Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Diabetes. Mar 10, 2016; 7(5): 101-111
Published online Mar 10, 2016. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i5.101
Published online Mar 10, 2016. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i5.101
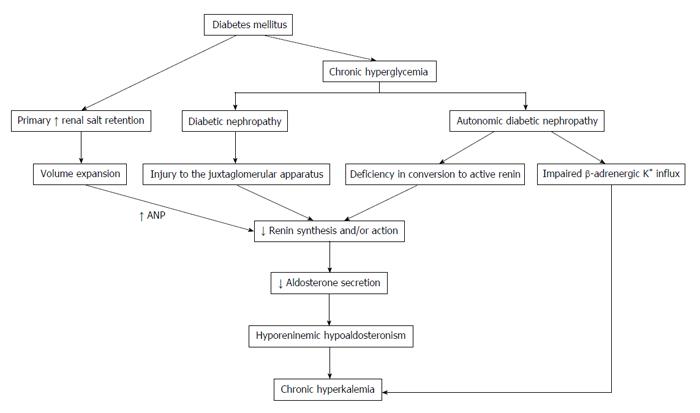
Figure 1 Pathophysiology of hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism related to diabetes mellitus.
ANP: Atrial natriuretic peptide; K+: Potassium.
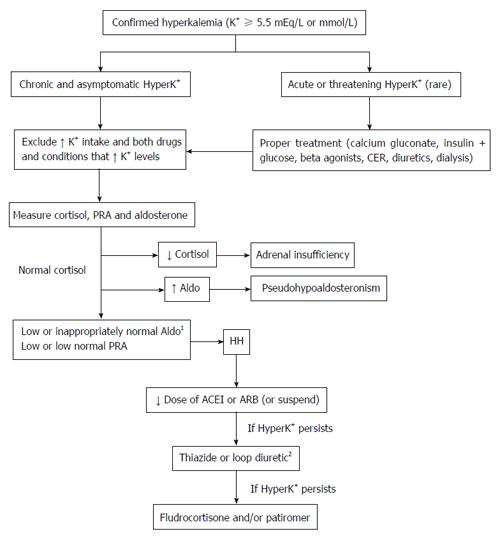
Figure 2 Diagnosis and management of hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism related to diabetes mellitus.
1In any cases, it might be necessary to activate the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (using a loop diuretic or the upright position); 2After using diuretics, the use of ACEIs or ARBs should be restarted (if suspended). ACEIs: Angiotensinogen-converting enzyme inhibitors; Aldo: Aldosterone; ARBs: Angiotensin receptor blockers; CER: Calcium exchange resins; HyperK+: Hyperkalemia; K+: Potassium; PRA: Plasma renin activity; HH: Hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism.
- Citation: Sousa AGP, Cabral JVS, El-Feghaly WB, Sousa LS, Nunes AB. Hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism and diabetes mellitus: Pathophysiology assumptions, clinical aspects and implications for management. World J Diabetes 2016; 7(5): 101-111
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v7/i5/101.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v7.i5.101