©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2017; 8(5): 172-186
Published online May 15, 2017. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v8.i5.172
Published online May 15, 2017. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v8.i5.172
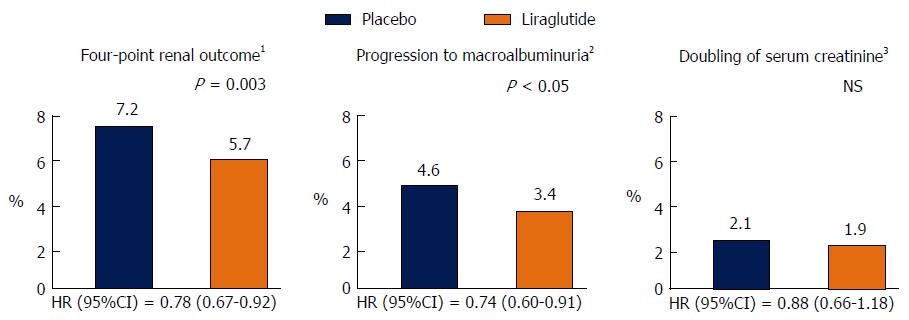
Figure 1 Renal outcomes in the trial Liraglutide Effect and Action in Diabetes: Evaluation of Cardiovascular Outcome.
1Four-point renal outcome = progression to macroalbuminuria, doubling of serum creatinine, initiation of RRT or death from renal disease; 2Macroalbuminuria = albumin to creatinine ratio > 30 mg/mmol; 3Plus eGFR < 45 mL/min per 1.73 m2. eGFR: Estimated glomerular filtration rate; HR: Hazard ratio; NS: Non statistically significant; RRT: Renal replacement therapy.
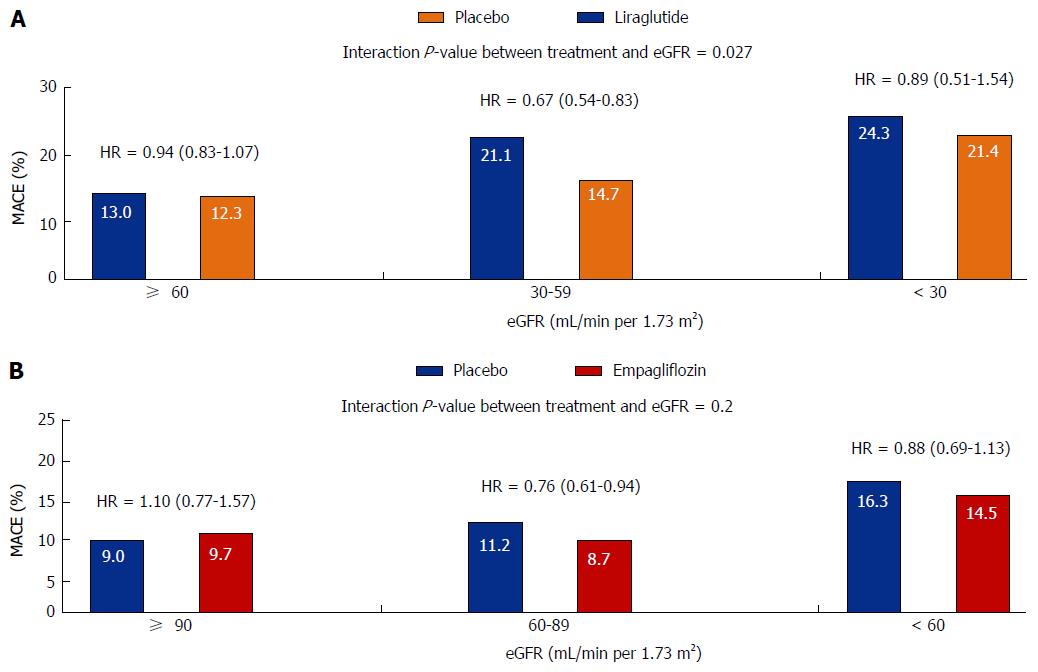
Figure 2 Cardiovascular outcomes in the Liraglutide Effect and Action in Diabetes: Evaluation of Cardiovascular Outcome (A) and cardiovascular safety trial of empagliflozin (B) studies according to estimated glomerular filtration rate.
MACE: Major adverse cardiovascular event; eGFR: Estimated glomerular filtration rate; HR: Hazard ratio.
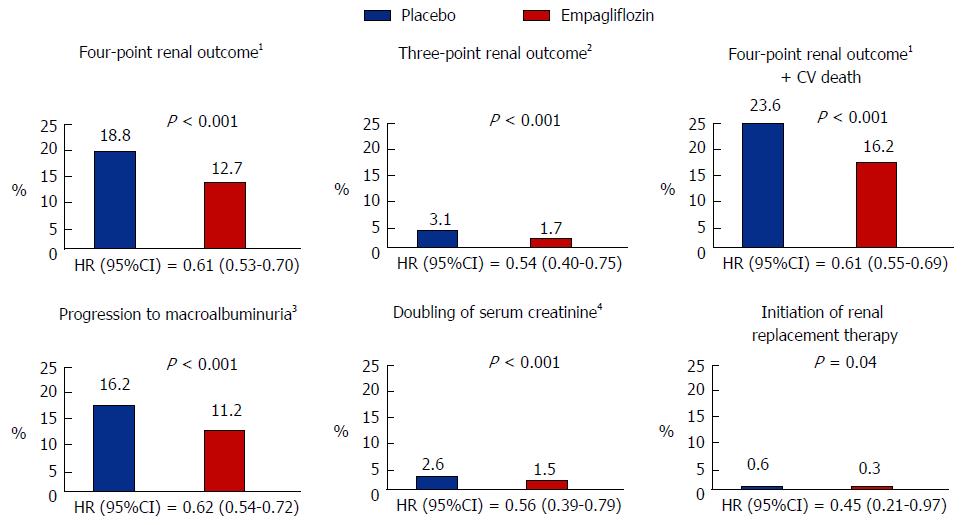
Figure 3 Renal outcomes in the cardiovascular safety trial of empagliflozin study.
1Four-point renal outcome = progression to macroalbuminuria plus three-point renal outcome; 2Three-point renal outcome = doubling of serum creatinine, initiation of RRT or death from renal disease; 3Macroalbuminuria = albumin to creatinine ratio > 30 mg/mmol; 4Plus eGFR < 45 mL/min per 1.73 m2. HR: Hazard ratio; eGFR: Estimated glomerular filtration rate; CV: Cardiovascular; RRT: Renal replacement therapy.
- Citation: MacIsaac RJ, Jerums G, Ekinci EI. Effects of glycaemic management on diabetic kidney disease. World J Diabetes 2017; 8(5): 172-186
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v8/i5/172.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v8.i5.172