©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2023; 14(4): 352-363
Published online Apr 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i4.352
Published online Apr 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i4.352
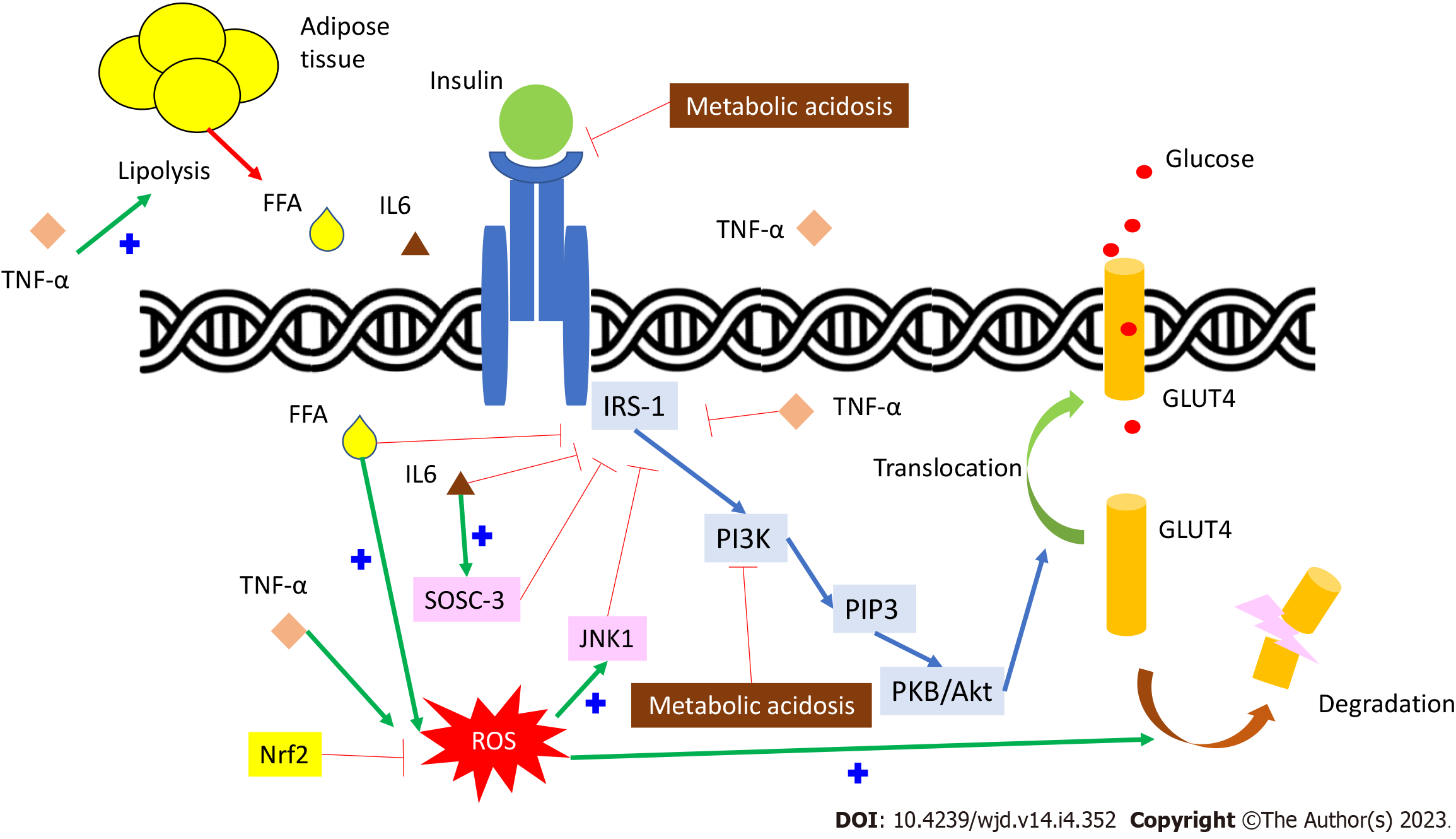
Figure 1 Insulin signaling pathway and inflammation and oxidative stress in insulin resistance.
