Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Diabetes. Jul 15, 2017; 8(7): 337-345
Published online Jul 15, 2017. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v8.i7.337
Published online Jul 15, 2017. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v8.i7.337
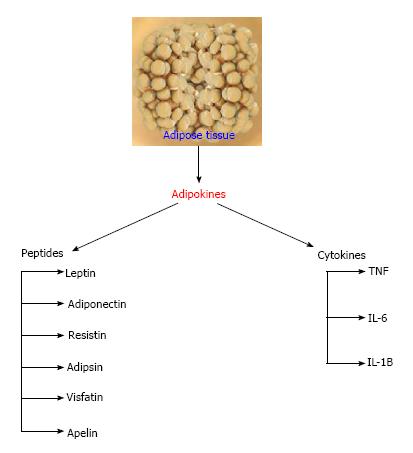
Figure 1 Peptides and cytokines secretion (adipokines) of the adipose tissue.
TNF: Tumor necrotic factor; IL: Interleukin.
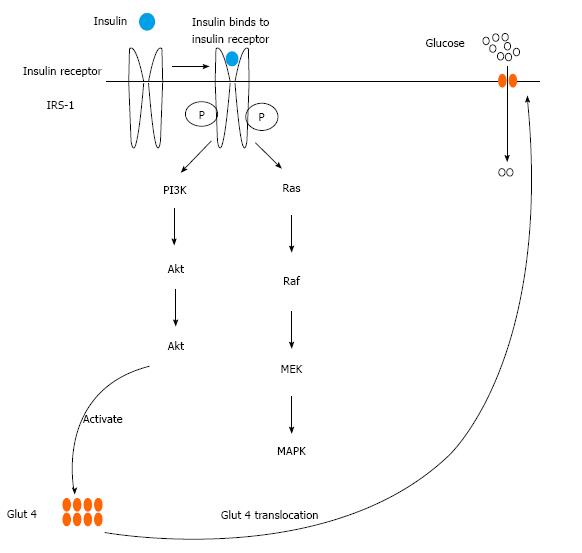
Figure 2 Insulin signaling leading to increase in adipocyte glucose uptake.
PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; Akt: Protein kinase B; MAPK: Mitogen activated protein kinase; Glut 4: Glucose transporter 4; Raf: Raf family of serine/threonine kinases; Ras: Superfamily of small GTPases; MEK: MAPK kinase; IRS-1: Insulin receptor substrate 1.
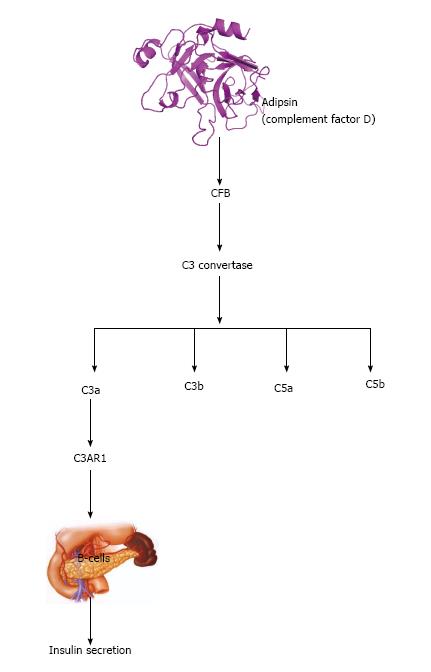
Figure 3 Adipsin and insulin secretion in beta cell.
Adipsin potentiates insulin secretion through cleavage of CFB to form C3 that is hydrolyzed to form C3a. C3a activates C3AR1, which acts on B-cells of the pancreas to secret insulin. CFB: Complement factor B.
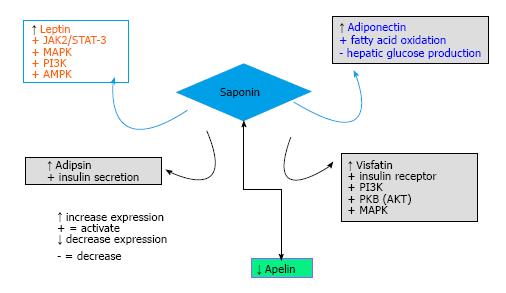
Figure 4 Modulation of adipokines (peptides) by saponin.
Saponin increases the expression of leptin, adiponectin, adipsin, visfatin but reduces the expression of apelin. PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; MAPK: Mitogen activated protein kinase; AMPK: 5’AMP-activated protein kinase; STAT3: Signal tranducer and activator of transcription 3; JAK2: Janus kinase 2.
- Citation: Elekofehinti OO, Ejelonu OC, Kamdem JP, Akinlosotu OB, Adanlawo IG. Saponins as adipokines modulator: A possible therapeutic intervention for type 2 diabetes. World J Diabetes 2017; 8(7): 337-345
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v8/i7/337.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v8.i7.337