©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Dec 15, 2025; 16(12): 111963
Published online Dec 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i12.111963
Published online Dec 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i12.111963
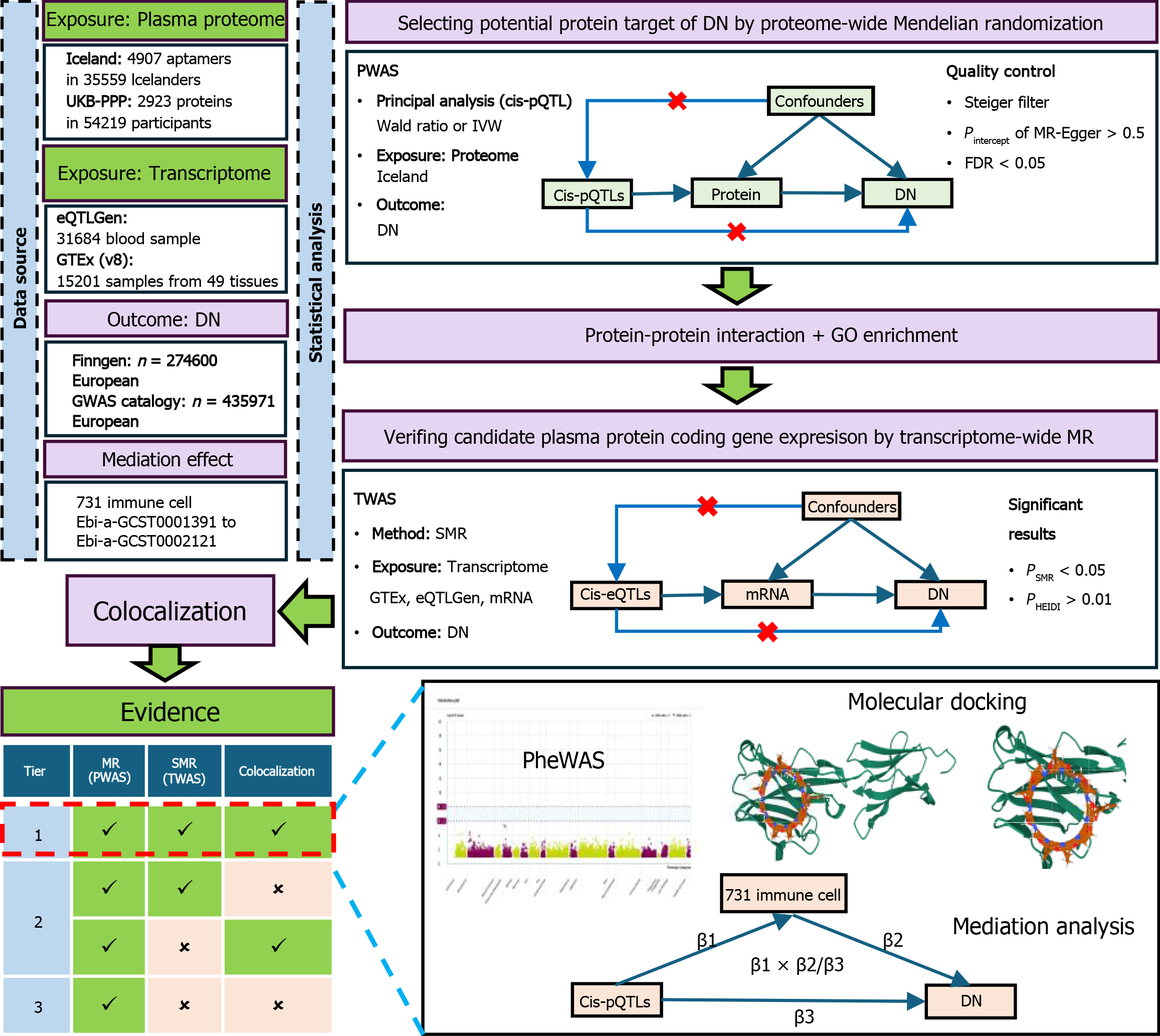
Figure 1 Overview of the study design in our Mendelian randomization and colocalization study.
