©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Diabetes. Aug 10, 2015; 6(9): 1097-1107
Published online Aug 10, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i9.1097
Published online Aug 10, 2015. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i9.1097
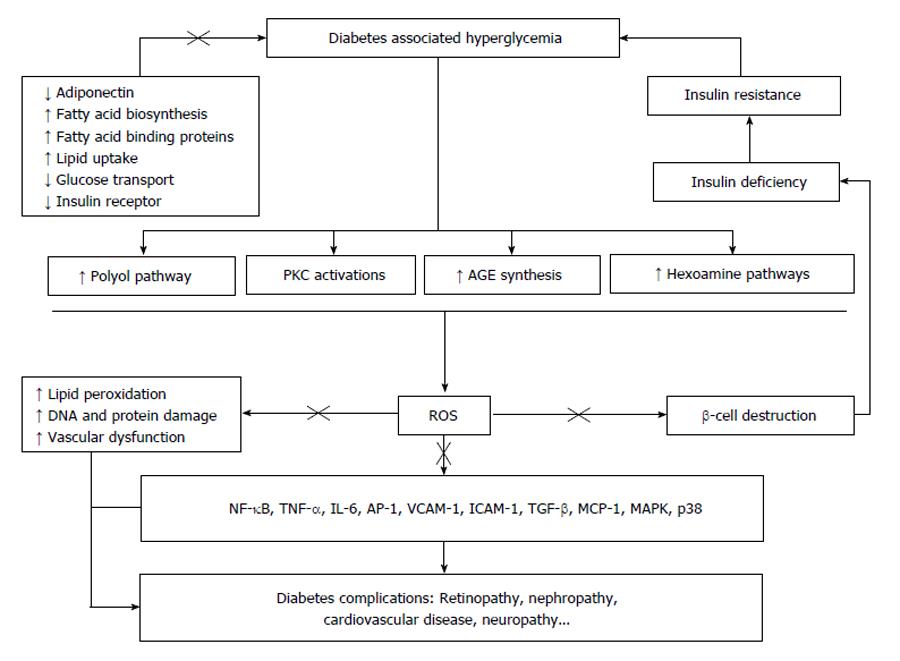
Figure 1 Oxidative stress and its possible pathways leading to diabetes complications.
“×” potential sites where aloesin may likely interfere. PKC: Protein kinase C; AGE: Advanced glycation end-products; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappaB; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL-6: Interleukin 6; AP-1: Activating protein-1; VCAM-1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; ICAM-1: Intercellular adhesion molecule-1; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor beta; MCP-1: Monocyte chemotactic protein-1; MAPK, p38: Mitogen-activated protein kinases, p38.
Figure 2 Cross-section of Aloe.
- Citation: Yimam M, Brownell L, Jia Q. Aloesin as a medical food ingredient for systemic oxidative stress of diabetes. World J Diabetes 2015; 6(9): 1097-1107
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v6/i9/1097.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i9.1097