IRS-1: Insulin receptor substrate-1; PI3K: Phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase (PI3K); PIP3: Phosphatidylinositol-triphosphate; PKB/Akt: Protein kinase B/Akt pathway; GLUT4: Glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4): FFA: Free fatty acids; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alfa; IL-6: Interleukin-6; SOSC-3: Suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 pathway; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; JNK1: C-Jun N-terminal kinase 1; Nrf2: Nuclear factor-erythroid-2-related factor-2.
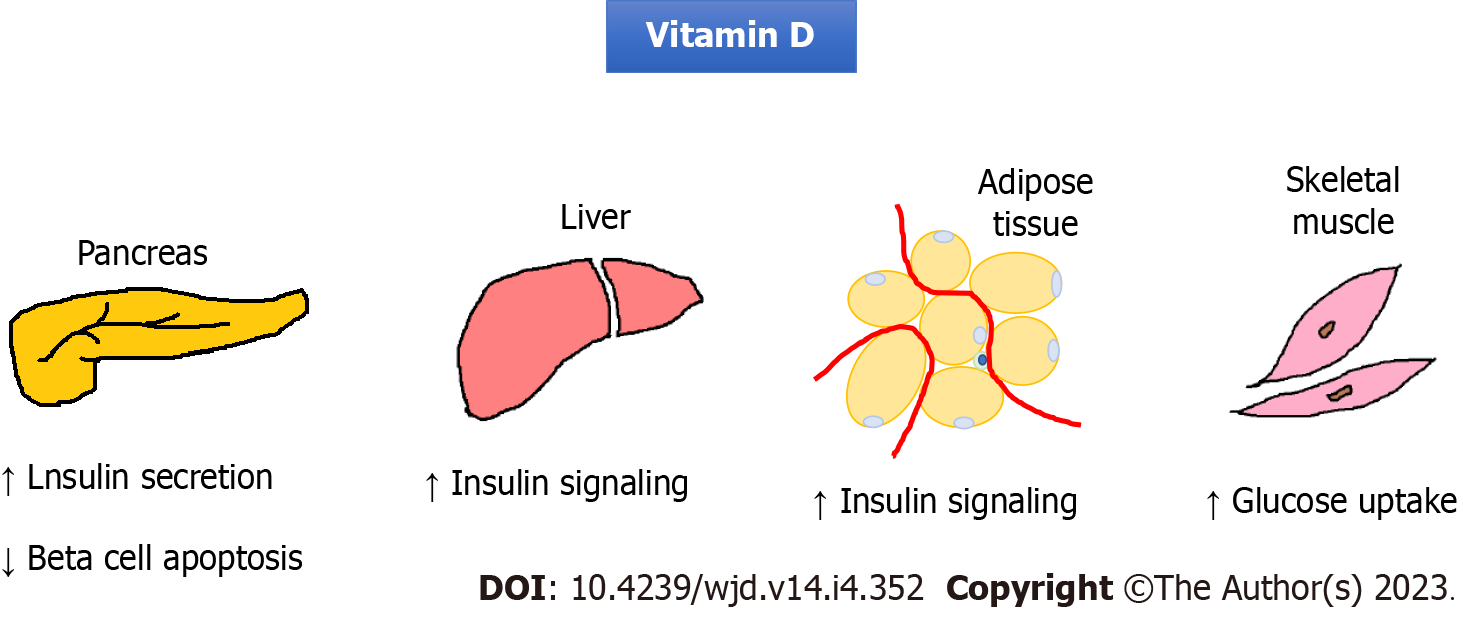
Figure 2 Effect of vitamin D on insulin secretion and signaling.
