©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2014; 5(2): 209-218
Published online Apr 15, 2014. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i2.209
Published online Apr 15, 2014. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i2.209
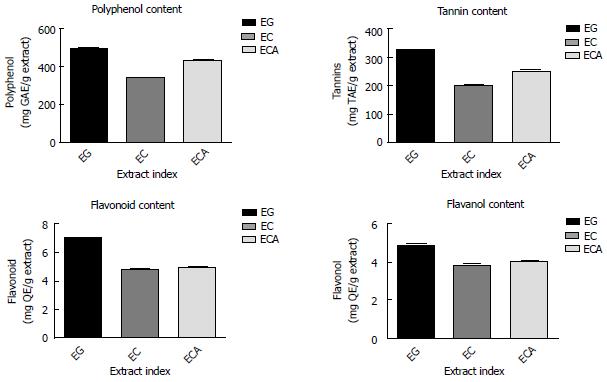
Figure 1 Graphical presentations of the presence of phytochemicals in Eucalyptus extracts.
Data are presented as the mean ± SD of each triplicate test. EG: E. globulus; EC: E. citriodora; ECA: E. camaldulensis.
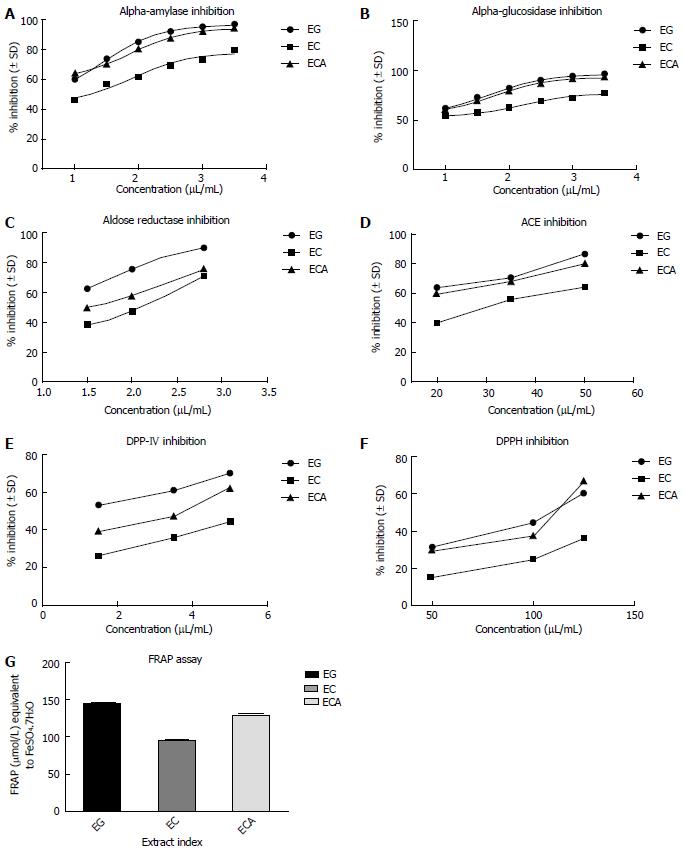
Figure 2 Eucalyptus extracts.
A: Alpha-amylase; B: Alpha-glucosidase; C: Aldose-reductase; D: Angiotensin converting enzyme; E: Dipeptidyl peptidase 4; F: 1,1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl; G: FRAP assay. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of each triplicate test. EG: E. globulus; EC: E. citriodora; ECA: E. camaldulensis; FRAP: Ferric reducing antioxidant power.
-
Citation: Dey B, Mitra A, Katakam P, Singla RK. Exploration of natural enzyme inhibitors with hypoglycemic potentials amongst
Eucalyptus Spp. byin vitro assays. World J Diabetes 2014; 5(2): 209-218 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v5/i2/209.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v5.i2.209