DN: Diabetic neuropathy; UKB-PPP: United Kingdom biobank pharma proteomics project; eQTL: Expression quantitative trait loci; GTEx: Genotype-tissue expression; GWAS: Genome-wide association studies; MR: Mendelian randomization; SMR: Summary-data-based Mendelian randomization; FDR: False discovery rate; GO: Gene Ontology; Cis-pQTL: Cis-protein quantitative trait loci; HEIDI: Heterogeneity dependency tool; PheWAS: Phenome-Wide Association Study.
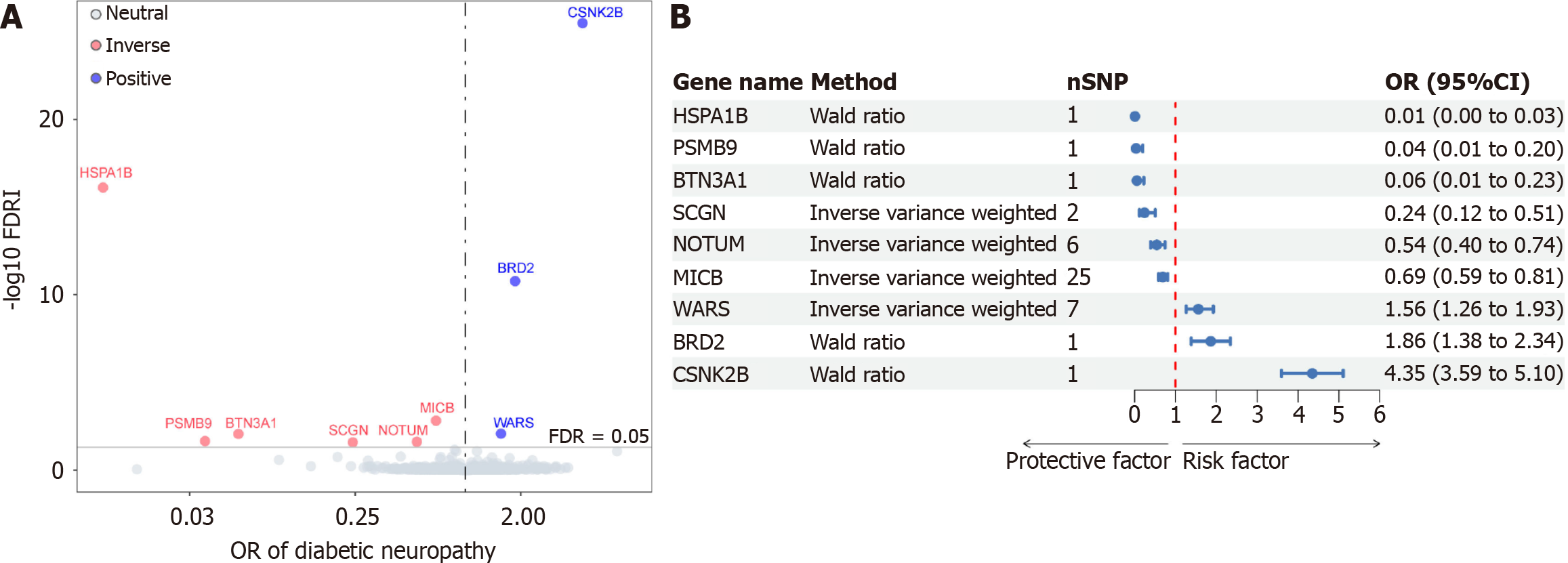
Figure 2 Result summary of Mendelian randomization analysis on the associations between plasma proteins and the risk of diabetic neuropathy.
A: Volcano plot of Mendelian randomization analysis; B: Forest plot of Mendelian randomization analysis. FDR: False discovery rate.
