©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Dec 15, 2025; 16(12): 112789
Published online Dec 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i12.112789
Published online Dec 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i12.112789
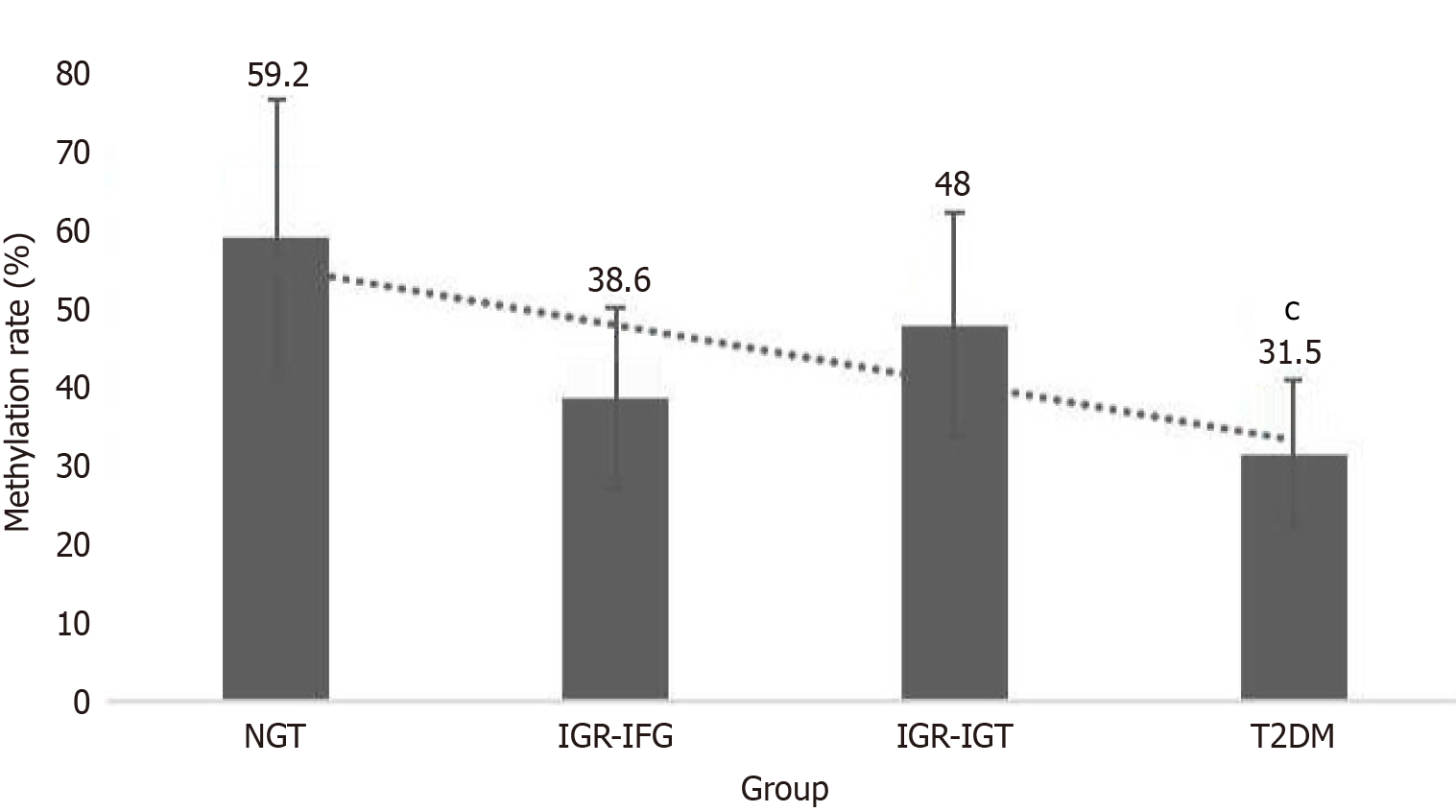
Figure 1 Leptin promoter methylation rates decrease significantly across glycemic states in lean Chinese adults (body mass index < 24 kg/m2).
Methylation levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus were 315% lower than normal glucose tolerance (NGT) (59.2%, P < 0.001) and lower than impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) (48%, P < 0.001). Error bars: 95%CI. Data derived from methylation-specific PCR analysis of peripheral leukocytes (n = 392). cP < 0.001: Compared to NGT and IGT. IGT: Impaired glucose tolerance; IGR: Impaired glucose regulation; NGT: Normal glucose tolerance; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Citation: Sun SQ, Liang SZ, Huang Q, Sun JZ. Methylation status of leptin gene promoter in relatively lean Chinese adults with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(12): 112789
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i12/112789.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i12.112789