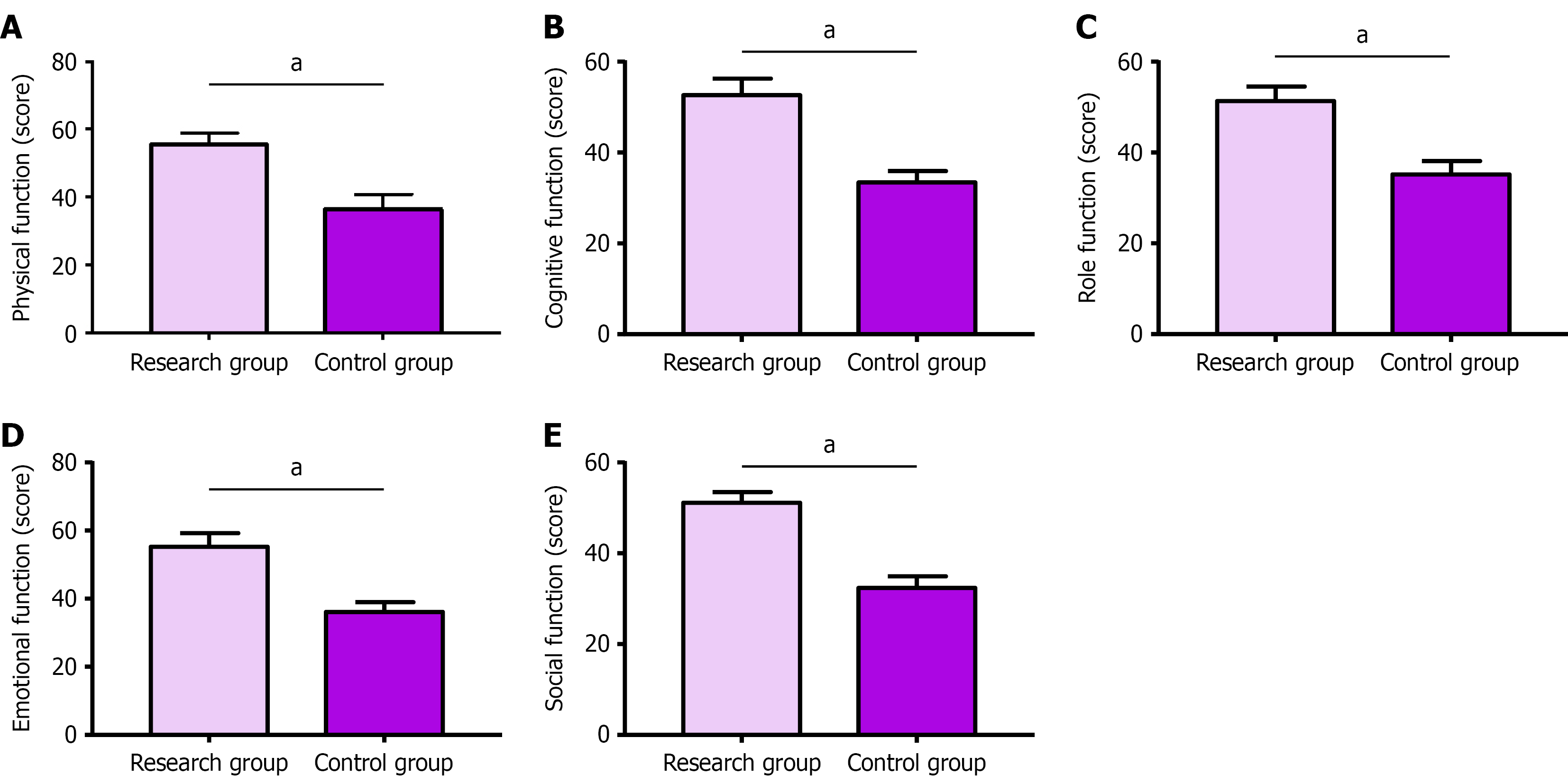
Figure 2 Comparative analysis of patients’ quality of life.
A: The research group had statistically higher physical function scores than the control group; B: The research group had statistically higher cognitive function scores than the control group; C: The research group had statistically higher role function scores than the control group; D: The research group had statistically higher emotional function scores than the control group; E: The research group had statistically higher social function scores than the control group. aP < 0.05.
- Citation: Li H, Gao HJ, Wan MD, Wang WZ, Wu X. Fast-track rehabilitation plus humanized nursing improves gastrointestinal function and quality of life in post-surgical gastric cancer patients. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(10): 106389
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i10/106389.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i10.106389