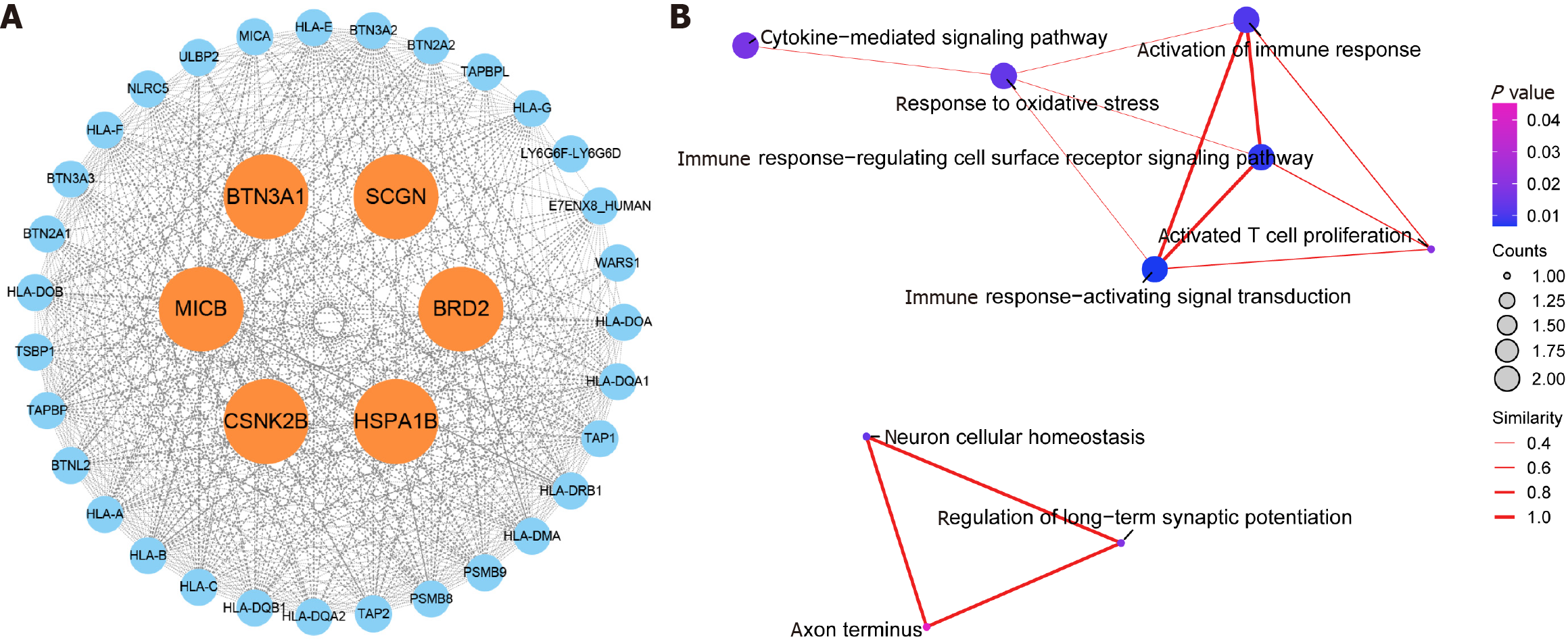
Figure 3 Results of protein–protein interaction network and Gene Ontology enrichment.
A: Protein-protein interaction network built with STRING; B: For Gene Ontology enrichment pathways.
