Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Mar 15, 2024; 15(3): 361-377
Published online Mar 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i3.361
Published online Mar 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i3.361
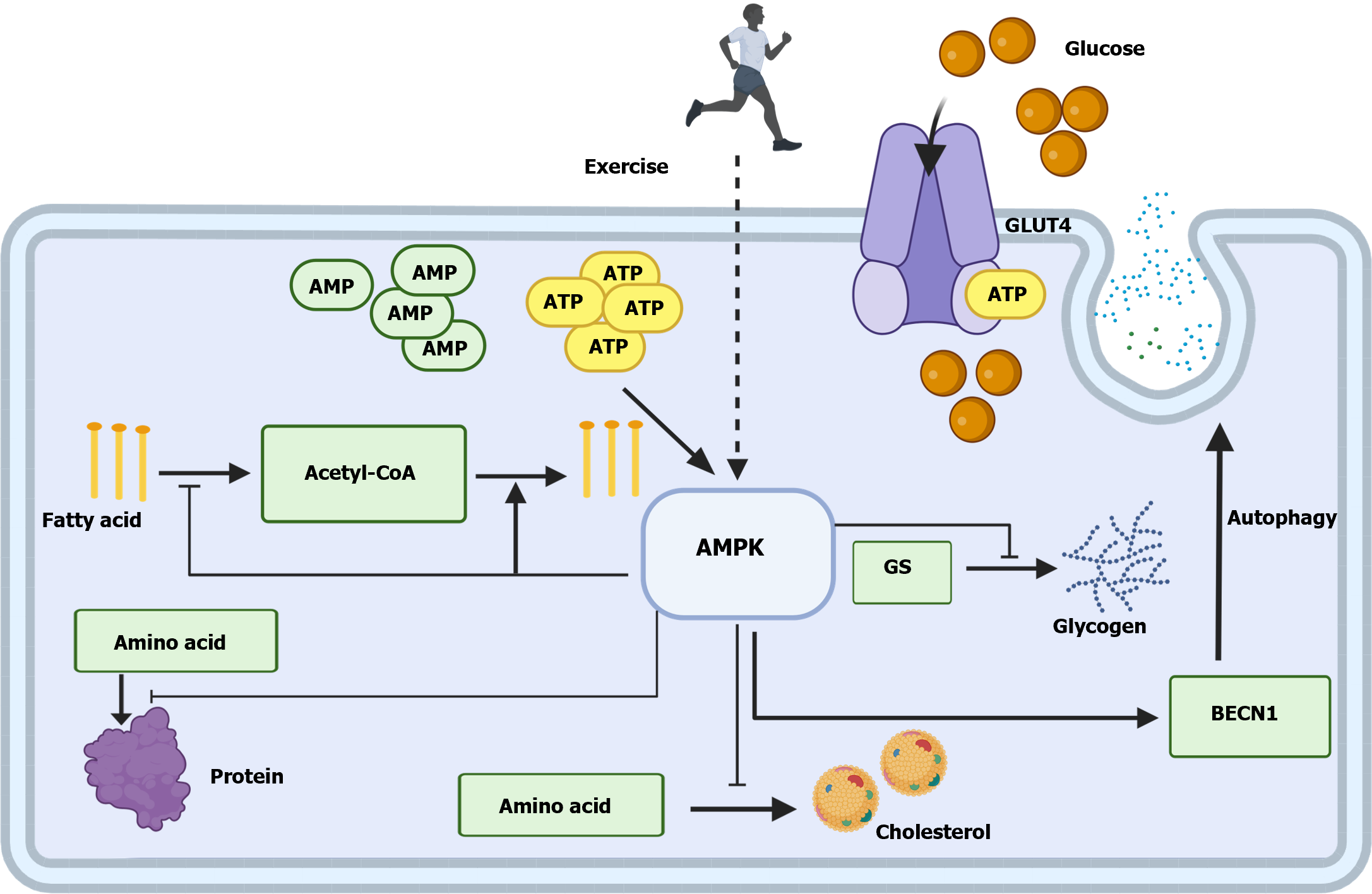
Figure 1 Adenosine 5‘-monophosphate-activated protein kinase as an important regulatory center of cellular metabolism.
