Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2025; 16(5): 101840
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101840
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101840
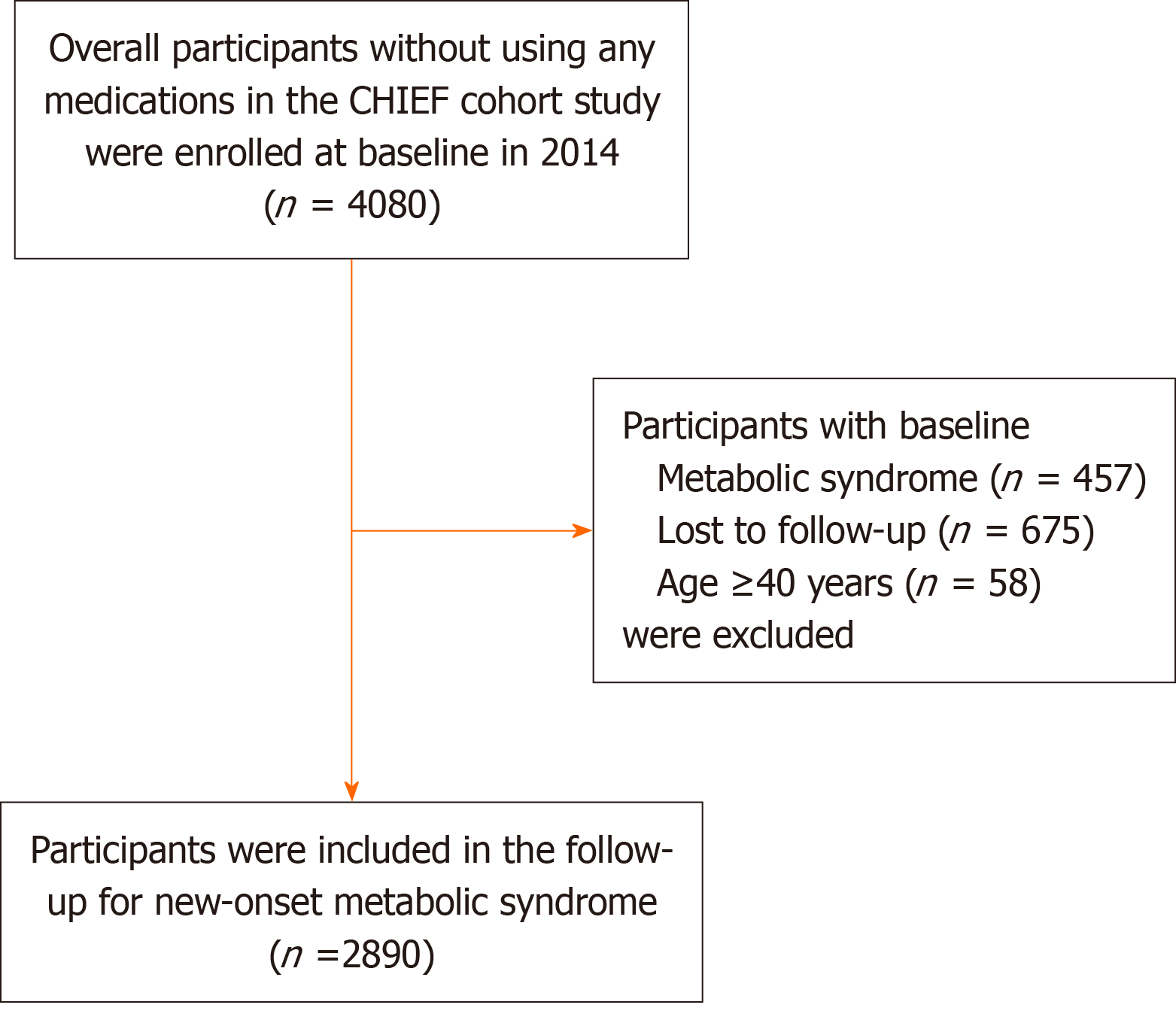
Figure 1 Flow diagram of selection of eligible participants for follow-up of new-onset metabolic syndrome in the CHIEF cohort study, 2014-2020.