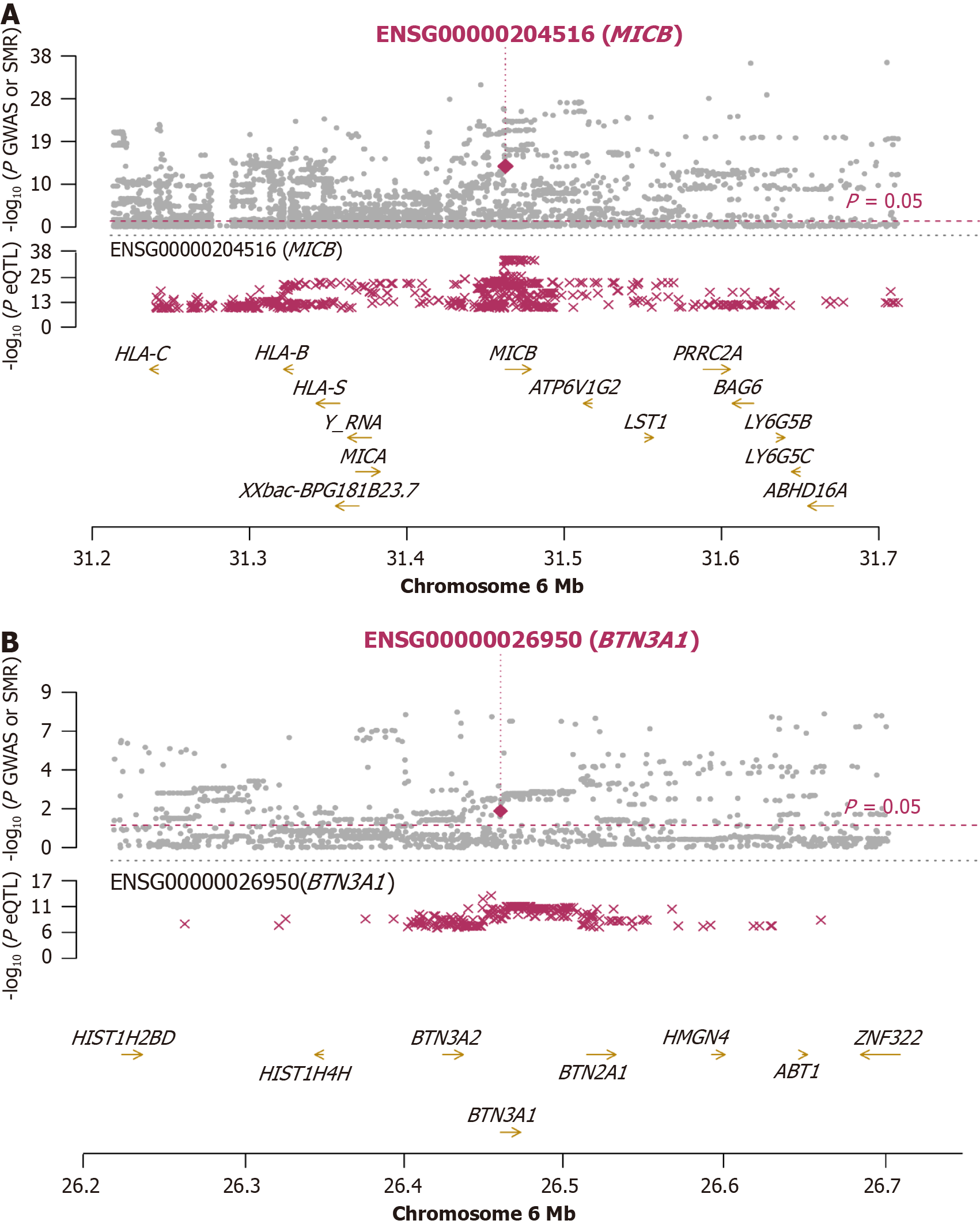
Figure 4 Summary data-based Mendelian randomization plot of the MICB and BTN3A1 locus.
The top panel depicts diabetic neuropathy genome-wide association studies P values (grey dots), the middle panel depicts expression quantitative trait loci P values, and the bottom panel depicts gene locations on chromosome 6. The red diamonds in the upper panel indicate the summary data-based Mendelian randomization test P values for positive genes, and the dashed lines indicate the significance thresholds. A: A locus plot of MICB; B: A locus plot of BTN3A1. eQTL: Expression quantitative trait loci; GWAS: Genome-wide association studies; SMR: Summary-data-based Mendelian randomization.