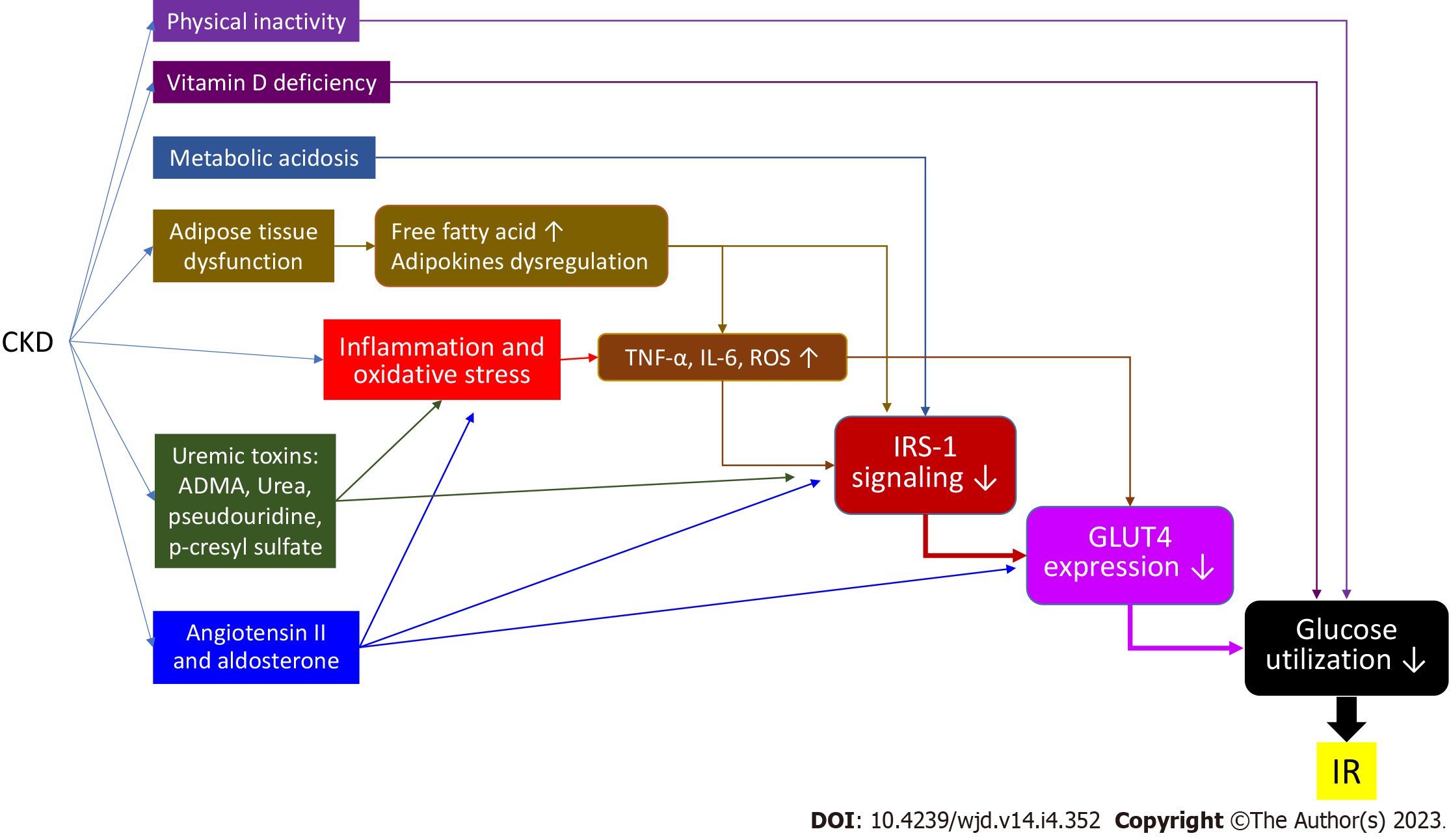
Figure 3 Summary of mechanisms of chronic kidney disease that induce insulin resistance.
CKD: Chronic kidney disease; IRS-1: Insulin receptor substrate-1; GLUT4: Glucose transporter 4: TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alfa; IL-6: Interleukin-6; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; ADMA: Asymmetric dimethylarginine.
- Citation: Lin WR, Liu KH, Ling TC, Wang MC, Lin WH. Role of antidiabetic agents in type 2 diabetes patients with chronic kidney disease. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(4): 352-363
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i4/352.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i4.352