AMP: Adenosine 5‘-monophosphate; GLUT4: Glucose transporter type 4; GS: Glycogen synthase; BECN1: Beclin 1; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase.
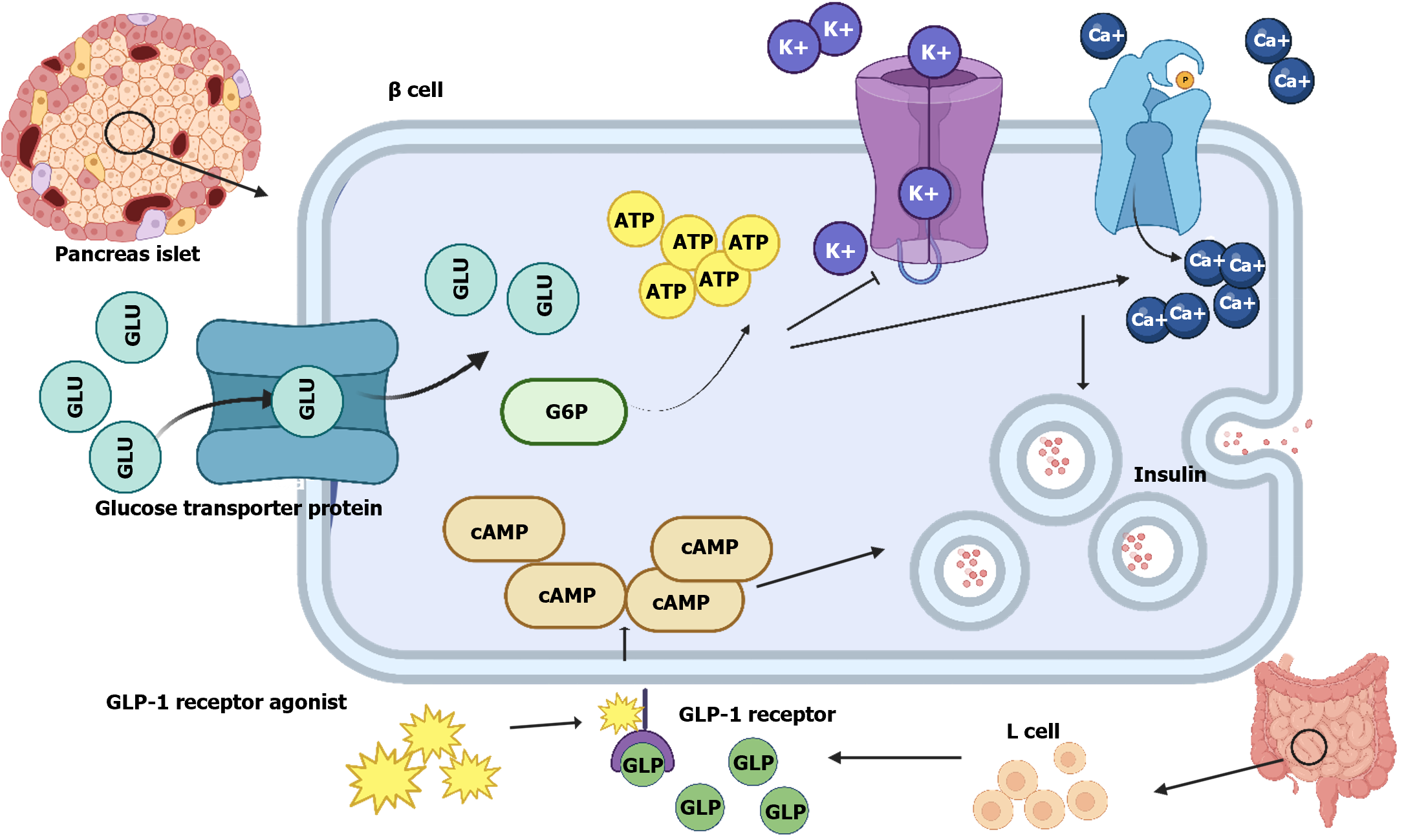
Figure 2 Glucagon-like peptide receptor agonist promotes insulin secretion.