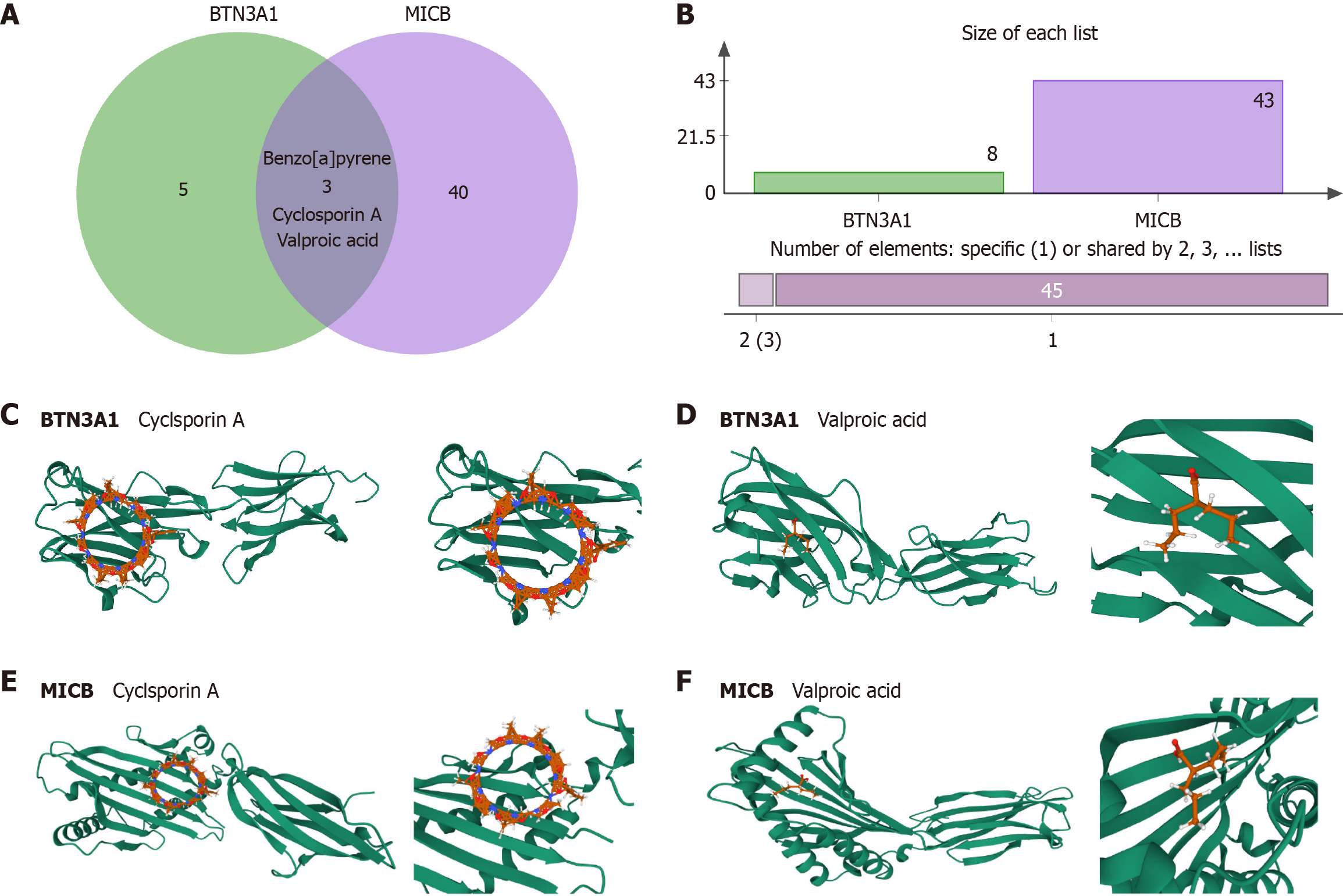
Figure 5 Drug prediction molecular docking.
A: Drug prediction molecular docking BTN3A1 and MICB-related drugs; B: Molecular docking plots of BTN3A1 with cyclosporin A and valproic acid; MICB with cyclosporin A and valproic acid; C-F: Predicted binding conformations of cyclosporin A and valproic acid with BTN3A1 and MICB.