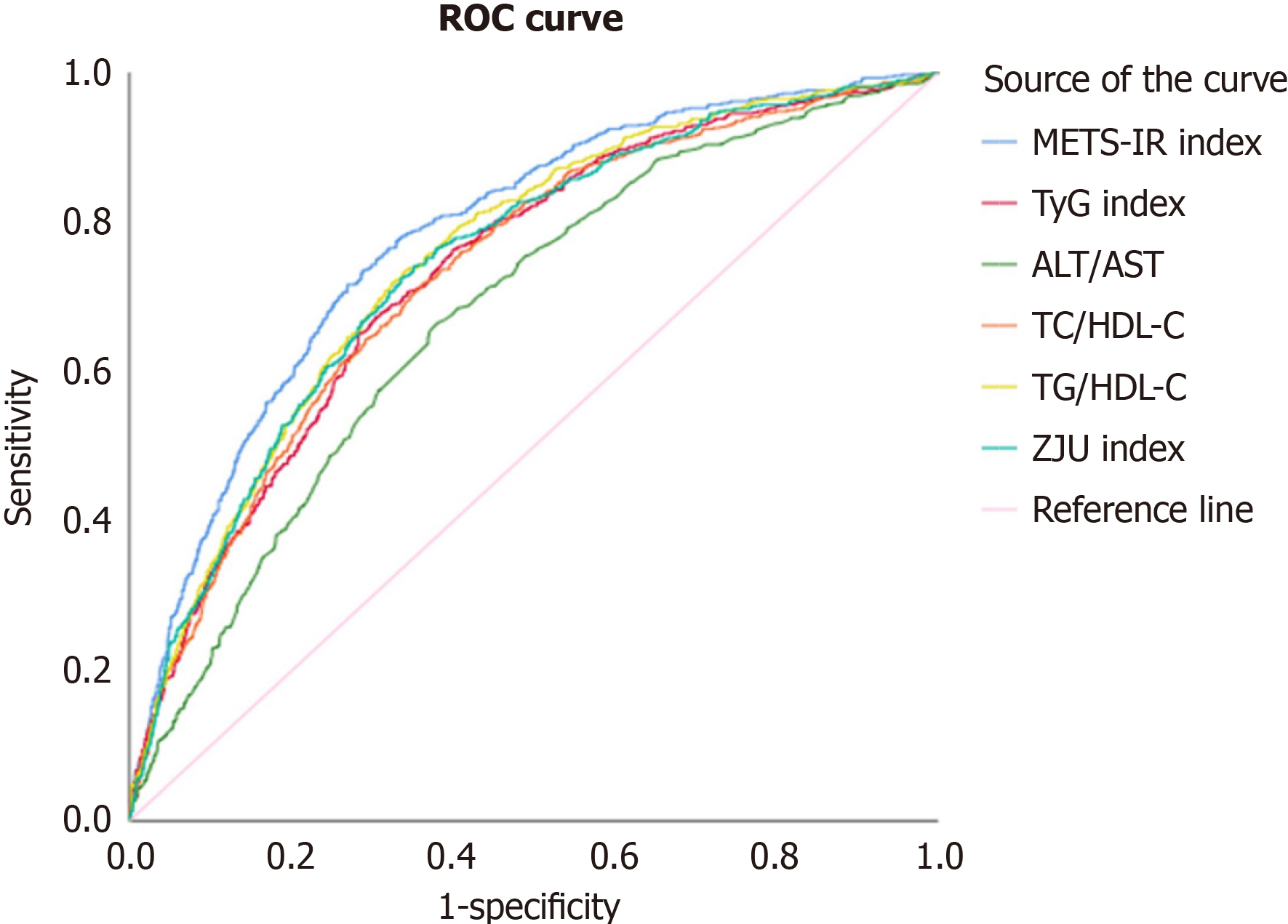
Figure 2 Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis of non-insulin-based insulin resistance indices for new-onset metabolic syndrome.
All non-insulin-based insulin resistance (NI-IR) indices demonstrated significant predictive capacities for incident metabolic syndrome. Among the NI-IR indices, the metabolic score for insulin resistance index revealed the greatest area under the receiver operating characteristic of 0.782 (optimal cut-off point: 2.03), followed by 0.752 (optimal cut-off point: 1.88) with the triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) ratio, 0.743 (optimal cut-off point: 125.71) with the Zhejiang University index, 0.734 (optimal cut-off point: 8.37) with the triglyceride glucose index, 0.731 (optimal cut-off point: 3.55) with the total cholesterol/HDL-C ratio, and 0.674 (optimal cut-off point: 0.95) with the alanine transaminase/aspartate transaminase ratio. ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; METS-IR: Metabolic score for insulin resistance; TyG: Triglyceride glucose; ALT: Alanine transaminase; AST: Aspartate transaminase; TC: Total cholesterol; HDL-C: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG: Triglyceride; ZJU: Zhejiang University.
- Citation: Liu WN, Hsu YC, Lin YP, Tsai KZ, Lin YC, Liu PY, Lin GM. Comparisons of various insulin resistance indices for new-onset metabolic syndrome before midlife: The CHIEF cohort study, 2014-2020. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(5): 101840
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i5/101840.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i5.101840