G6P: Glucose-6-phosphate; GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1; GLU: Glucose; SGLT2: Sodium–glucose cotransporter 2.
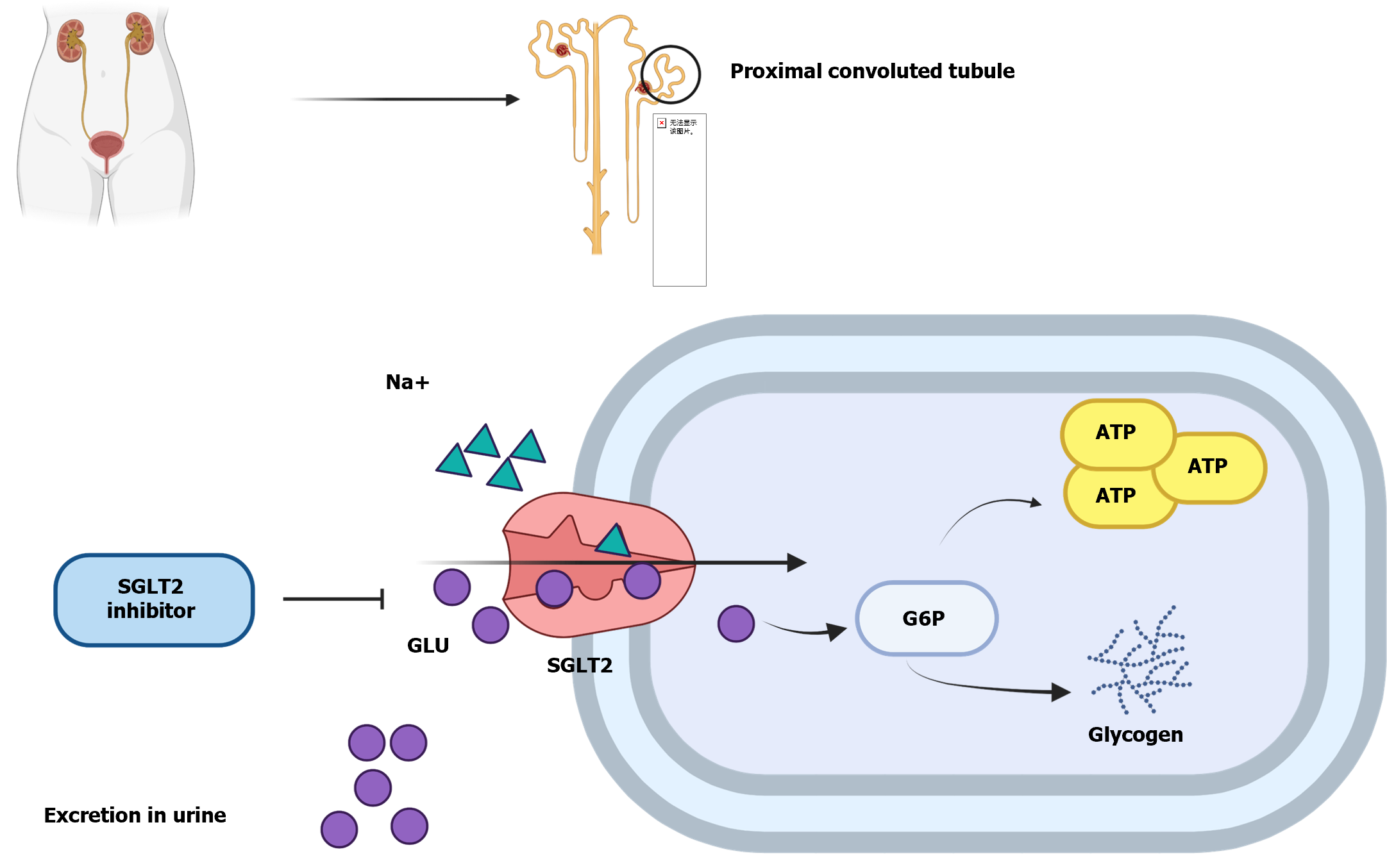
Figure 3 Sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors block the glucose reabsorption process.
G6P: Glucose-6-phosphate; GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1; GLU: Glucose; SGLT2: Sodium–glucose cotransporter 2.