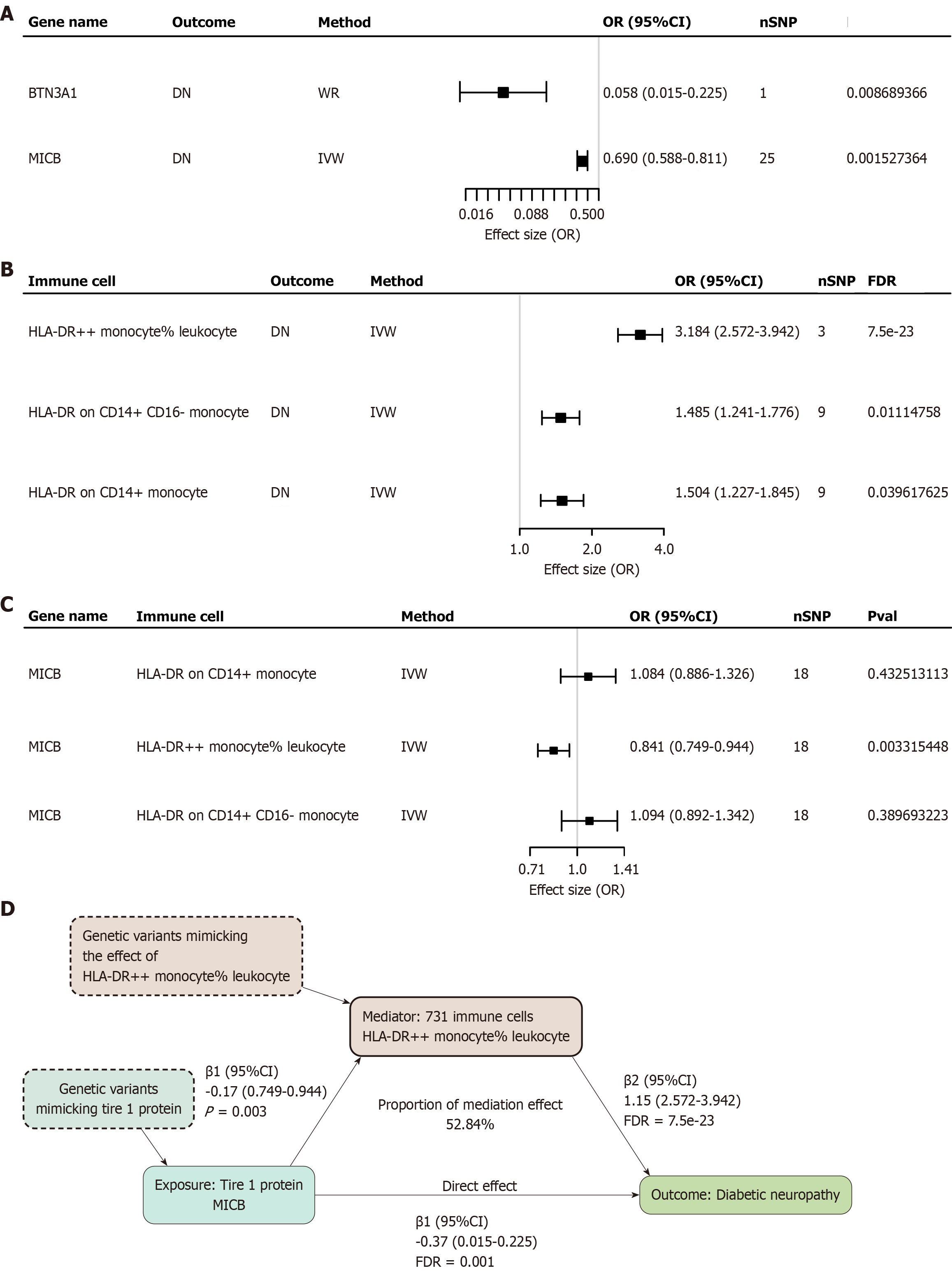
Figure 6 731 association of immune cells with diabetic neuropathy and mediation analysis.
A: Forest plot of proteins with diabetic neuropathy (DN) Mendelian randomization analysis; B: Forest plot of immune cells vs DN Mendelian randomization analysis; C: Forest plot of identified proteins with Mendelian randomization analysis of positive immune cell; D: The effect of MICB on DN may be partially mediated by the human leukocyte antigen-DR (++) monocyte% leukocyte, with a mediating effect of 52.84%. DN: Diabetic neuropathy; WR: Wald ratio; nsnp: Number of single nucleotide polymorphisms; SNP: Single nucleotide polymorphisms; FDR: False discovery rate; HLA-DR: Human leukocyte antigen-DR; IVW: Inverse variance-weighted; OR: Odds ratio; CI: Confidence interval; Pval: P value.
- Citation: Ding XF, Dang X, Lin S. Identification of novel therapeutic targets for diabetic neuropathy through integrated proteomics and transcriptomics approaches. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(12): 111963
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i12/111963.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i12.111963