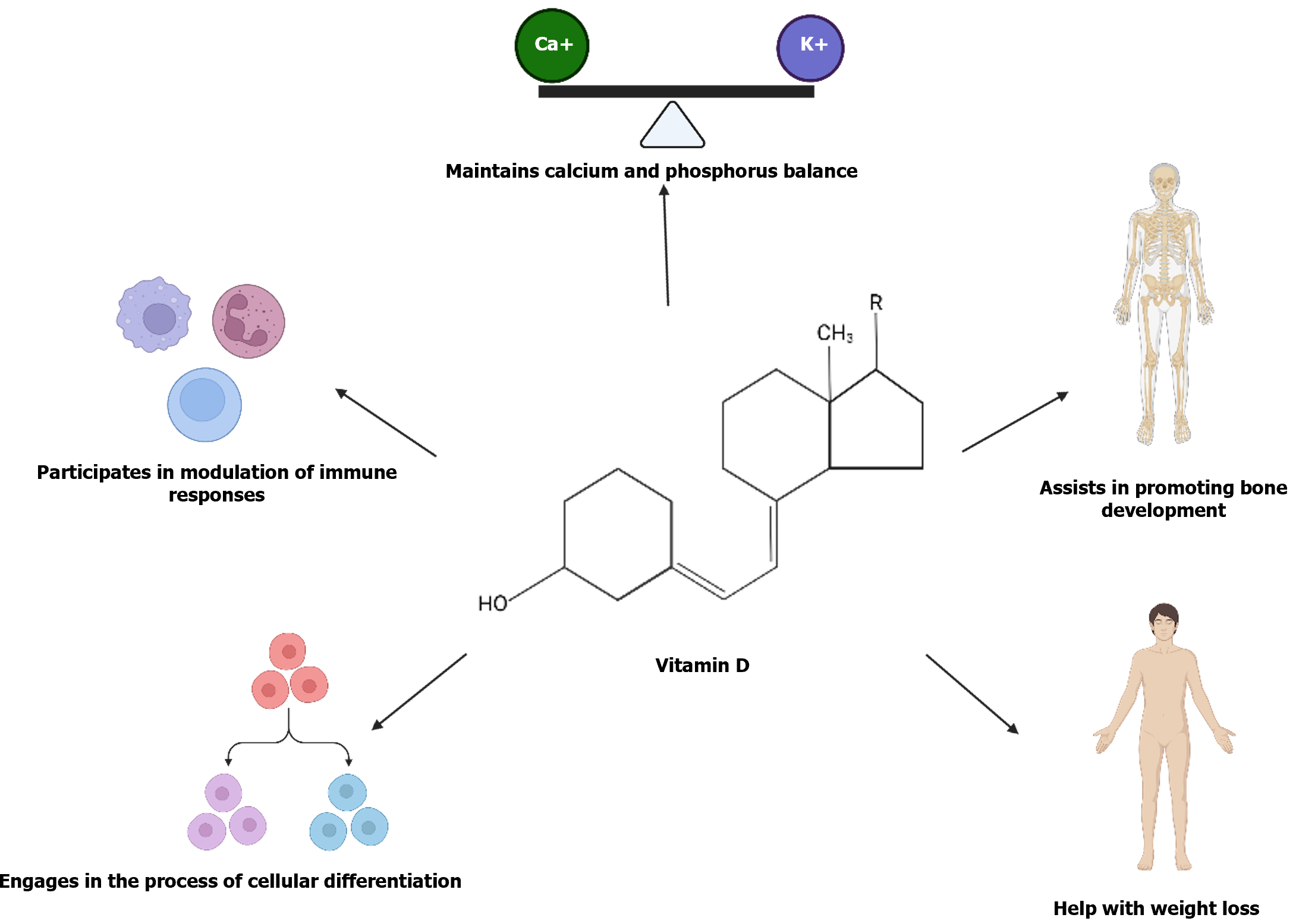
Figure 4 Vitamin D contributes to the maintenance of normal bodily functions.
- Citation: Ping WX, Hu S, Su JQ, Ouyang SY. Metabolic disorders in prediabetes: From mechanisms to therapeutic management. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(3): 361-377
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i3/361.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i3.361